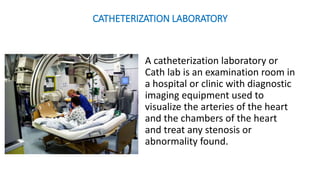
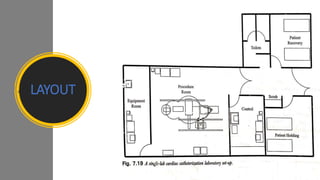
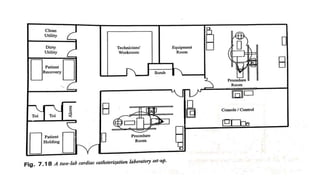
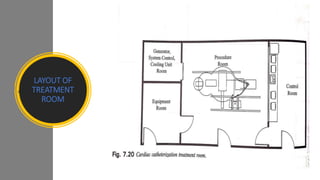
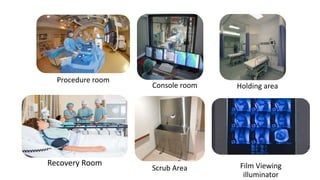
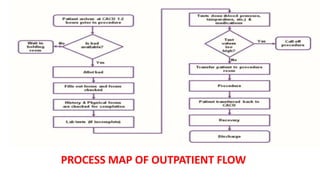
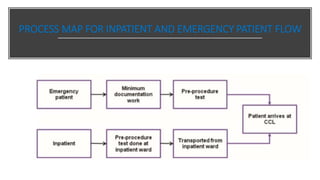
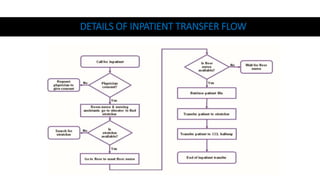
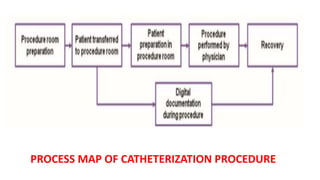
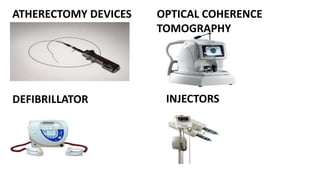
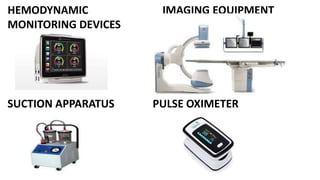
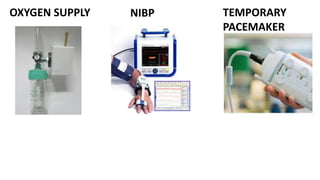
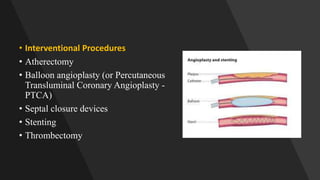
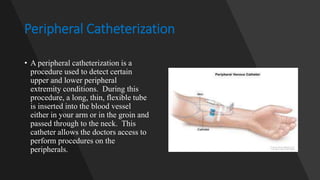
A catheterization laboratory (cath lab) is a specialized facility in hospitals for diagnosing and treating heart conditions using advanced imaging and interventional technologies. It focuses on delivering high-quality care while maintaining patient privacy and comfort, and includes various equipment and procedural rooms designed for efficient workflow and patient care. The document outlines the design, staffing, procedures, and quality control measures associated with cath labs to enhance operational efficiency and patient outcomes.