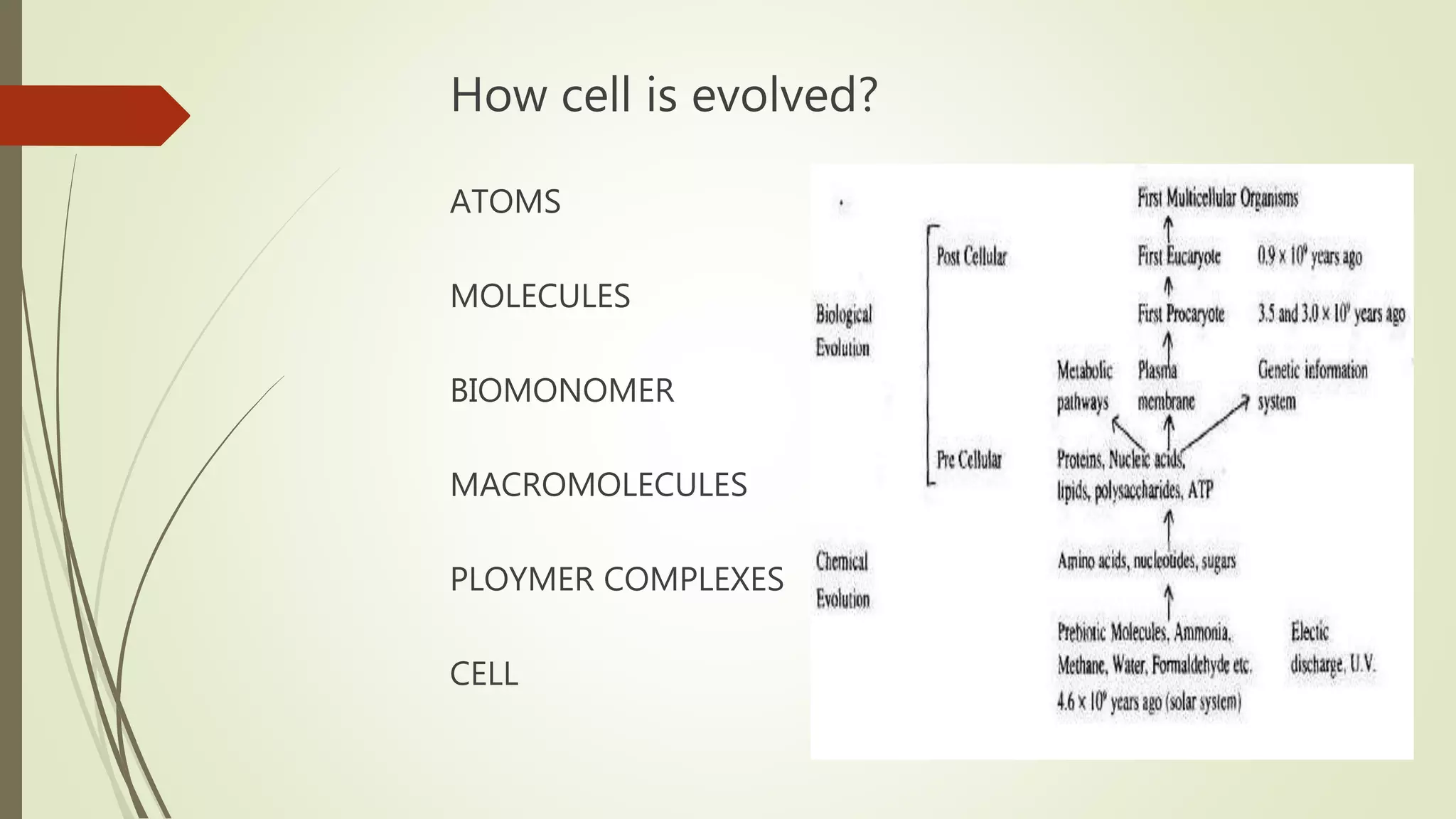
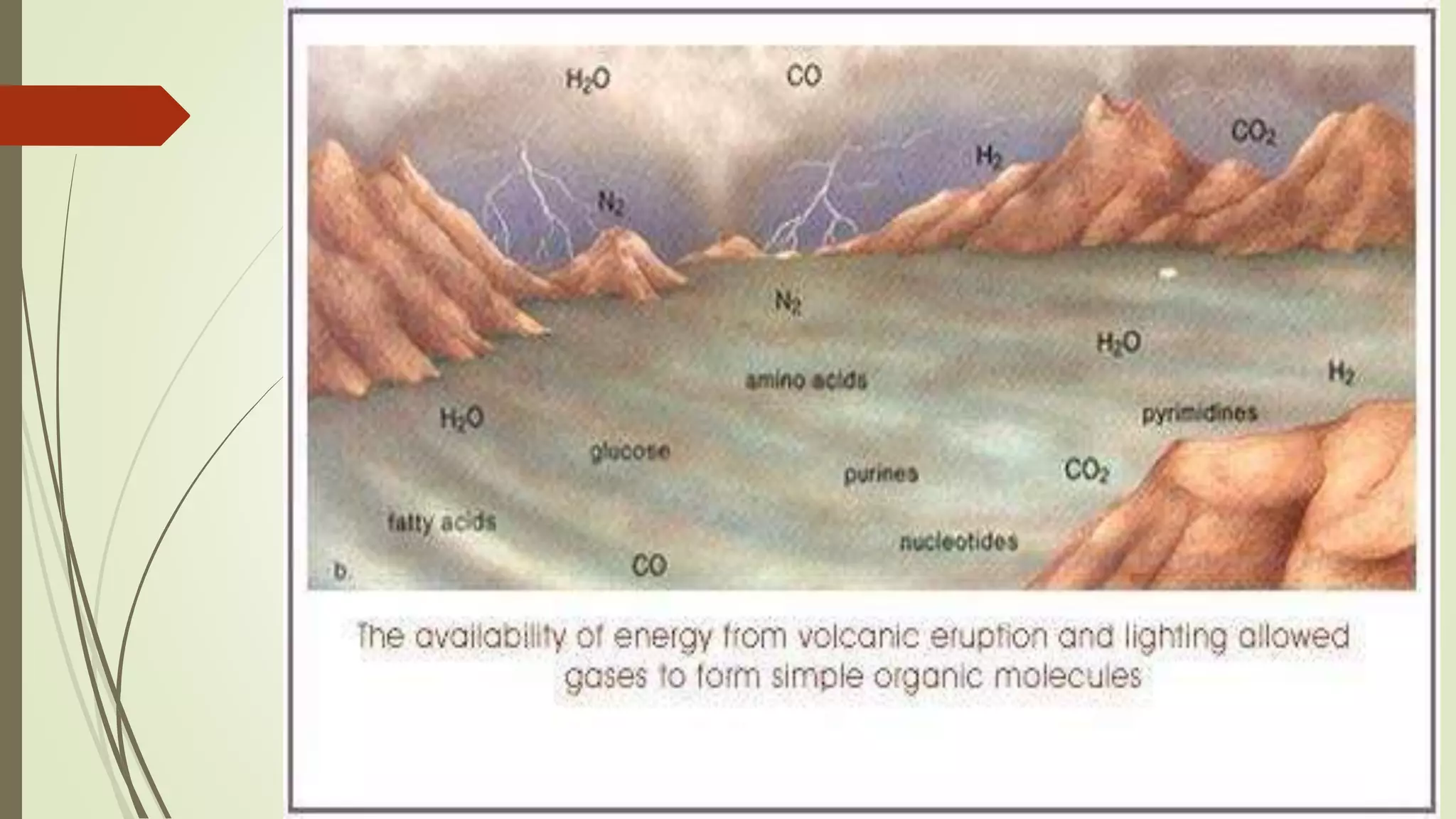
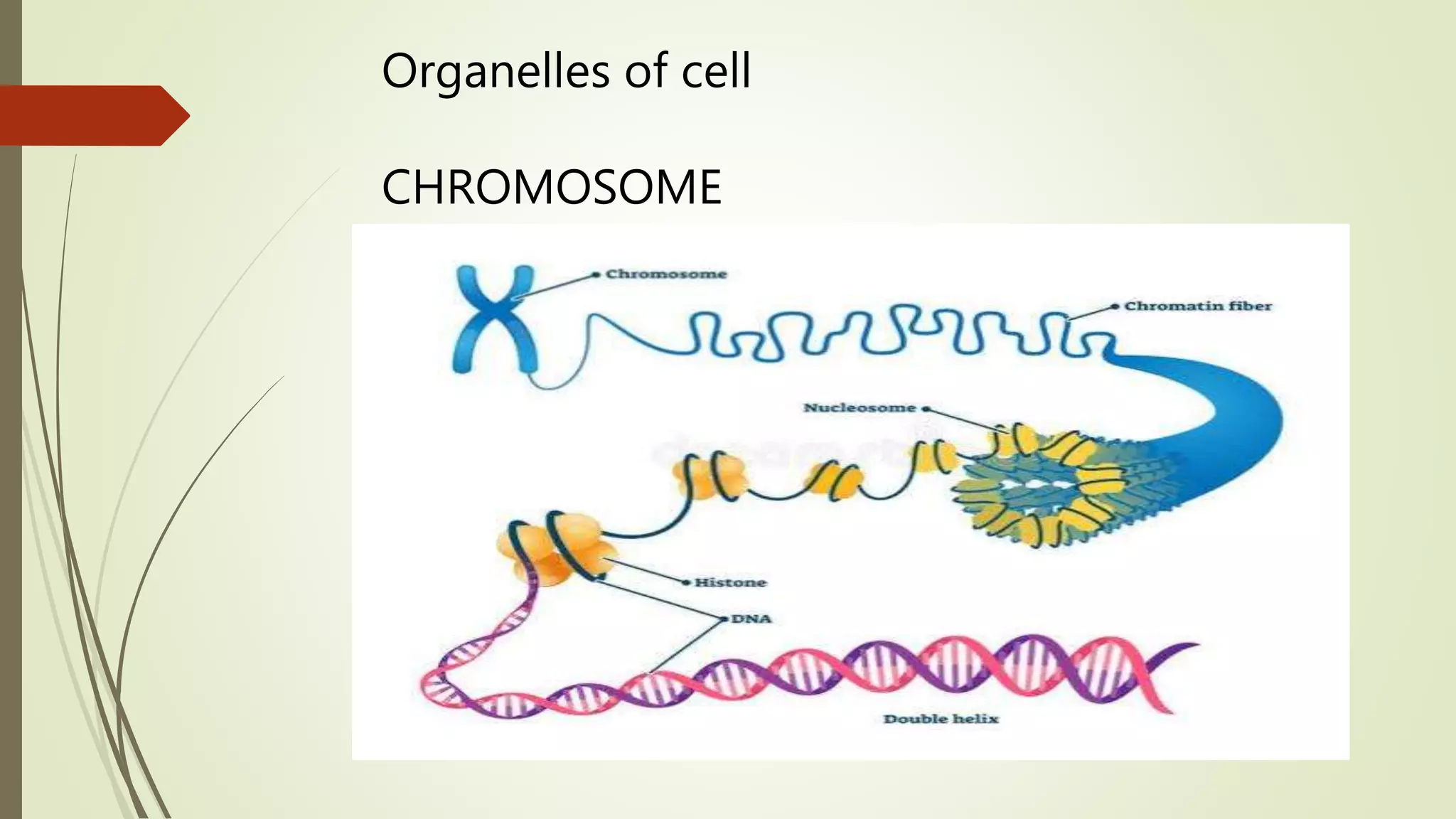
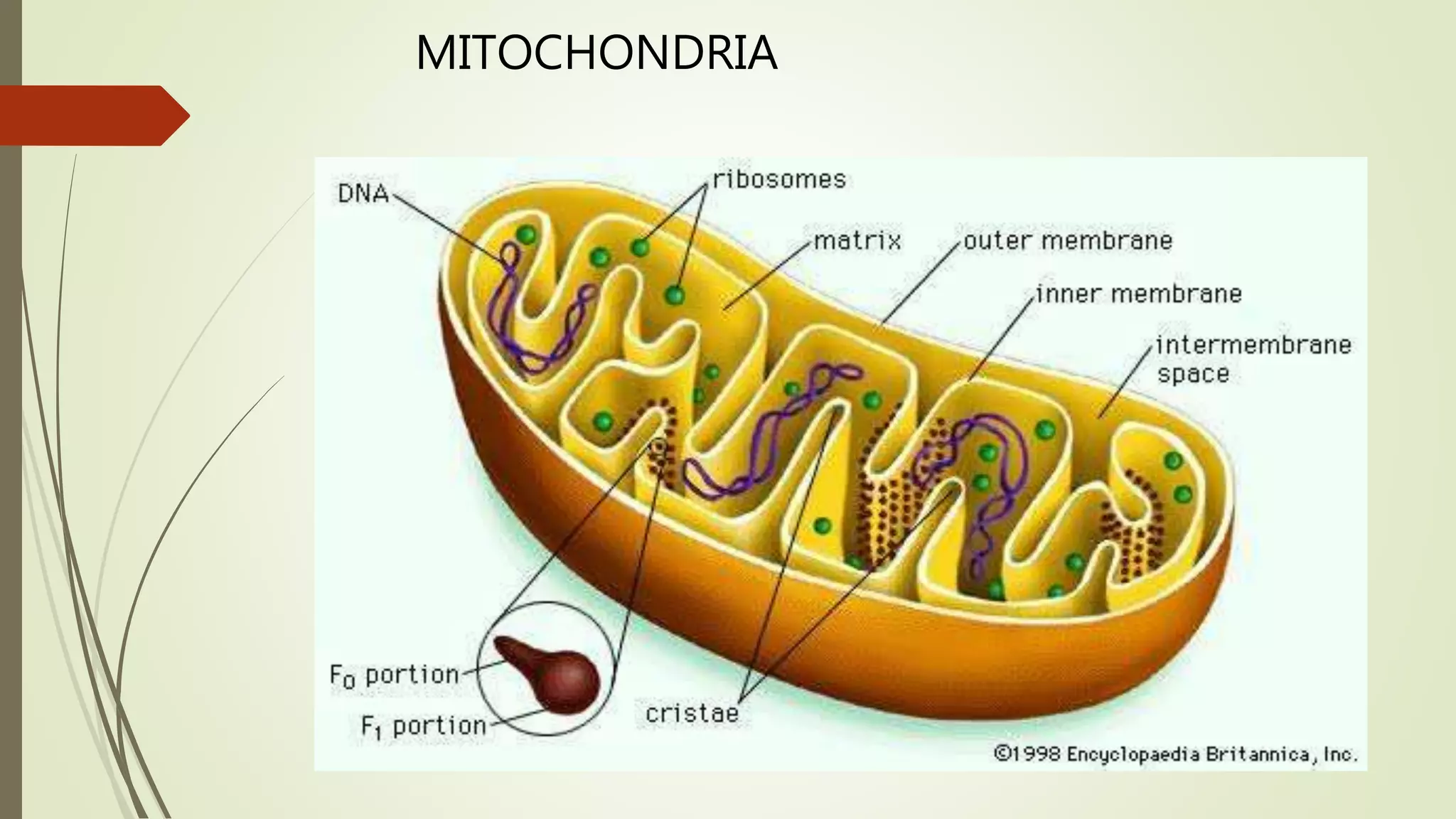
The document summarizes the evolution of cells from early molecules to modern cells. It describes how early Earth had conditions suitable for the formation of organic molecules. Through chemical reactions in the primordial soup, nucleotides and other biomolecules formed. RNA molecules emerged and were able to store and replicate genetic information, marking the RNA world hypothesis. Eventually, DNA arose as a more stable carrier of genetic code, while cells formed through the enclosure of RNA and other molecules in membranes. Key cellular components like chromosomes, ribosomes, and mitochondria developed as cells became more complex and specialized into prokaryotic and eukaryotic forms.