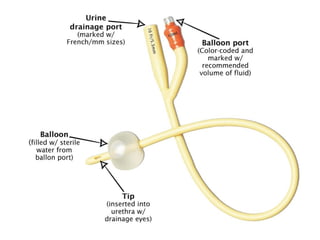
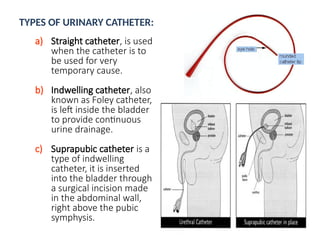
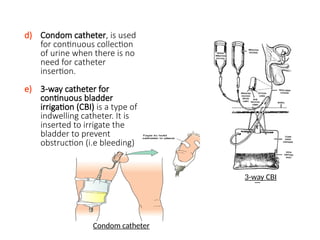
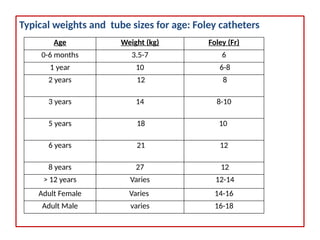
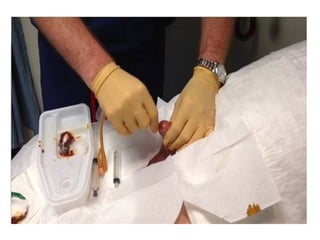
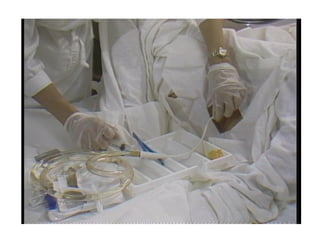
Urinary catheterization involves inserting a hollow tube through the urethra into the bladder to remove urine, requiring sterile equipment. It serves various purposes such as relieving urinary retention, obtaining sterile urine specimens, and measuring urine output. Different types of catheters are available, each designed for specific uses, and a detailed procedural guide is provided for safe catheterization.