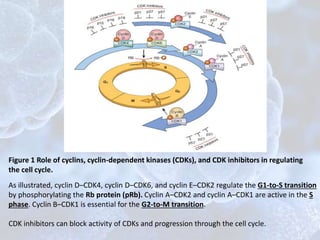
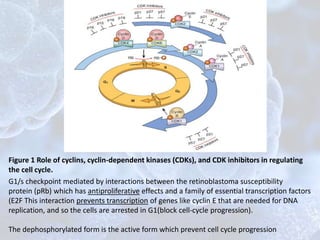
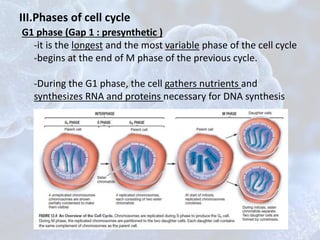
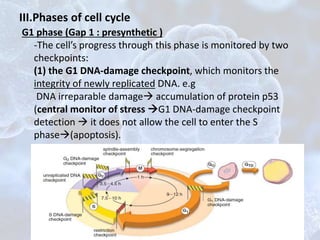
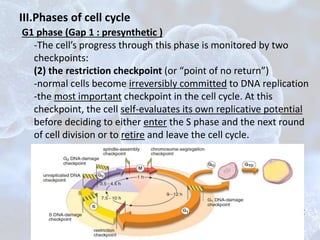
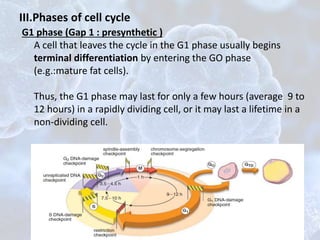
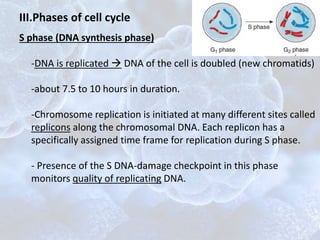
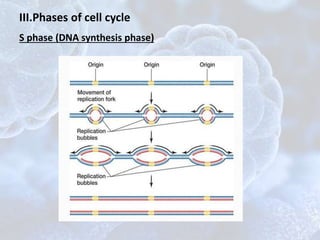
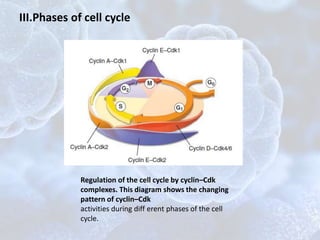
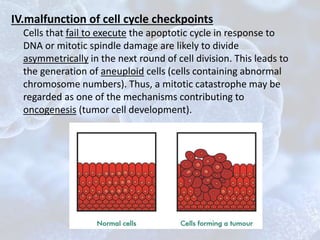
The cell cycle is the regulated process by which cells grow and divide to produce two daughter cells. It has two main phases: interphase and mitosis. Interphase consists of G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA. Mitosis is when the cell divides. The cell cycle is regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and CDK inhibitors. Checkpoints ensure DNA quality and control cell cycle progression. Cell cycle dysregulation can lead to uncontrolled cell division and cancer.