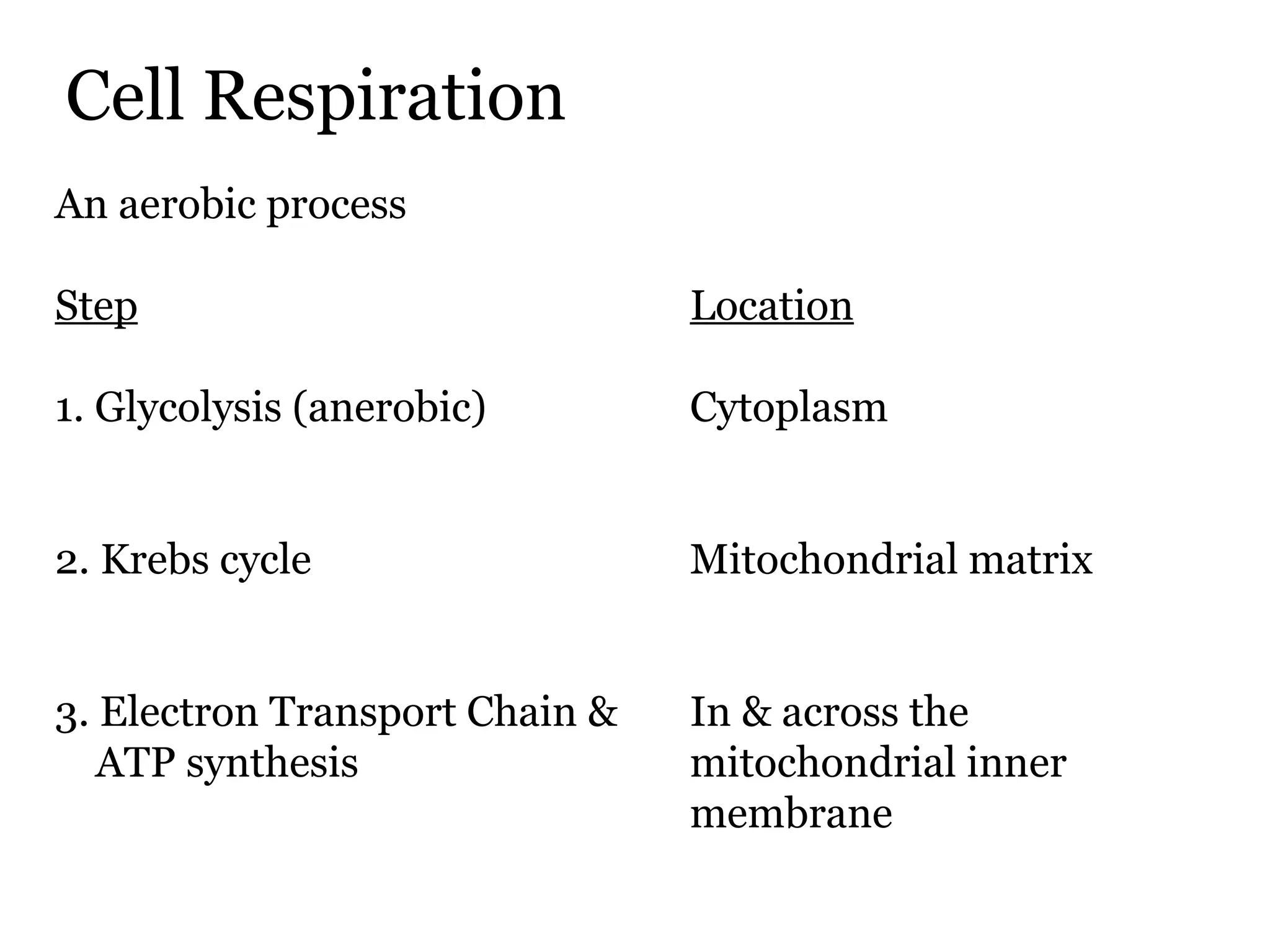
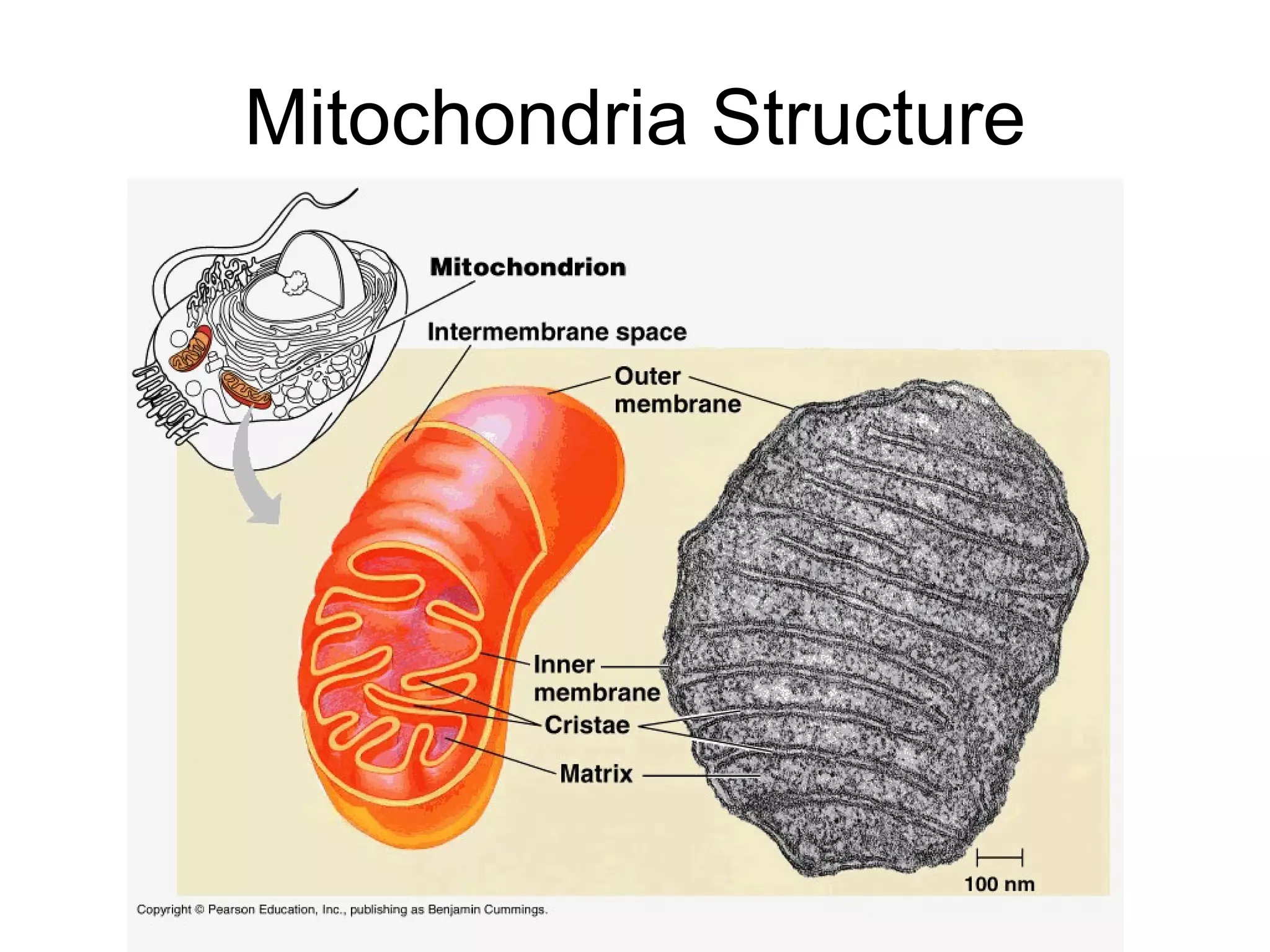
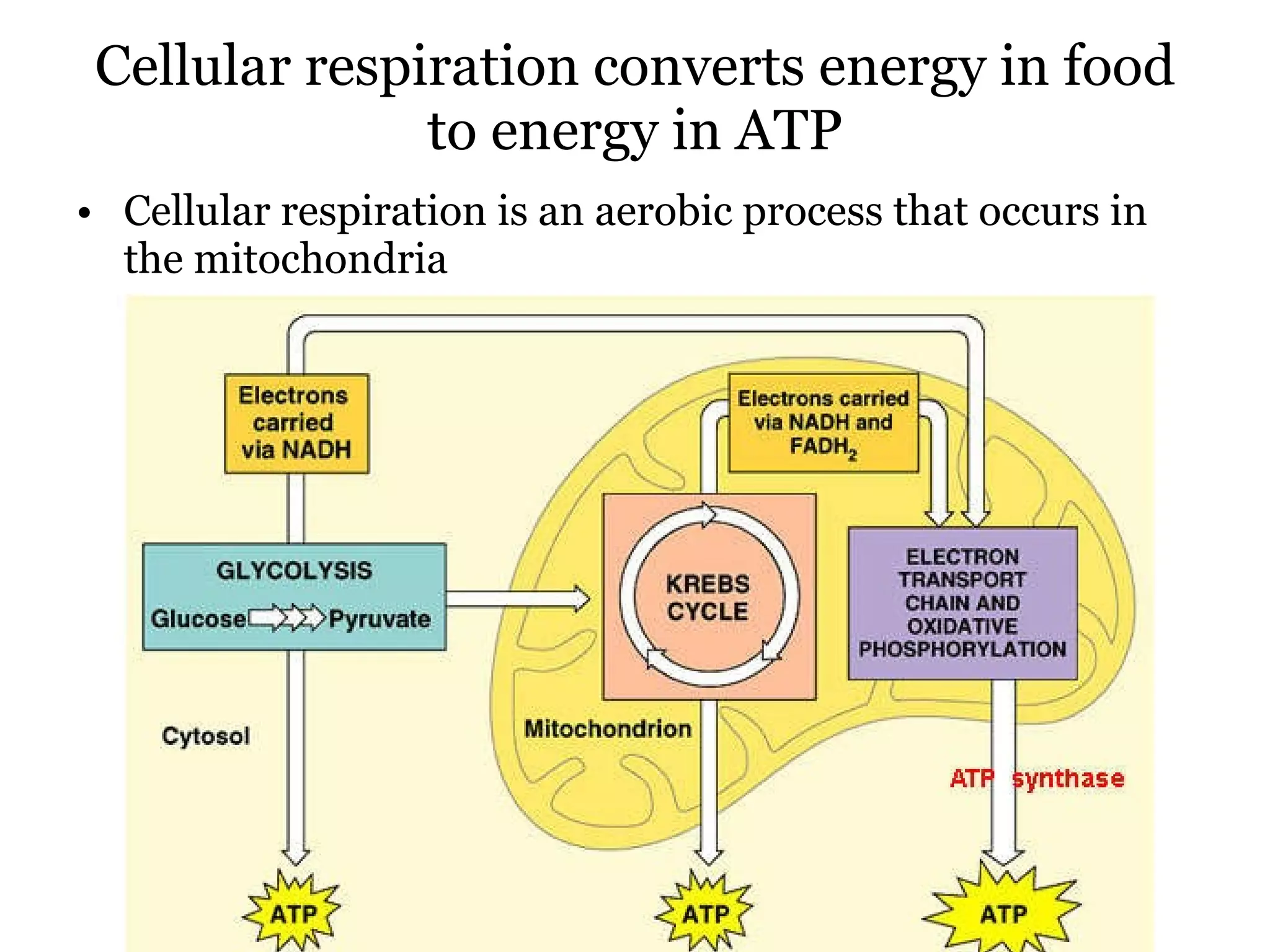
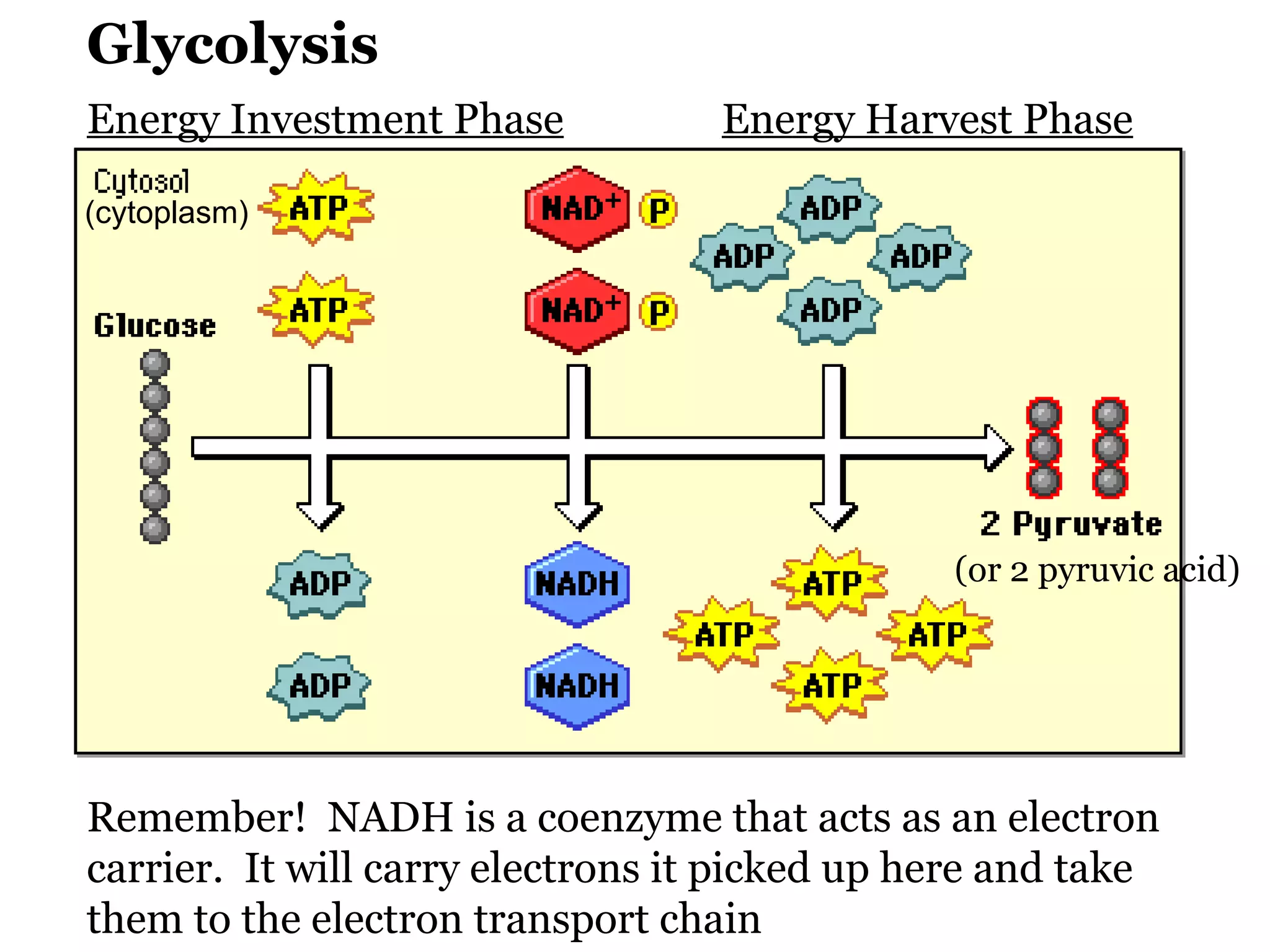
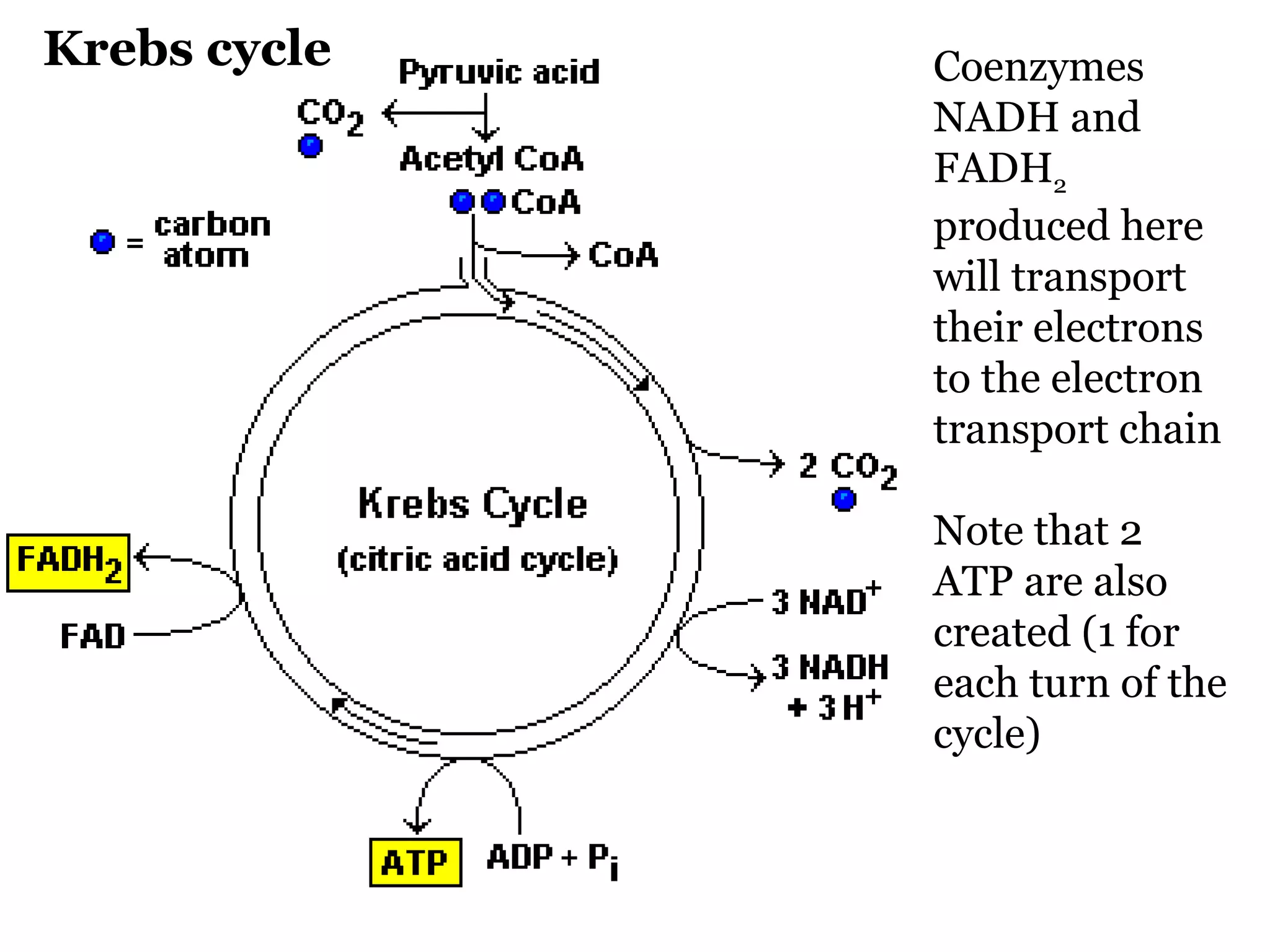
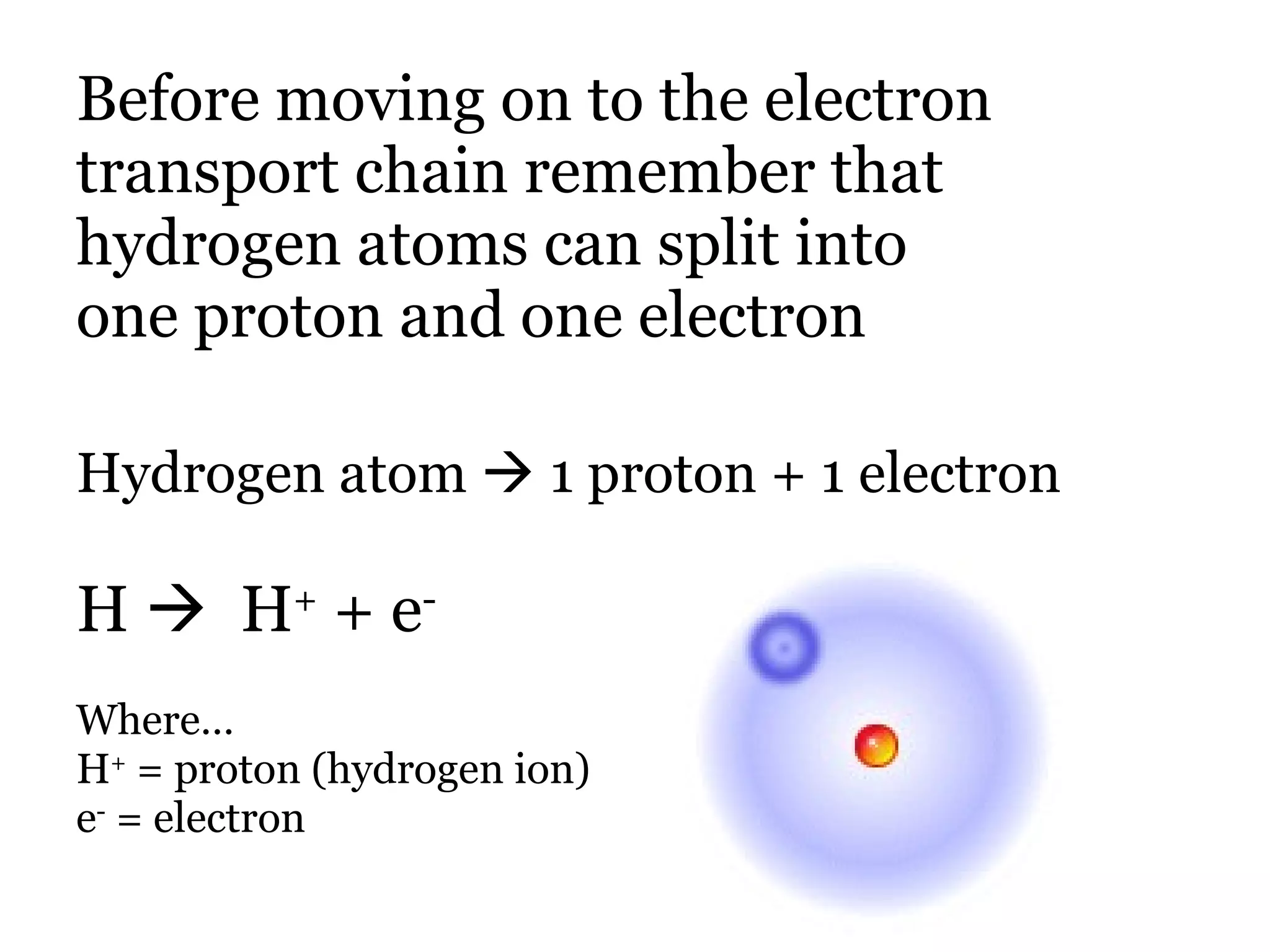
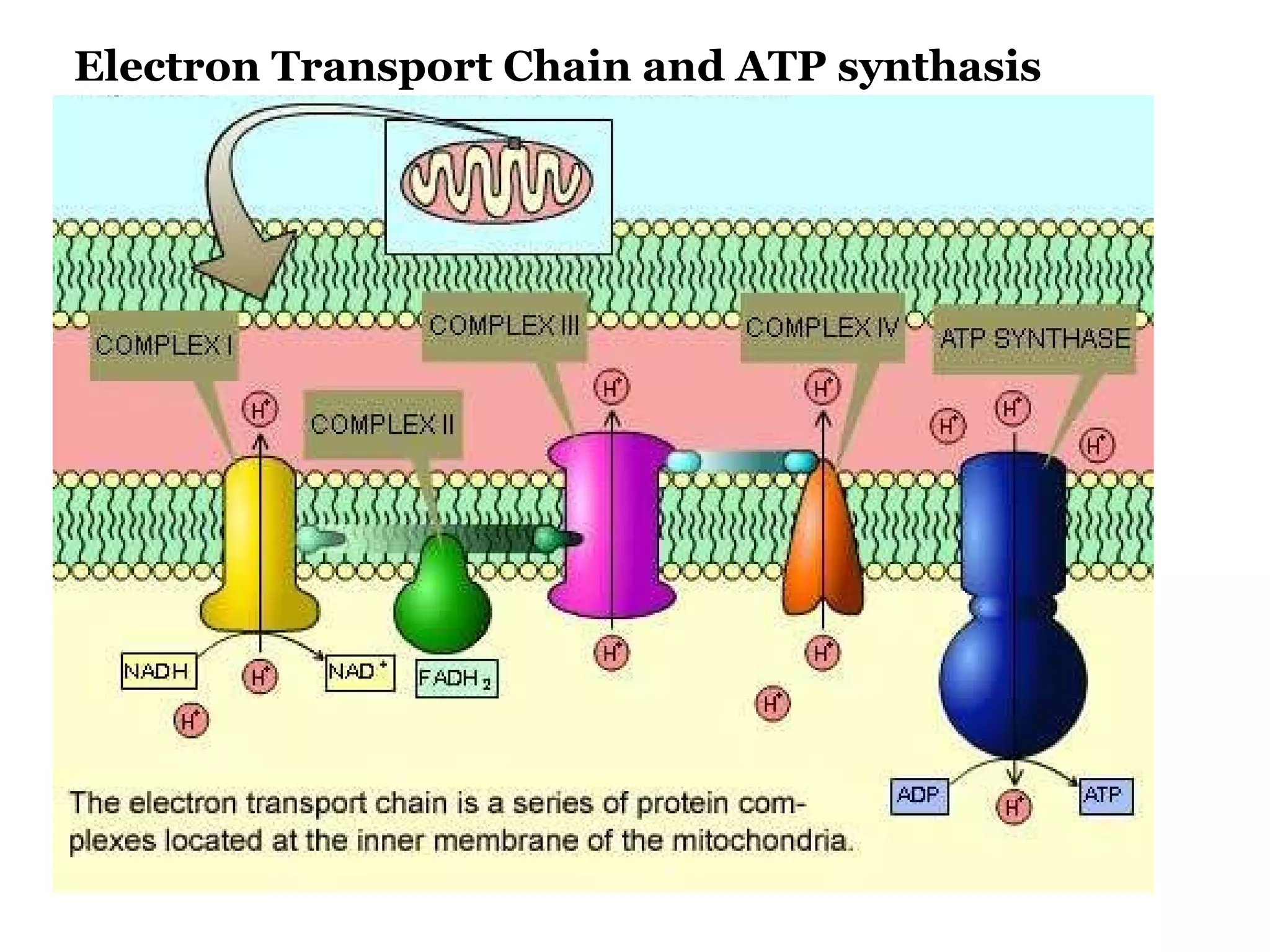
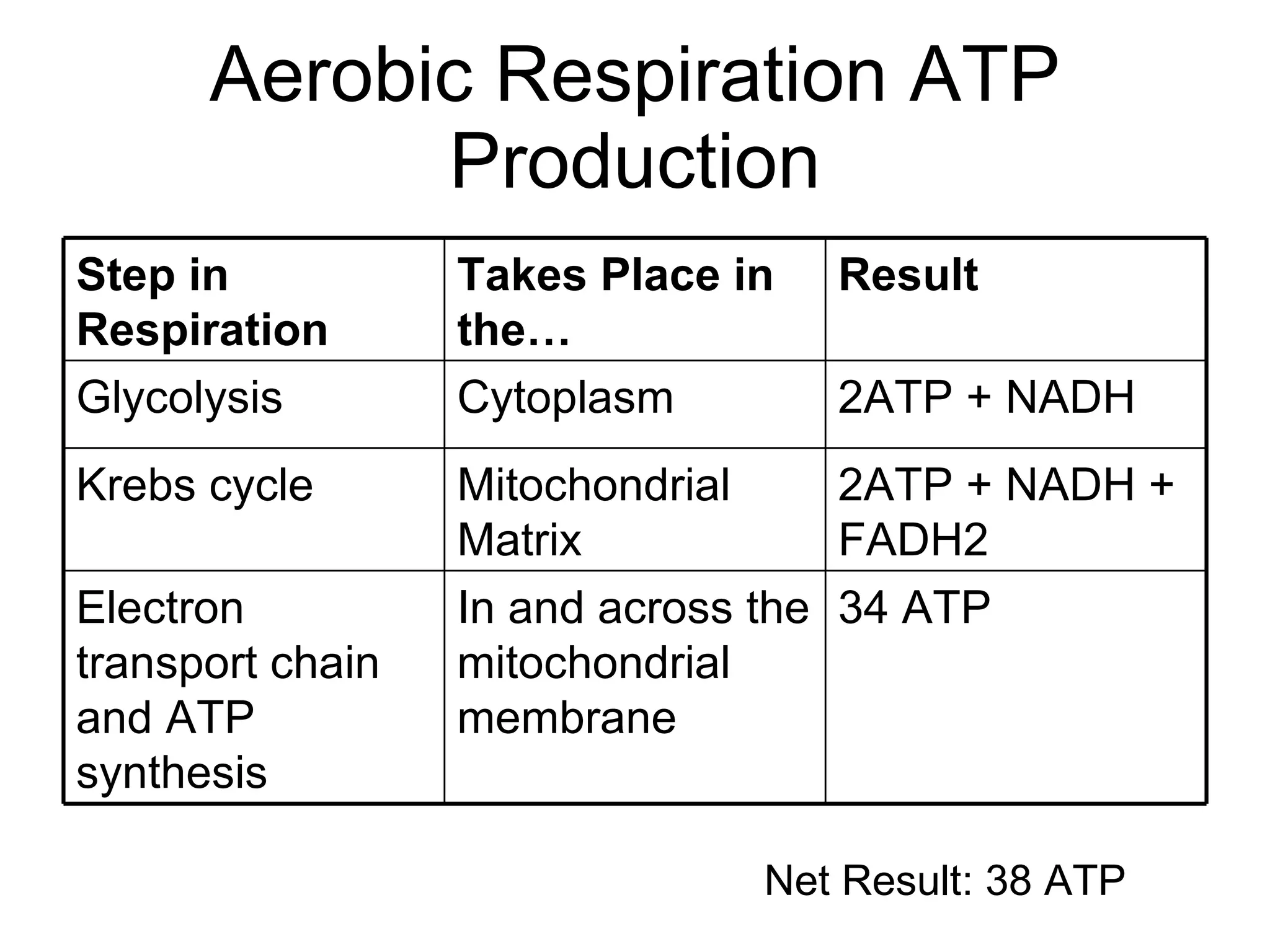
The document provides an overview of cellular respiration and outlines an in-class activity and homework assignments on the topic. Students will have a lecture on cell respiration, complete a card sorting activity to test their understanding, and be quizzed on chapter 7. They are to continue working on the activity at home if unfinished or study the cards. A test will be given on Friday.