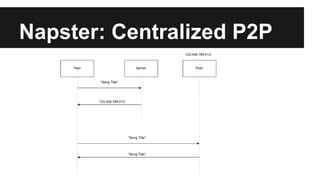
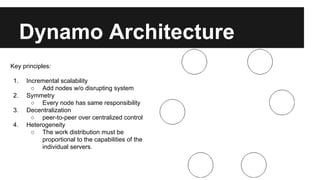
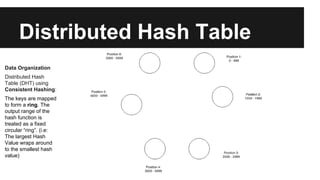
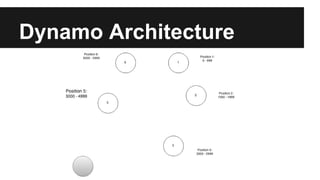
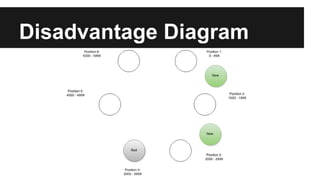
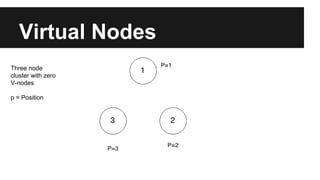
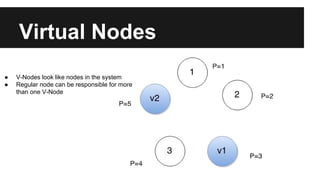
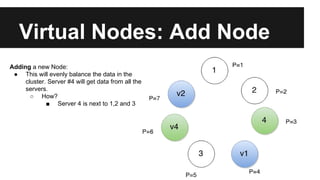
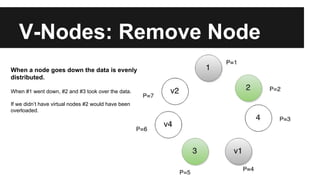
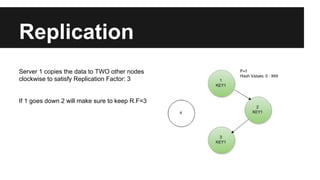
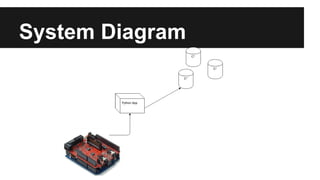
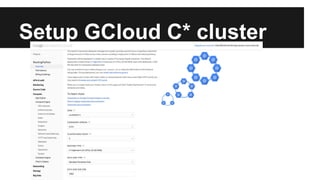
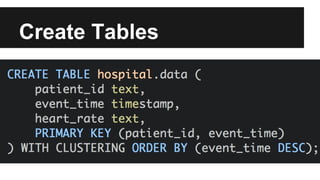
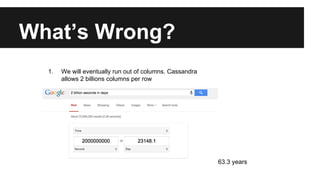
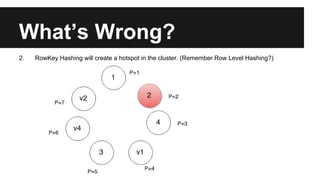
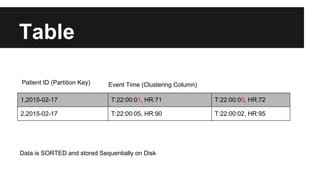
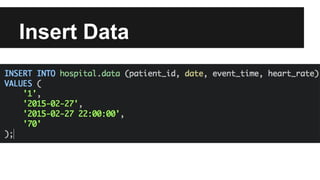
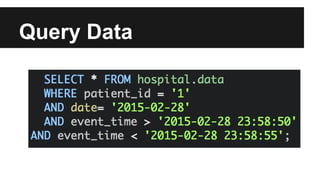
This document provides an overview of Apache Cassandra's history and architecture. It discusses how Cassandra was influenced by Amazon's Dynamo paper and Google's BigTable. Key aspects of Cassandra covered include its use of consistent hashing to organize data, replication for high availability, and best practices for modeling time series data to address limitations of row-level hashing.