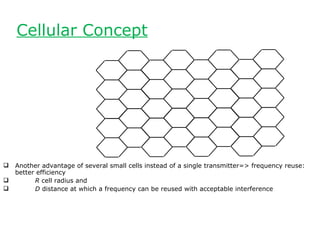
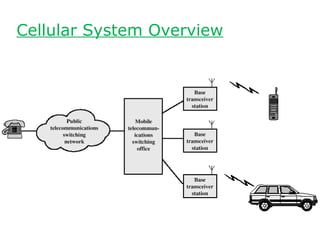
The document discusses the evolution of cellular networks from first generation (1G) to second generation (2G). 1G networks, introduced in the 1980s, primarily used analog communication for voice with significant security flaws, while 2G systems transitioned to digital transmission, enabling data services and offering improved security, compression, and error correction. Key differences between the generations include the transition from analog to digital technology, the introduction of encryption, and enhanced channel utilization.