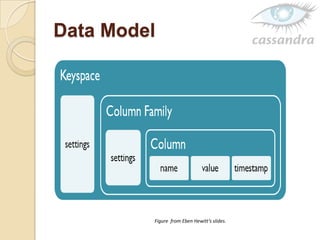
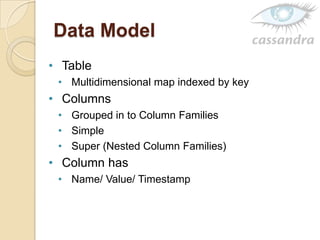
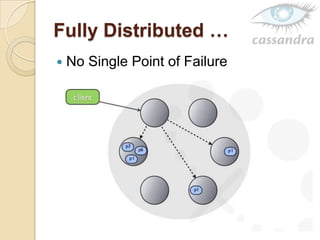
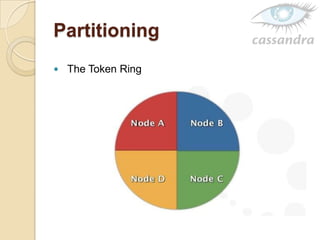
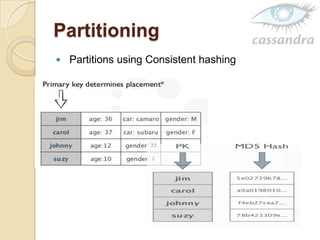
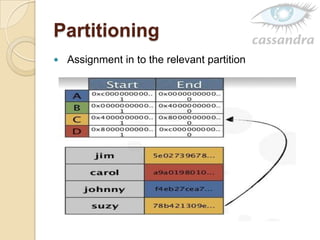
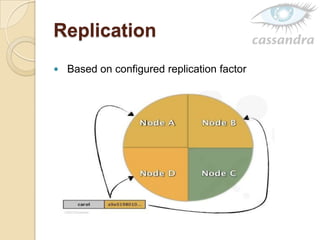
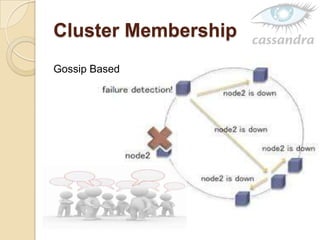
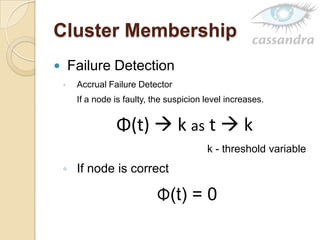
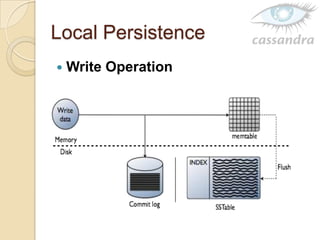
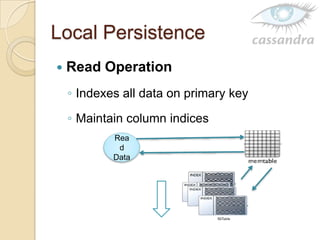
Cassandra is a decentralized structured storage system developed at Facebook to handle large amounts of structured data across many servers. It uses a distributed architecture with no single point of failure and dynamically replicates data across nodes for high availability. Cassandra uses a column-oriented data model and supports operations like insert, get, and delete. It partitions and distributes data using consistent hashing and handles failures through gossip-based cluster membership and an anti-entropy protocol.