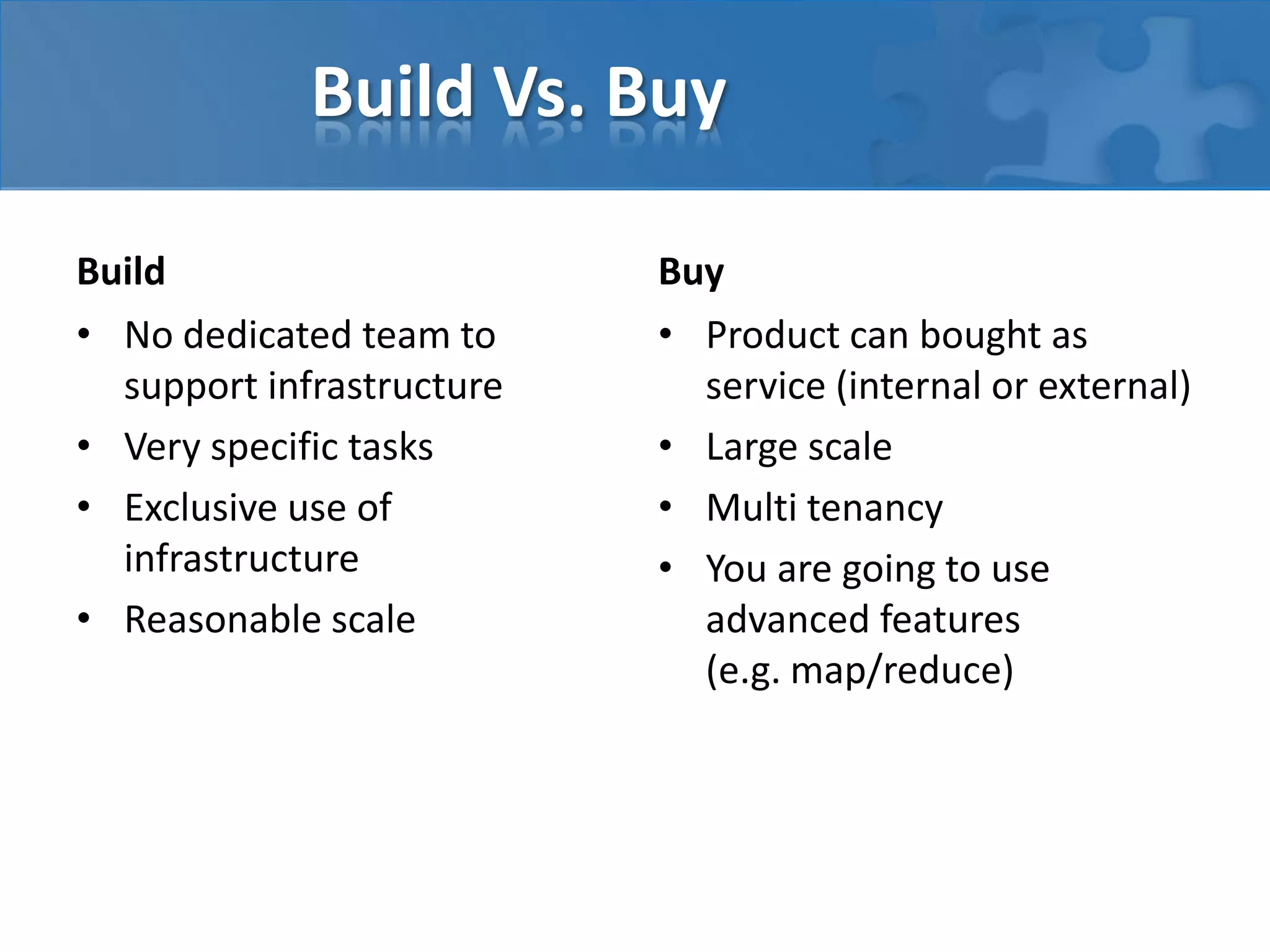
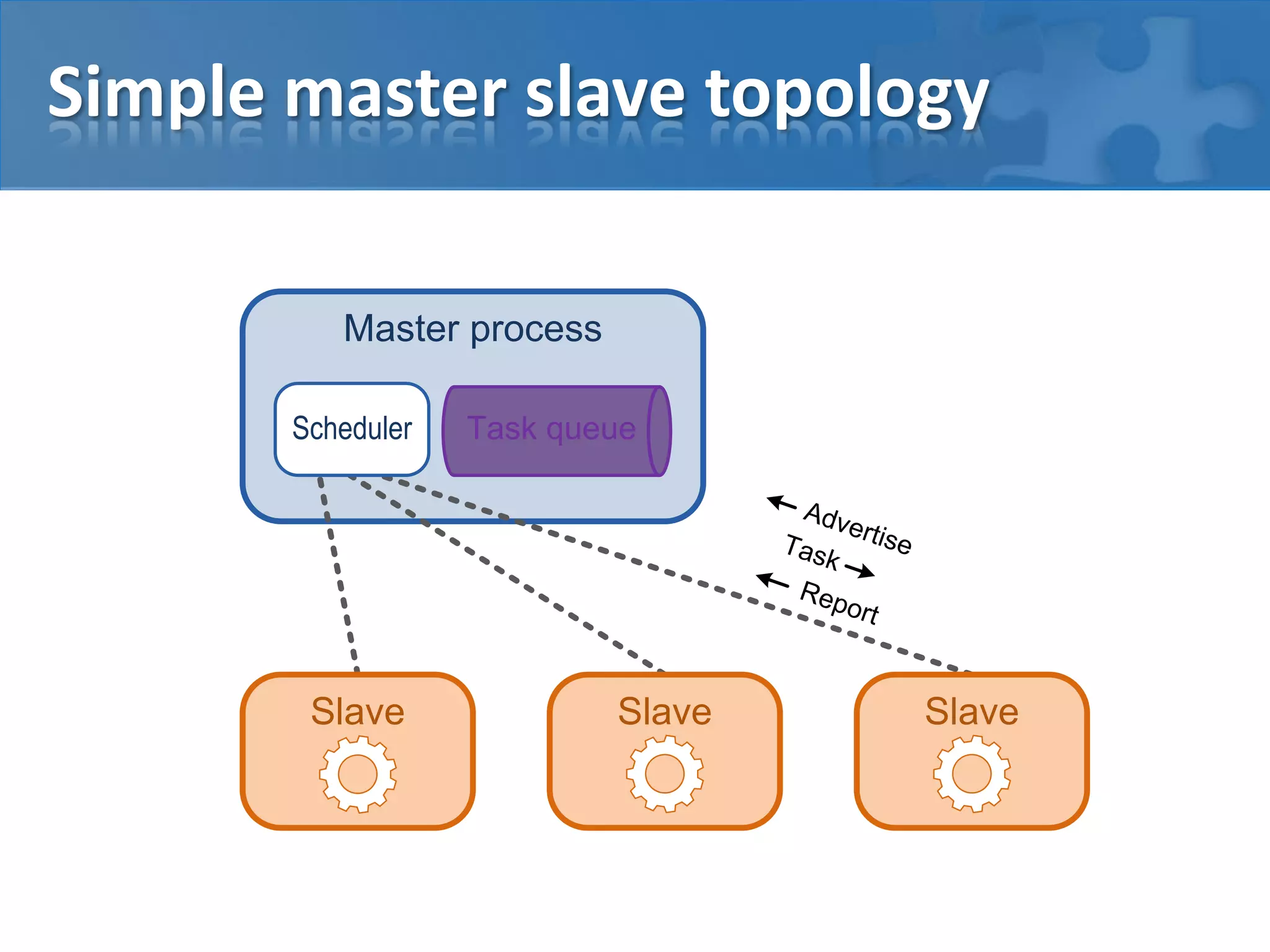
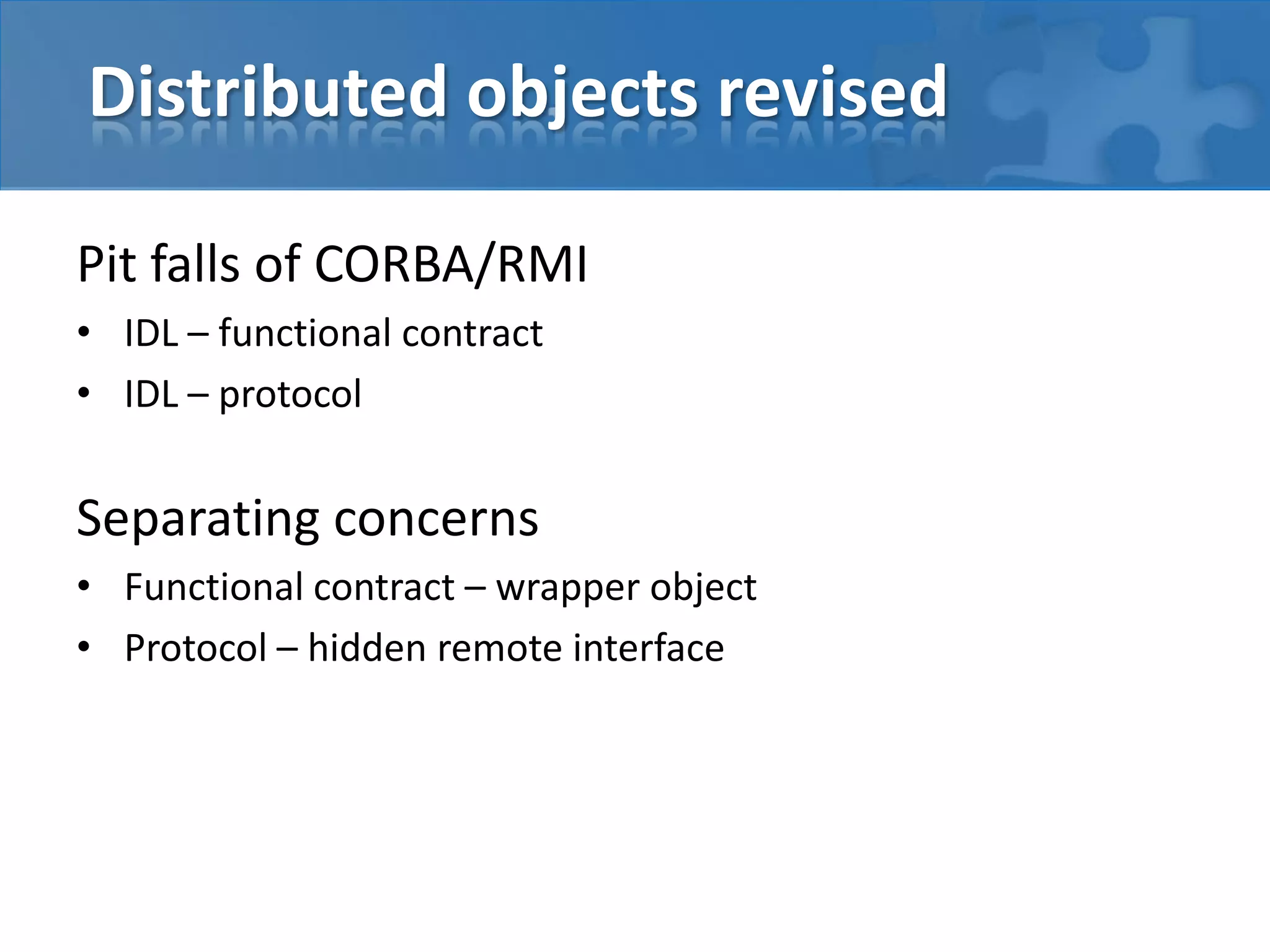
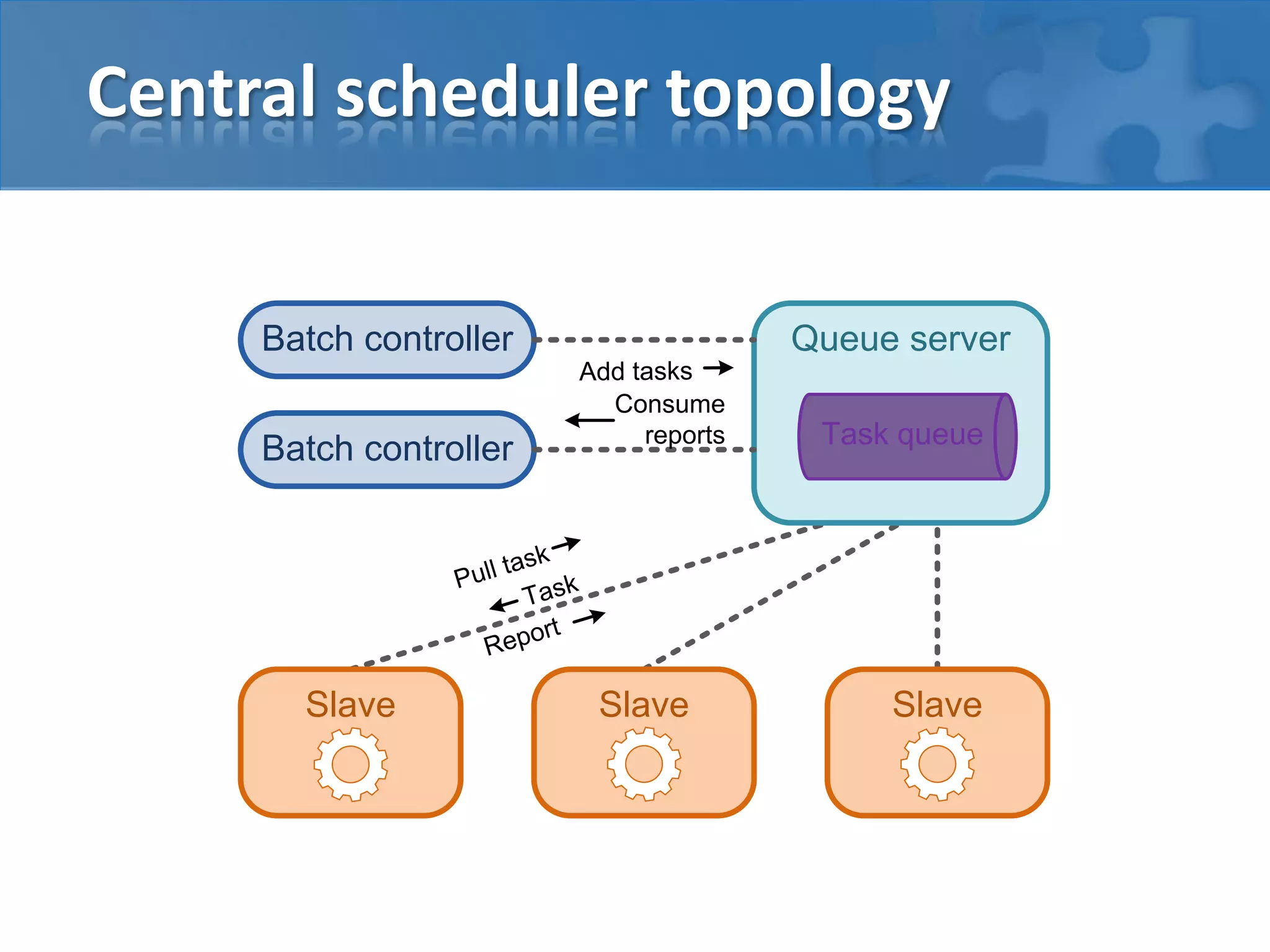
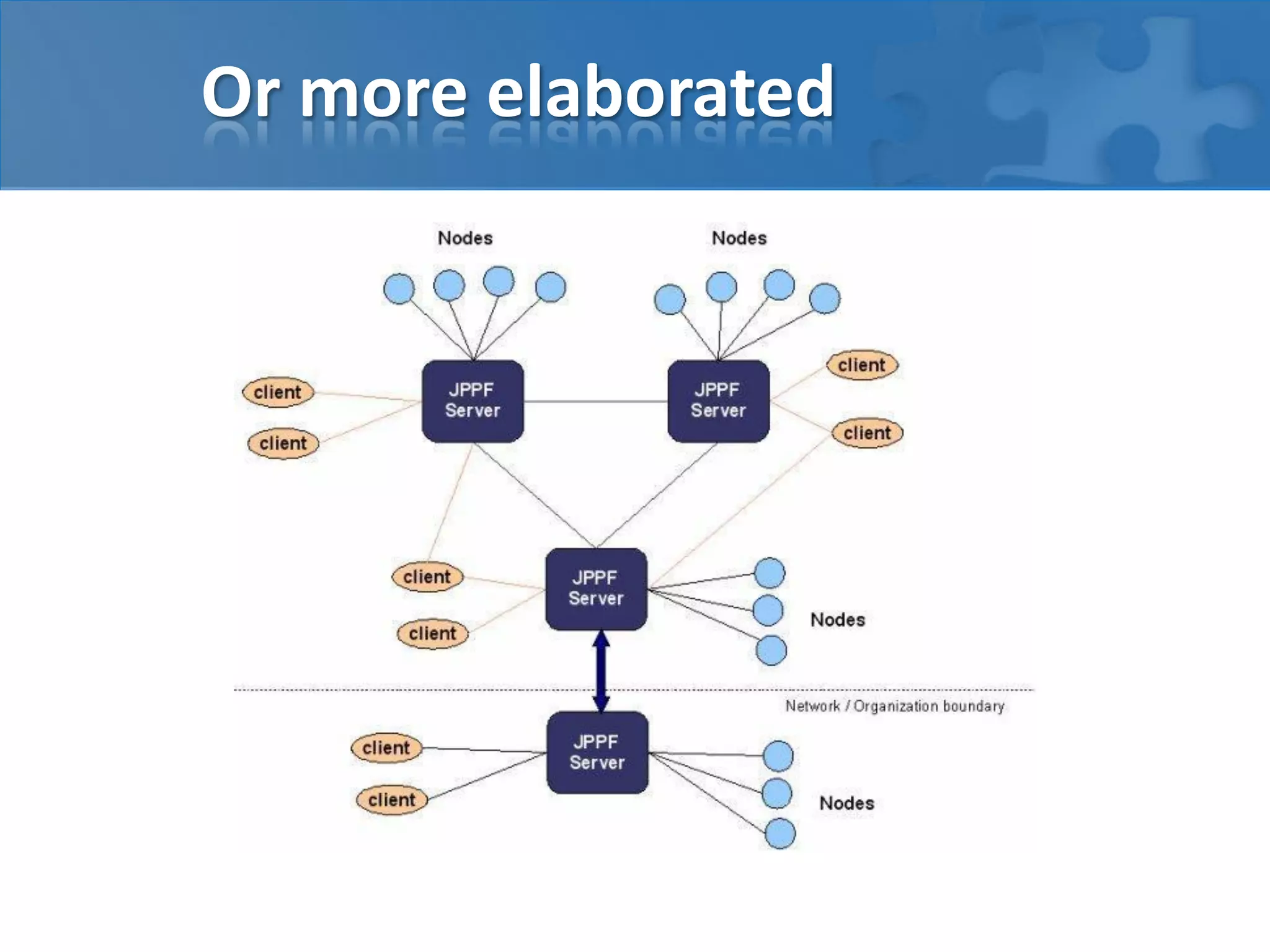
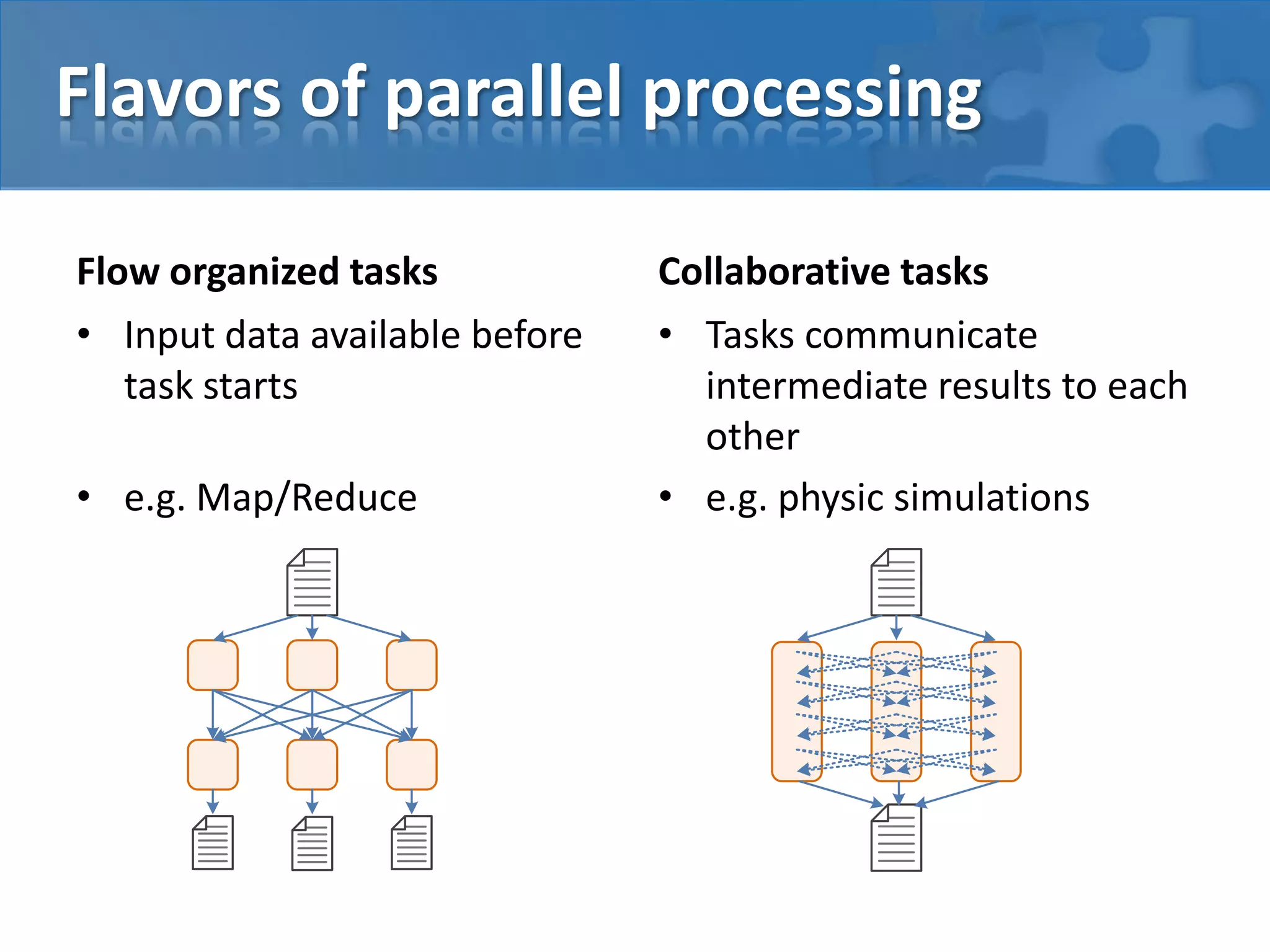
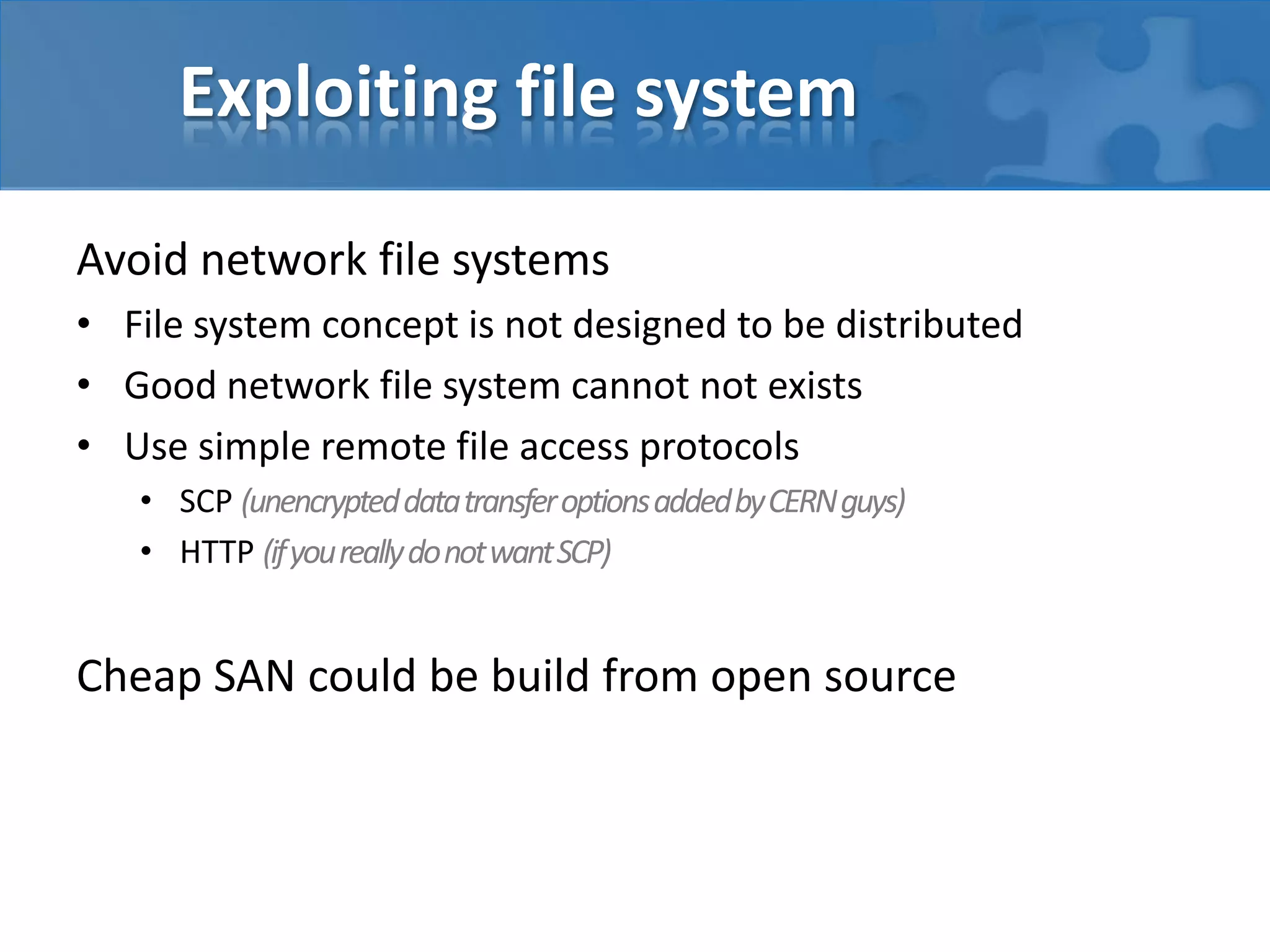
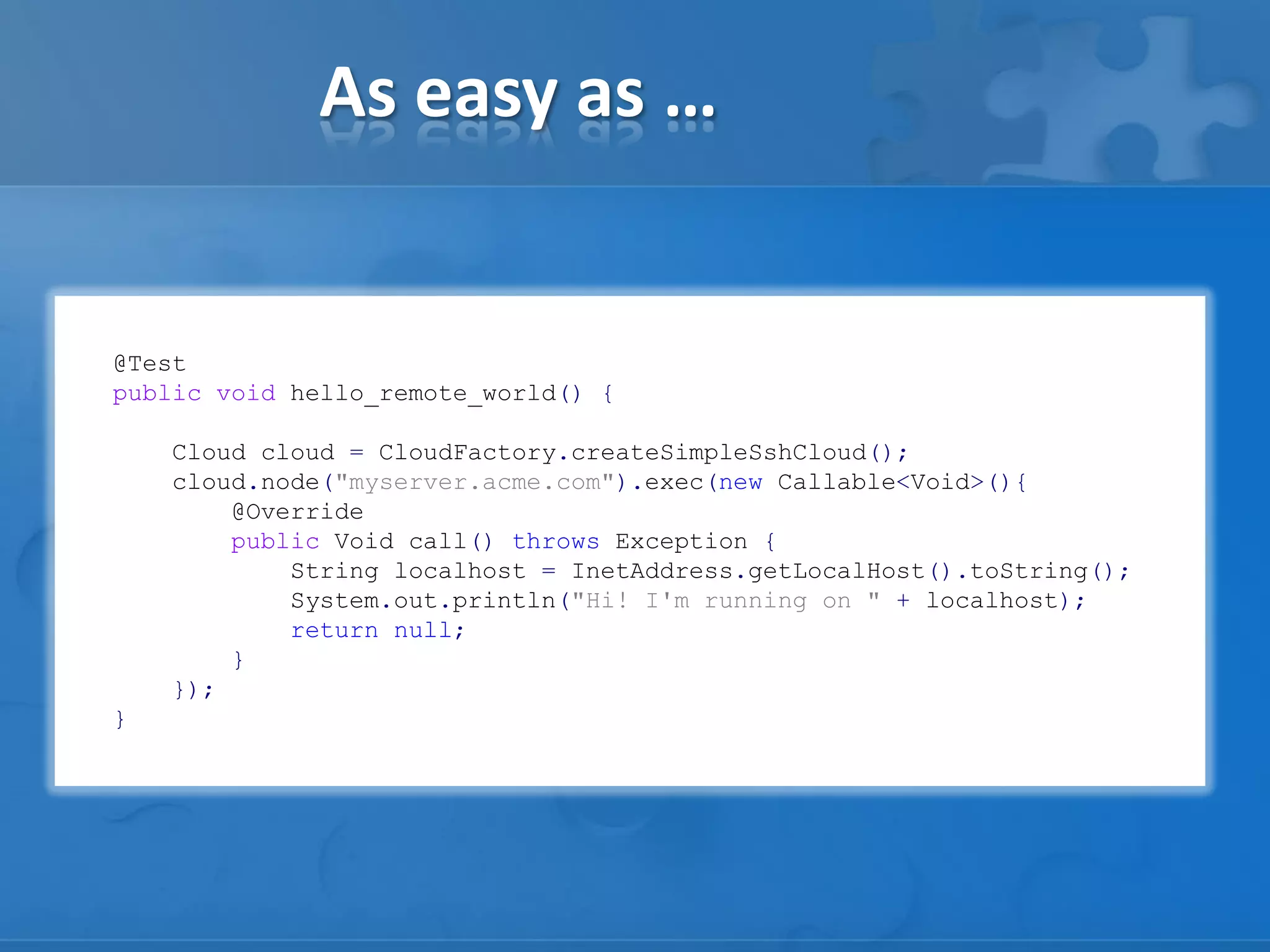
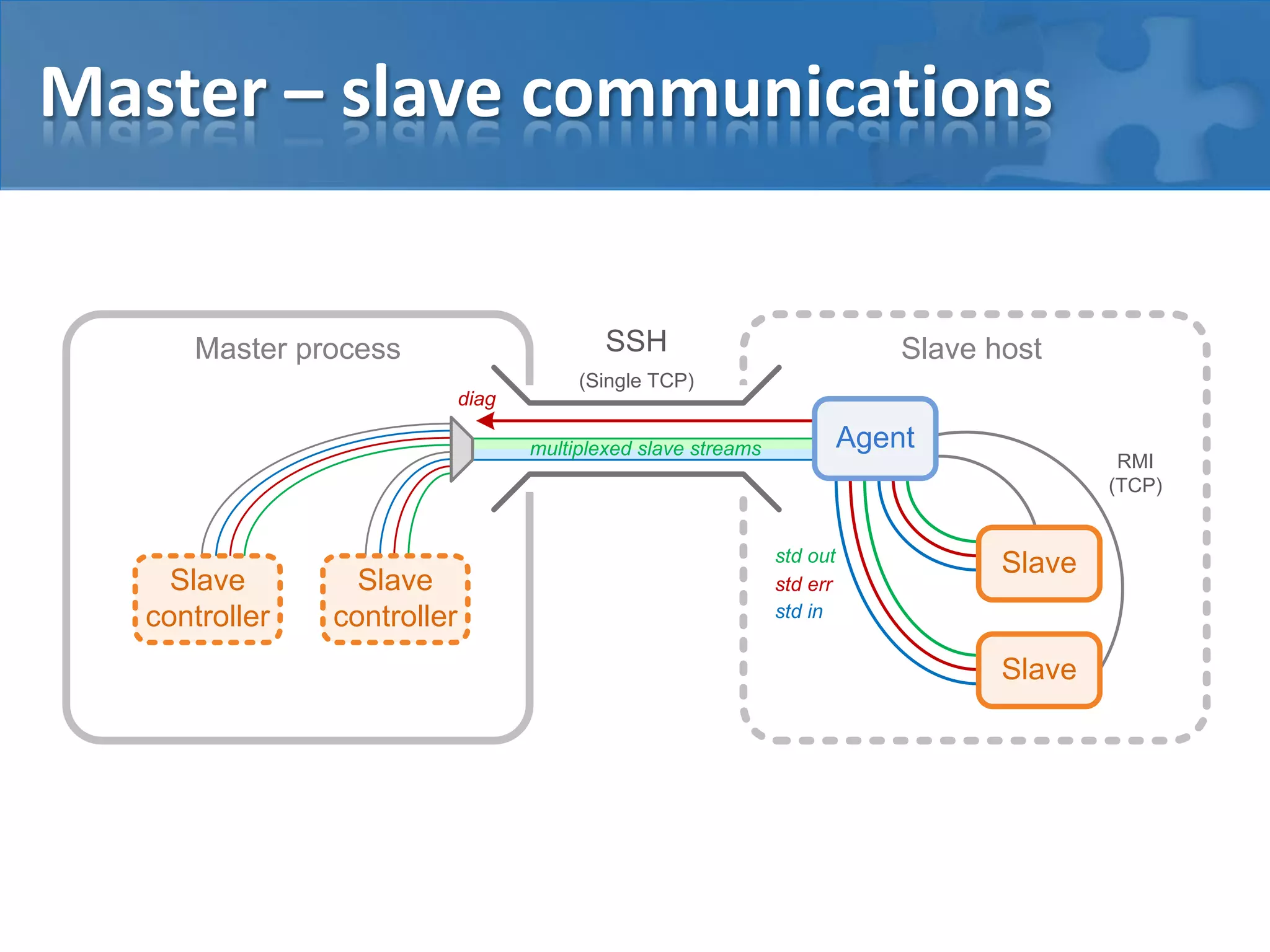
This document discusses strategies for casual mass parallel data processing using Java. It describes using a simple master-slave topology with a task queue and scheduler to distribute work. The data plane should avoid sending data over RMI and instead use local file systems or in-memory databases. NanoCloud is introduced as a way to drastically simplify coding for computing clusters by allowing remote code execution over SSH.