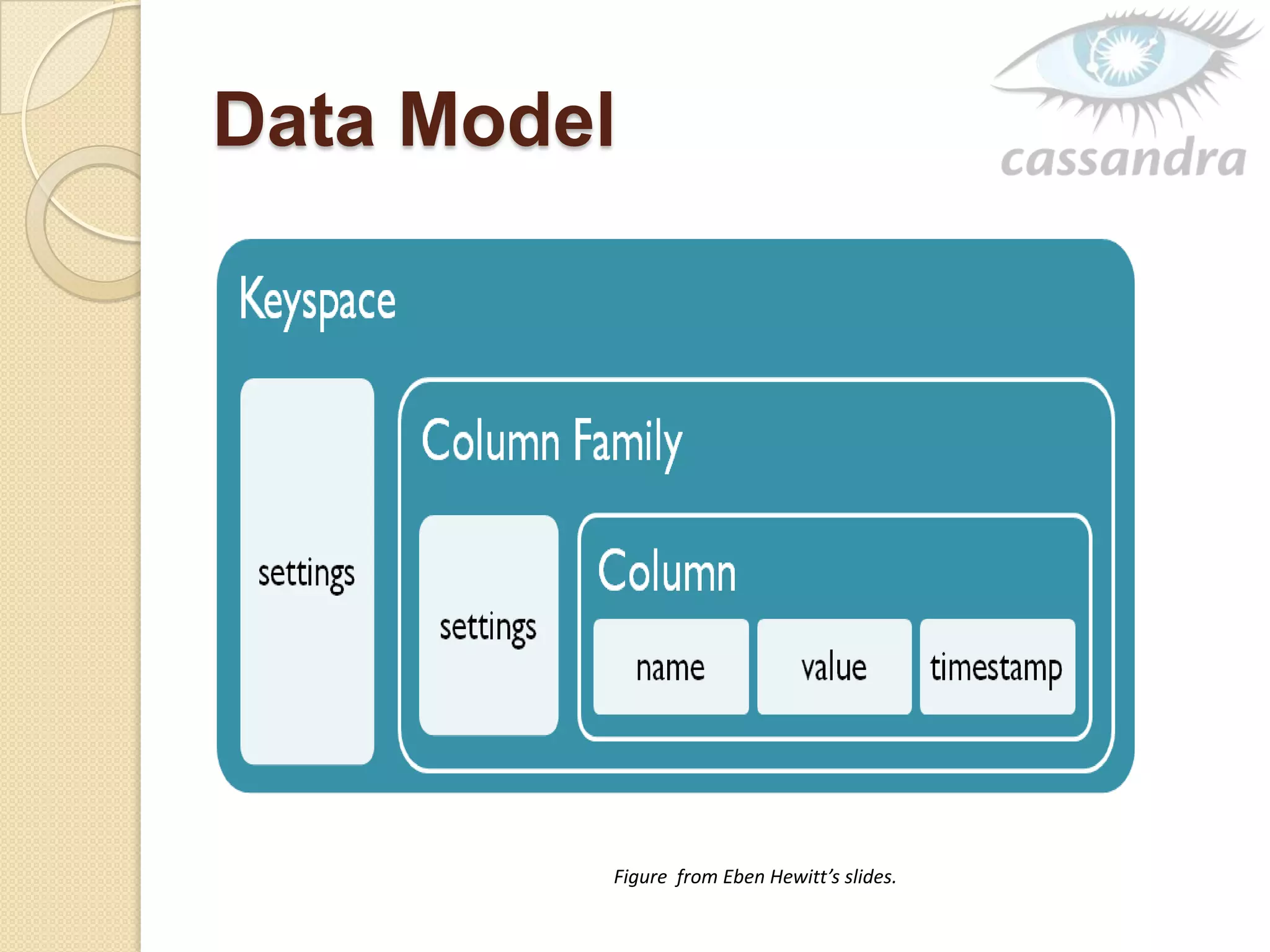
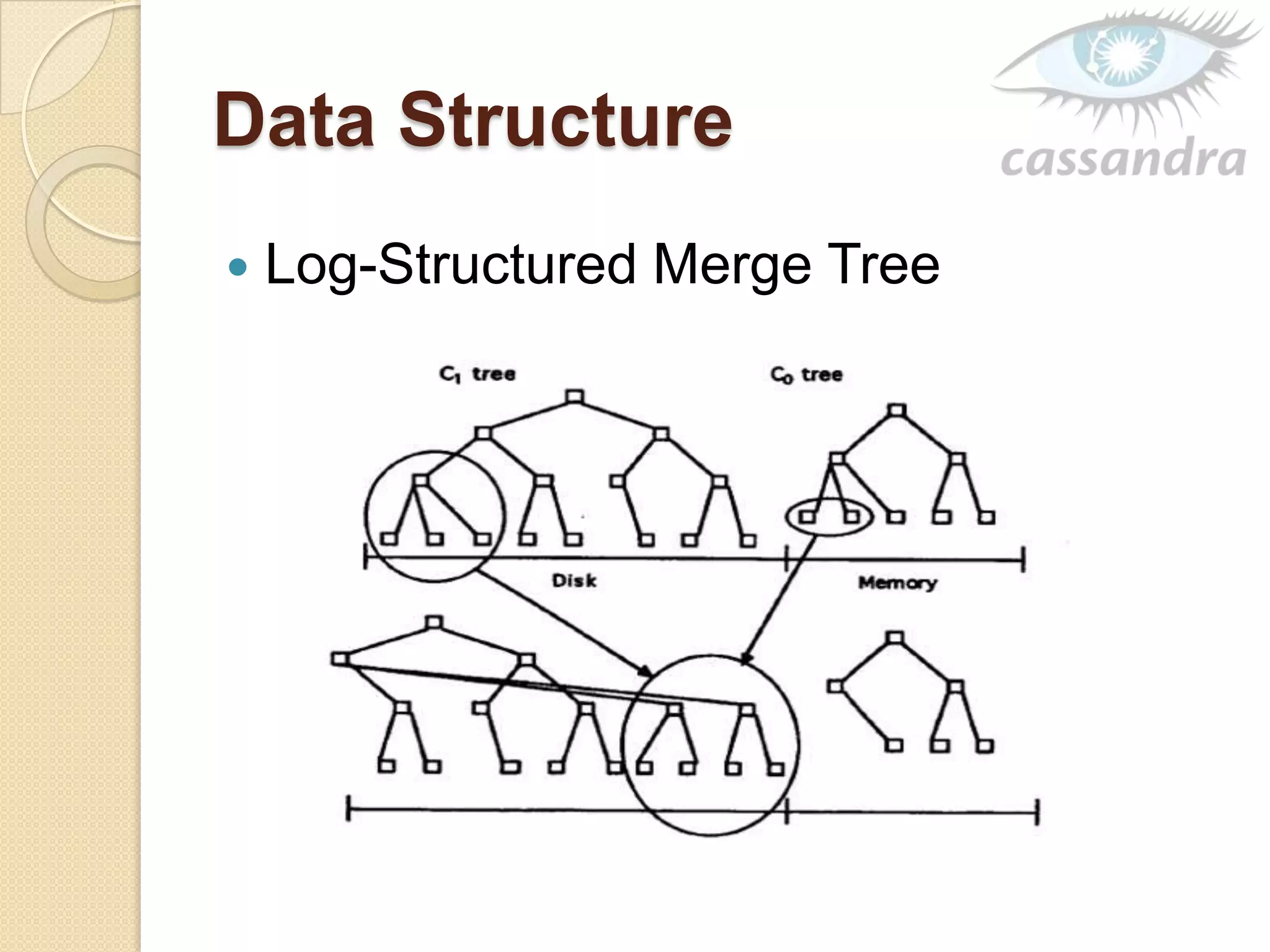
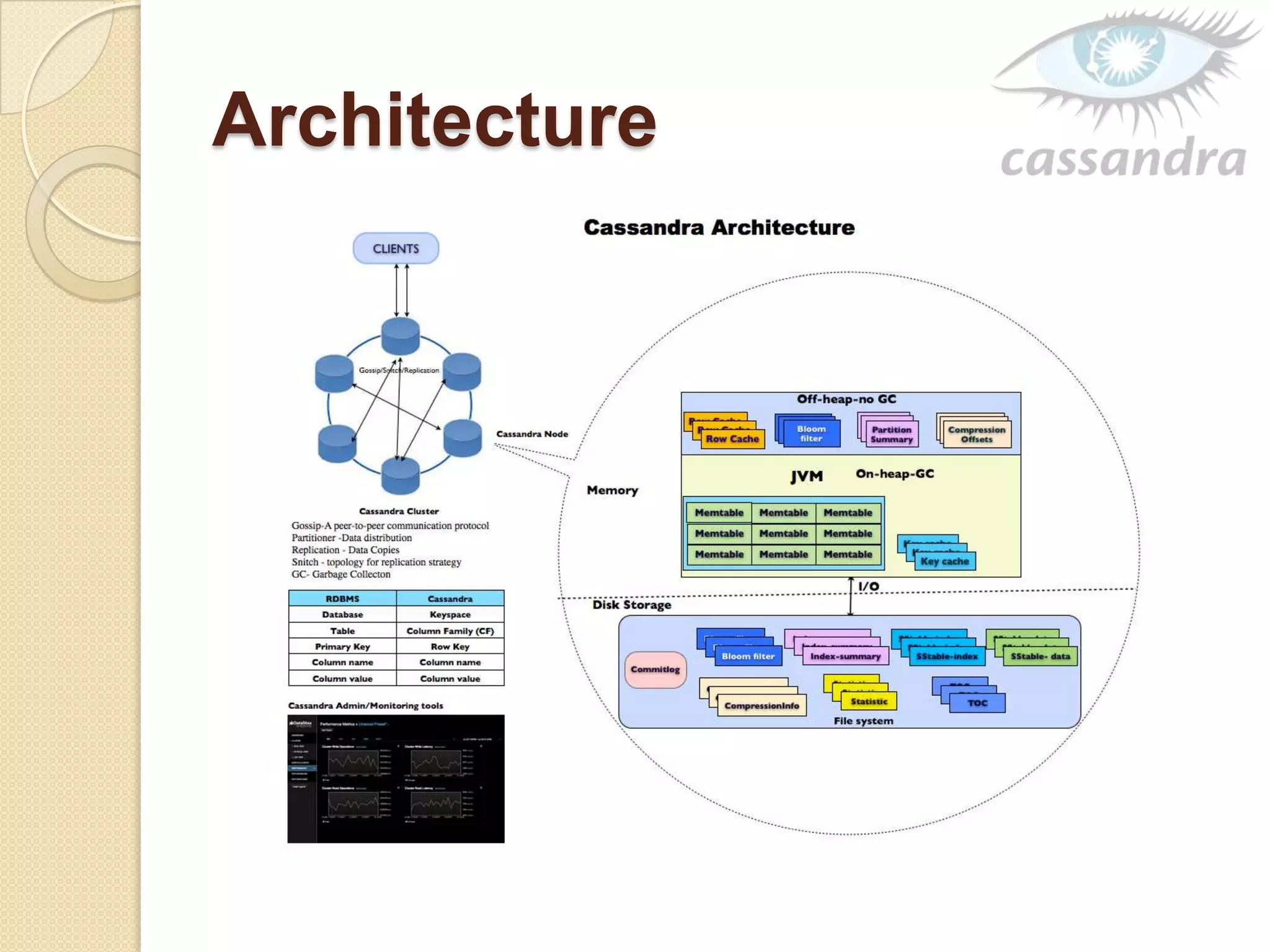
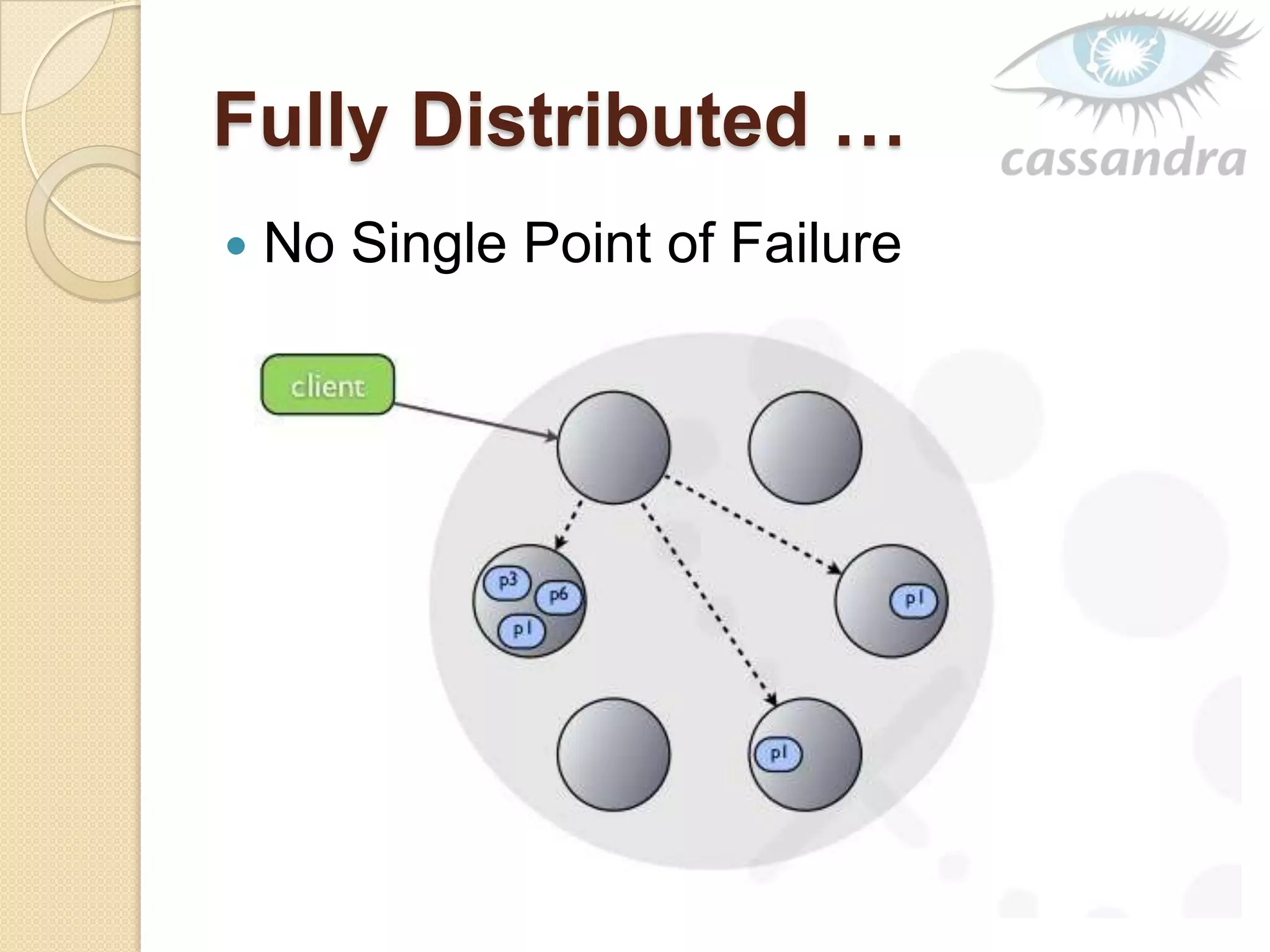
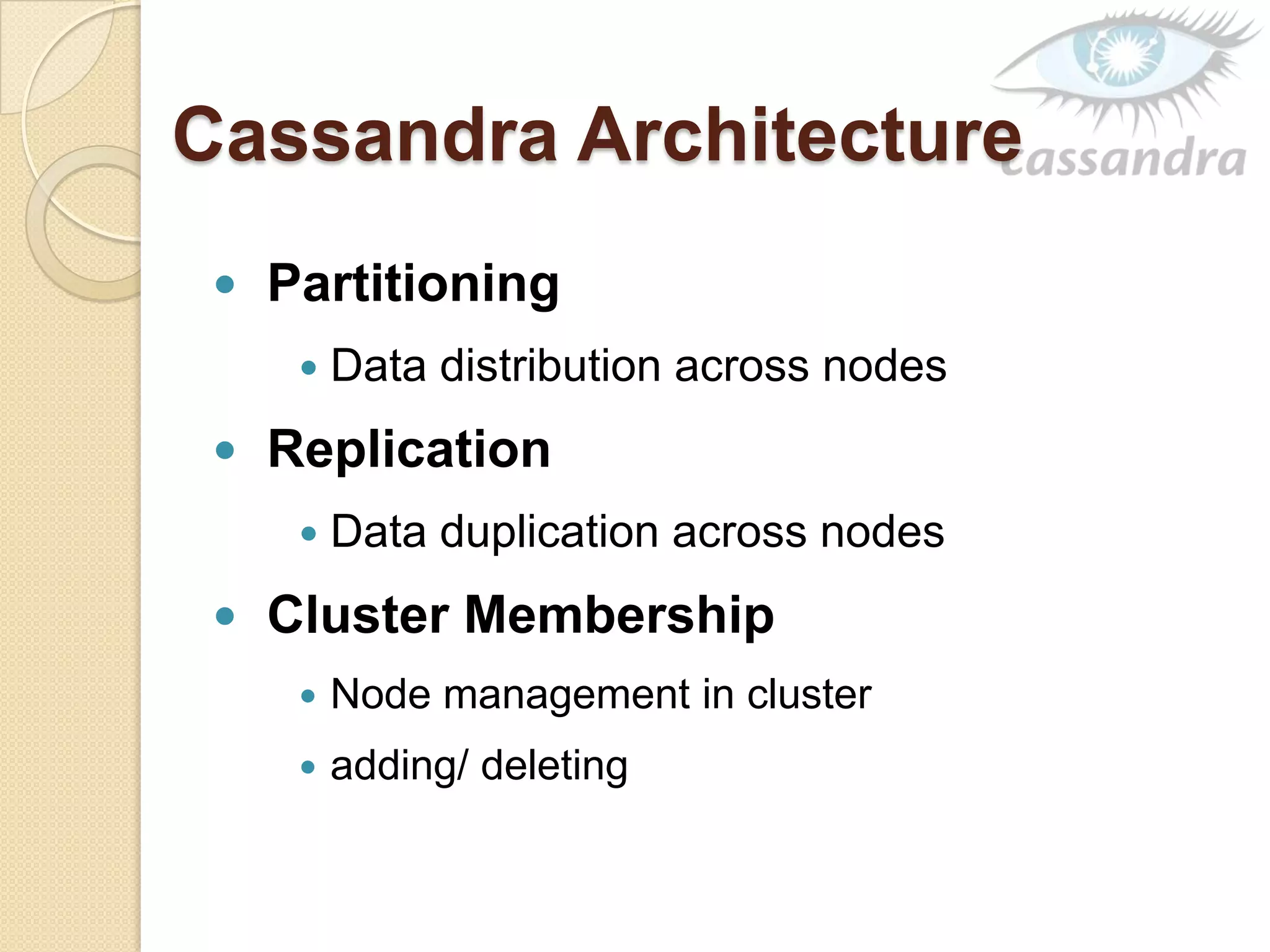
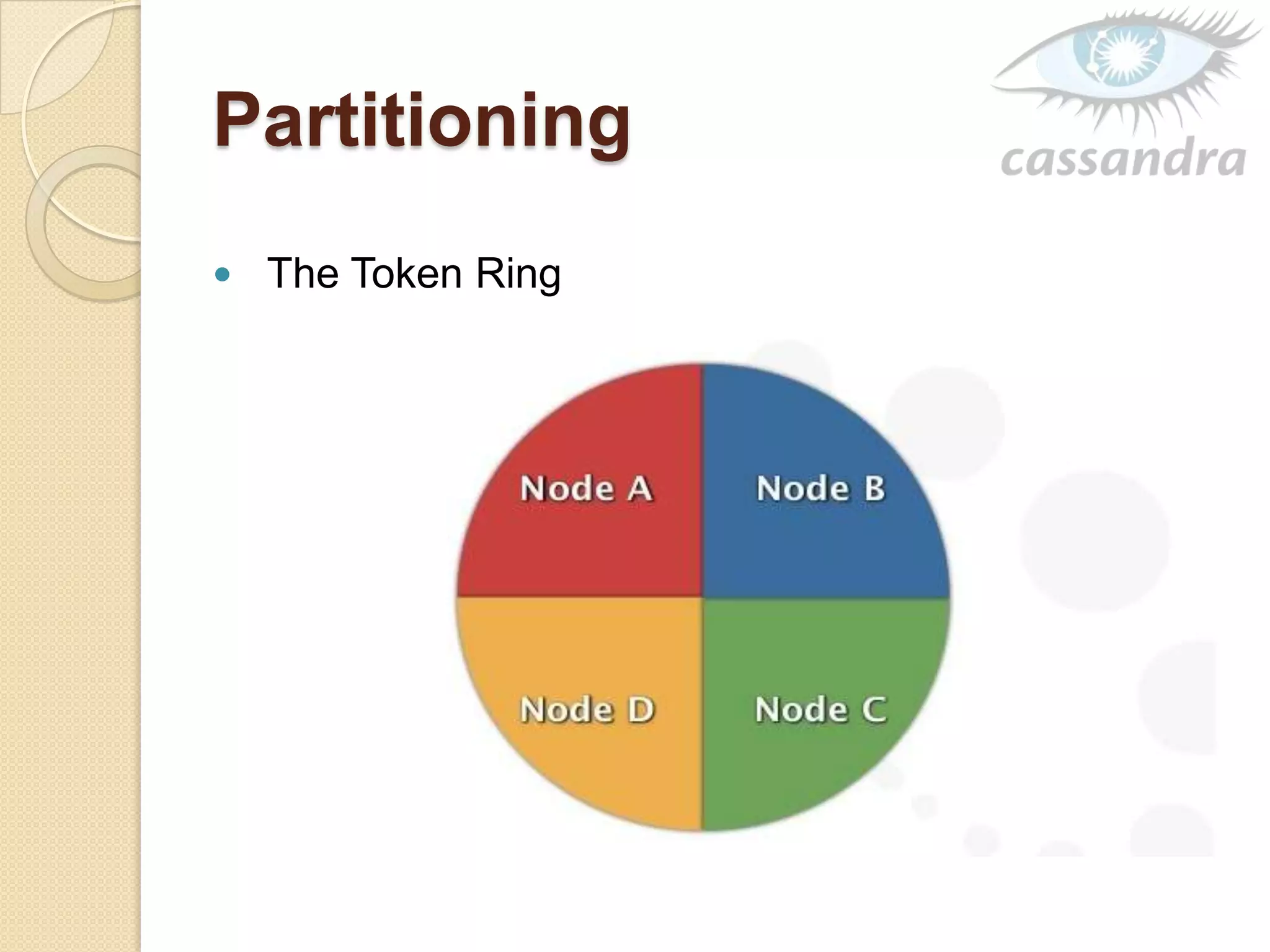
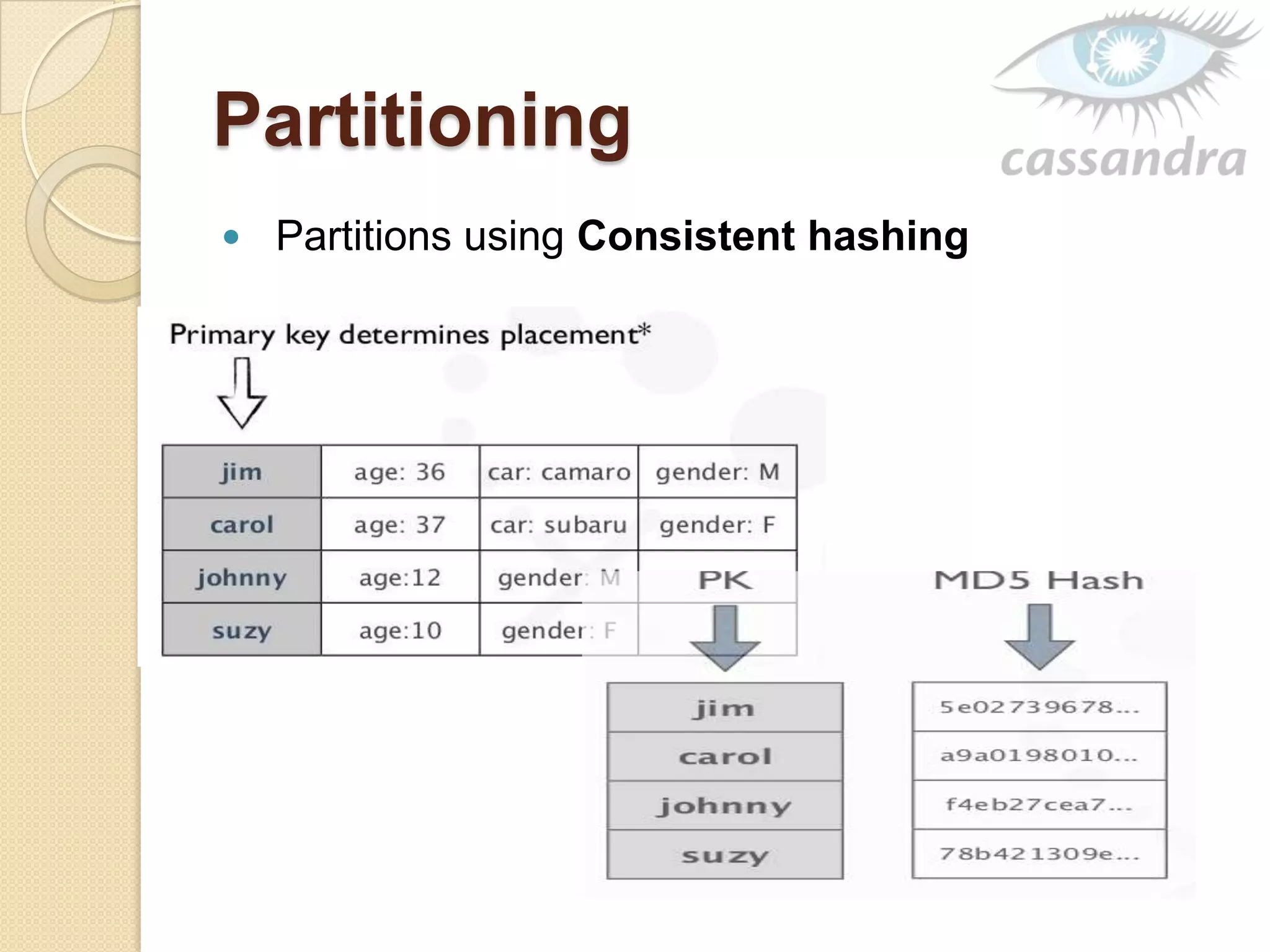
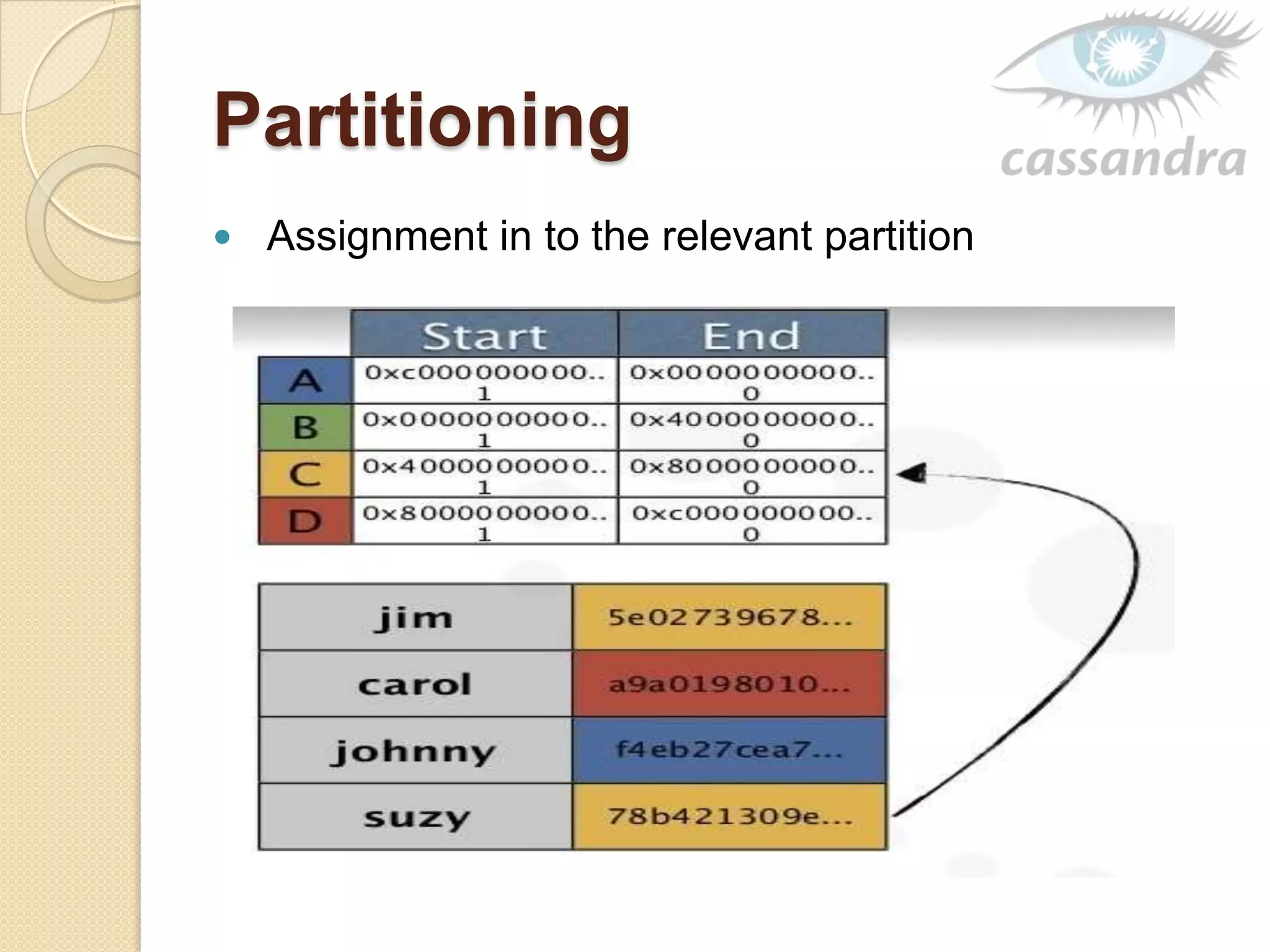
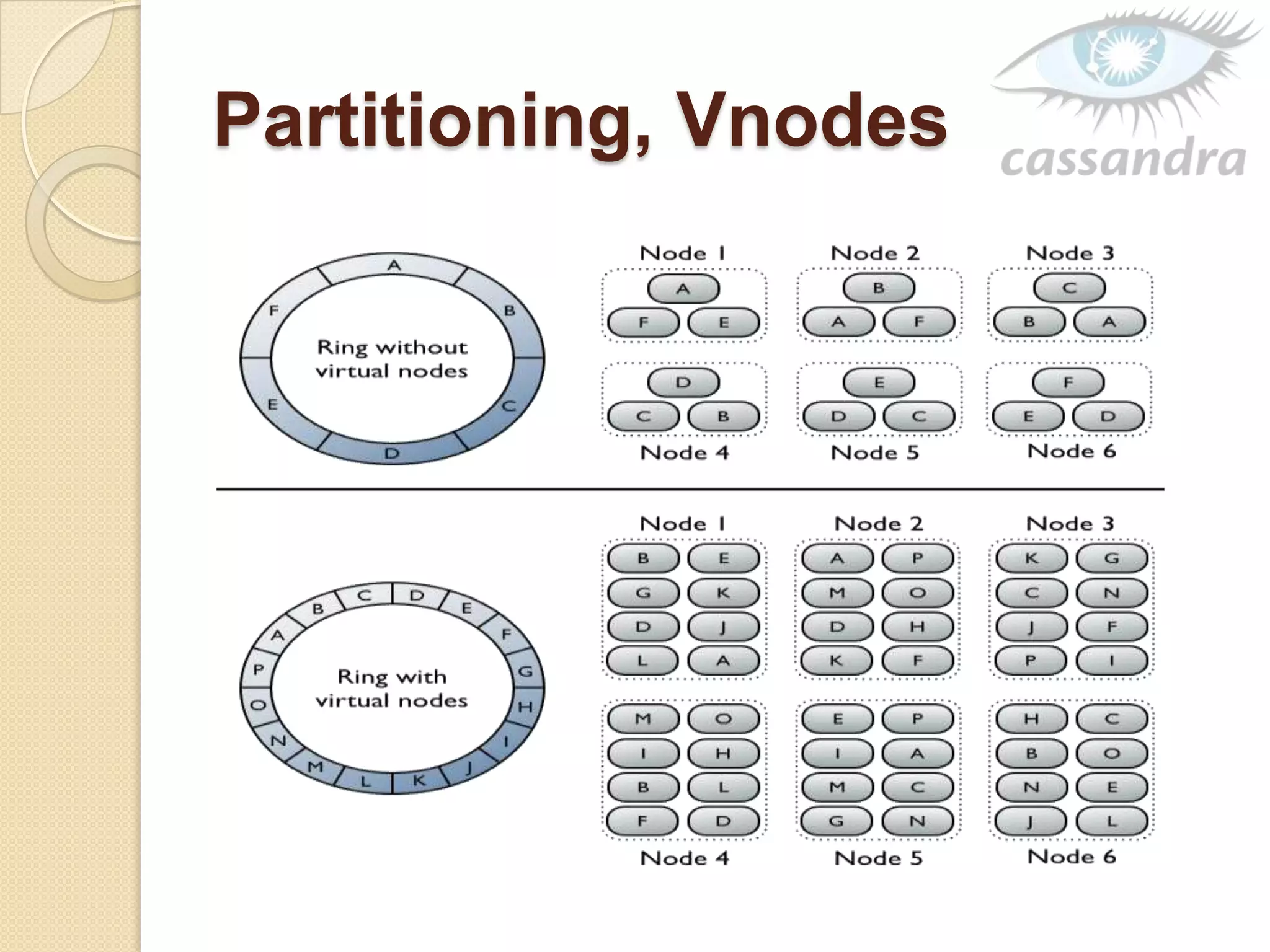
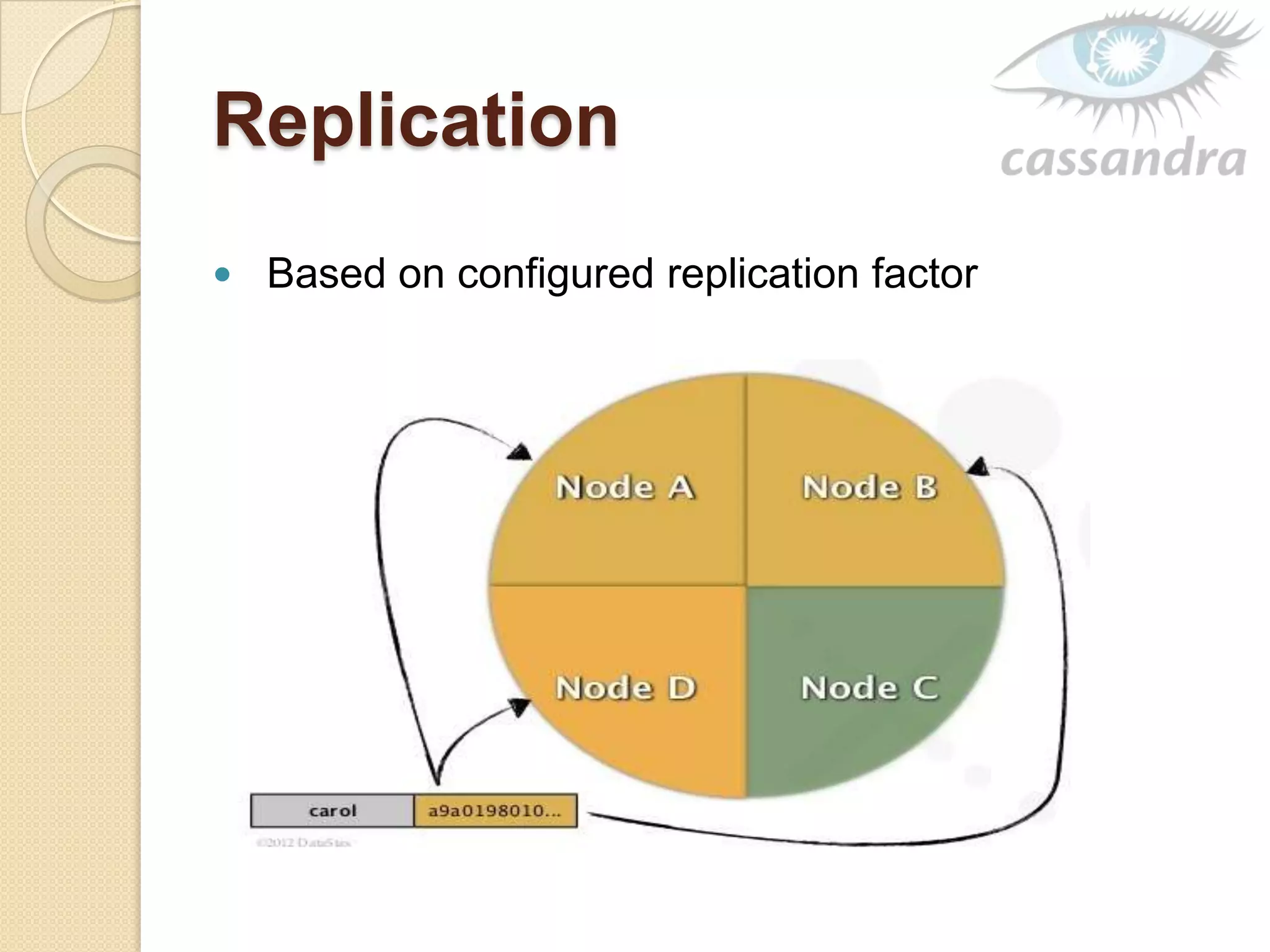
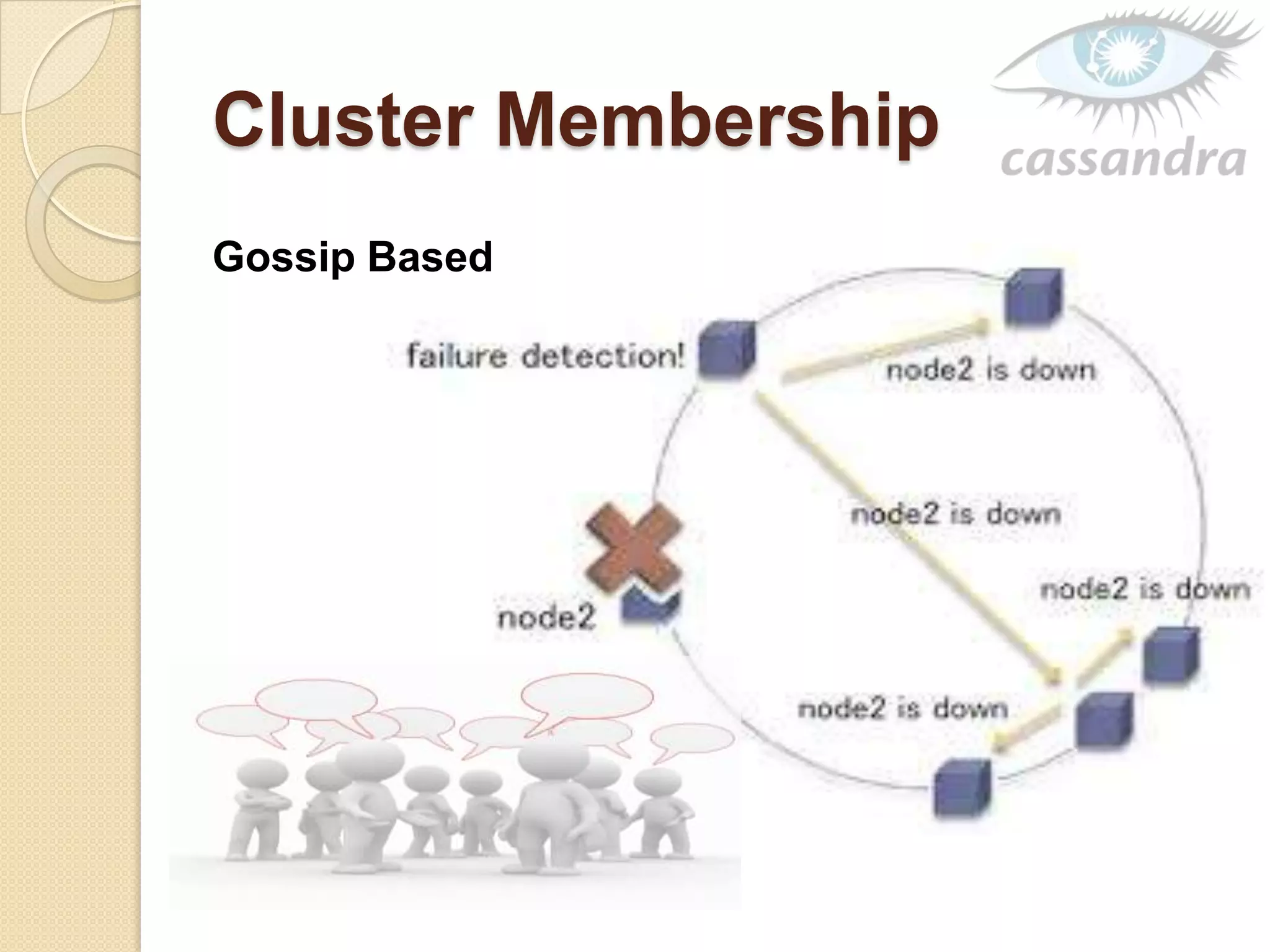
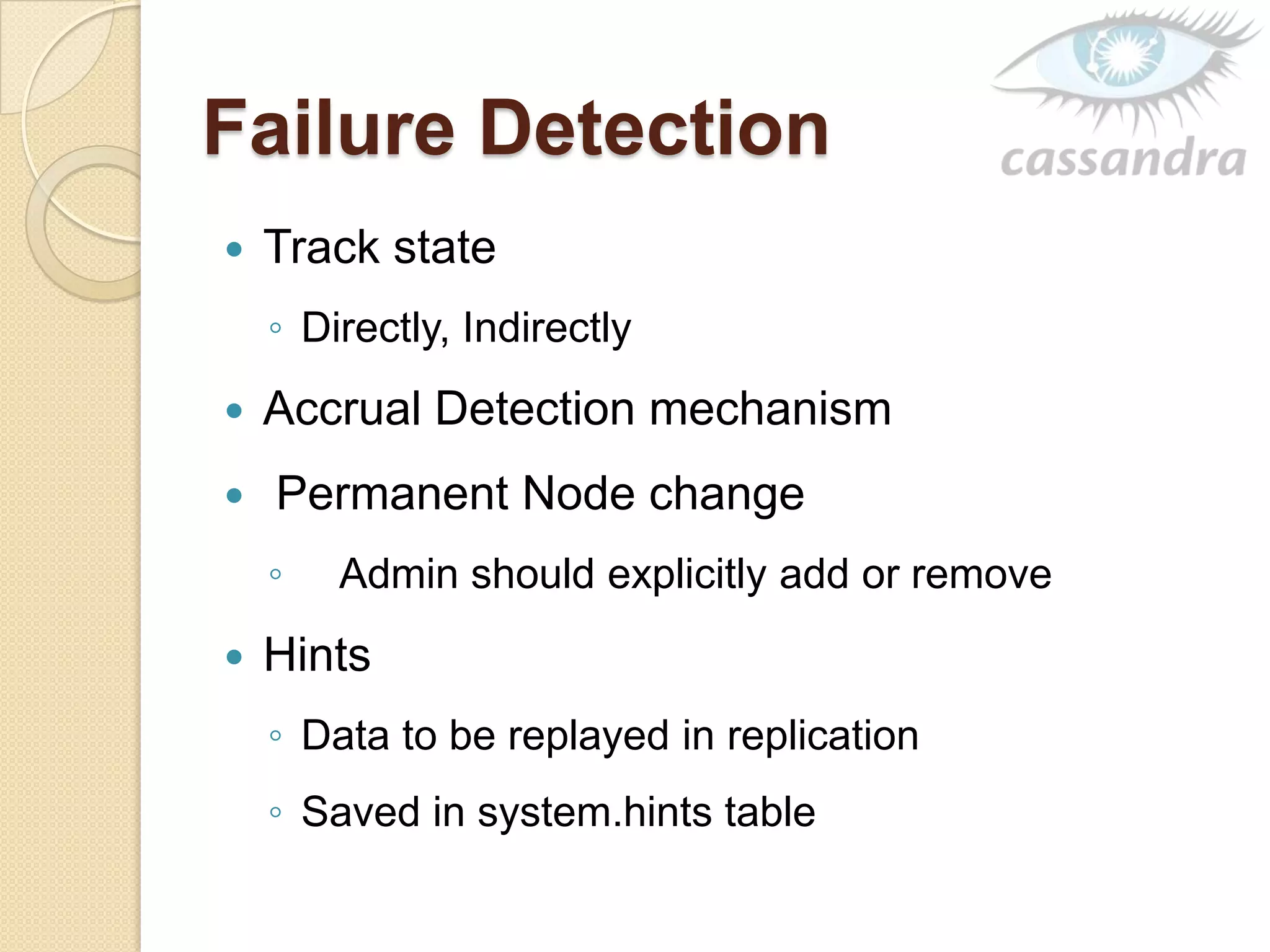
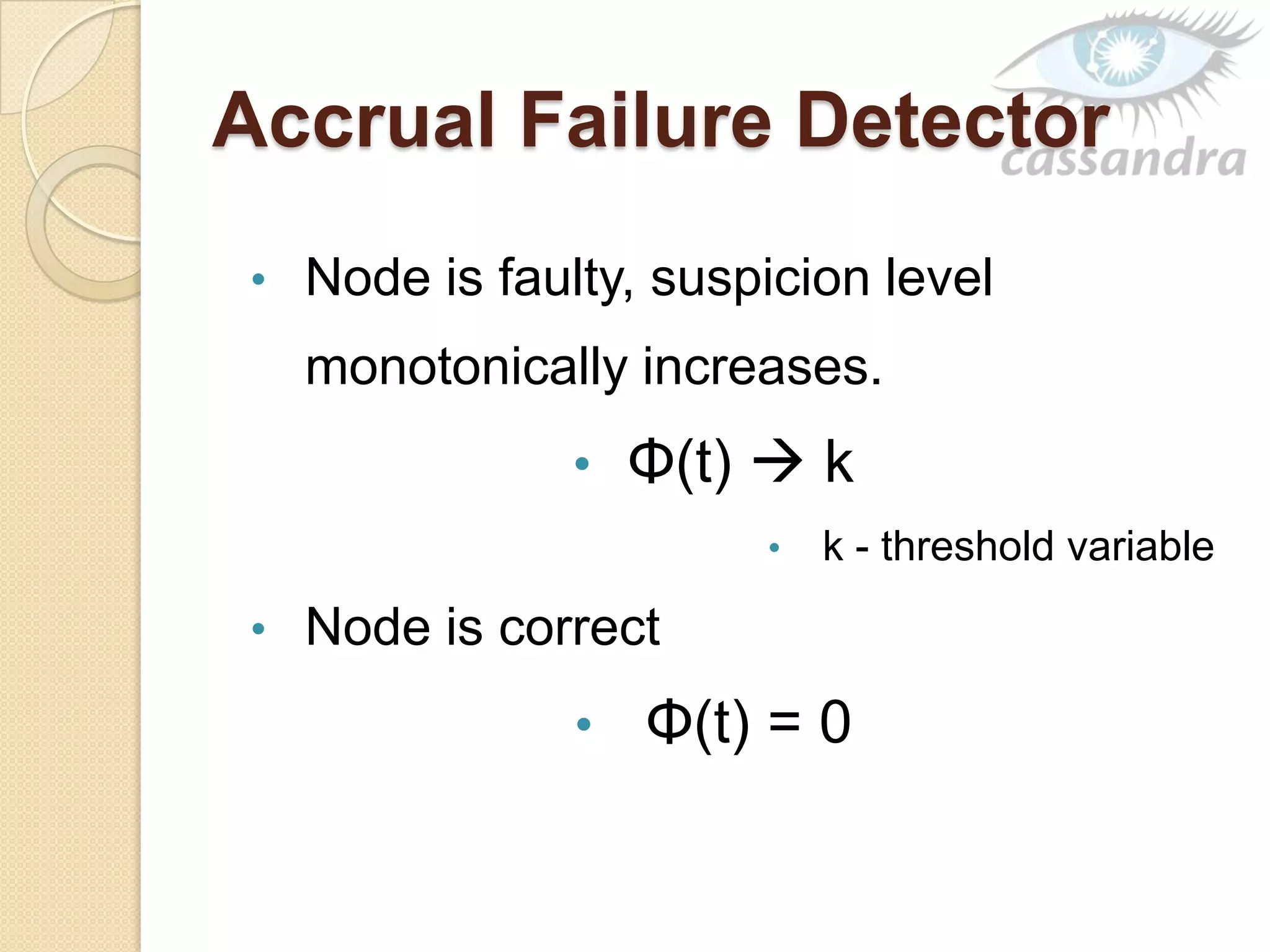
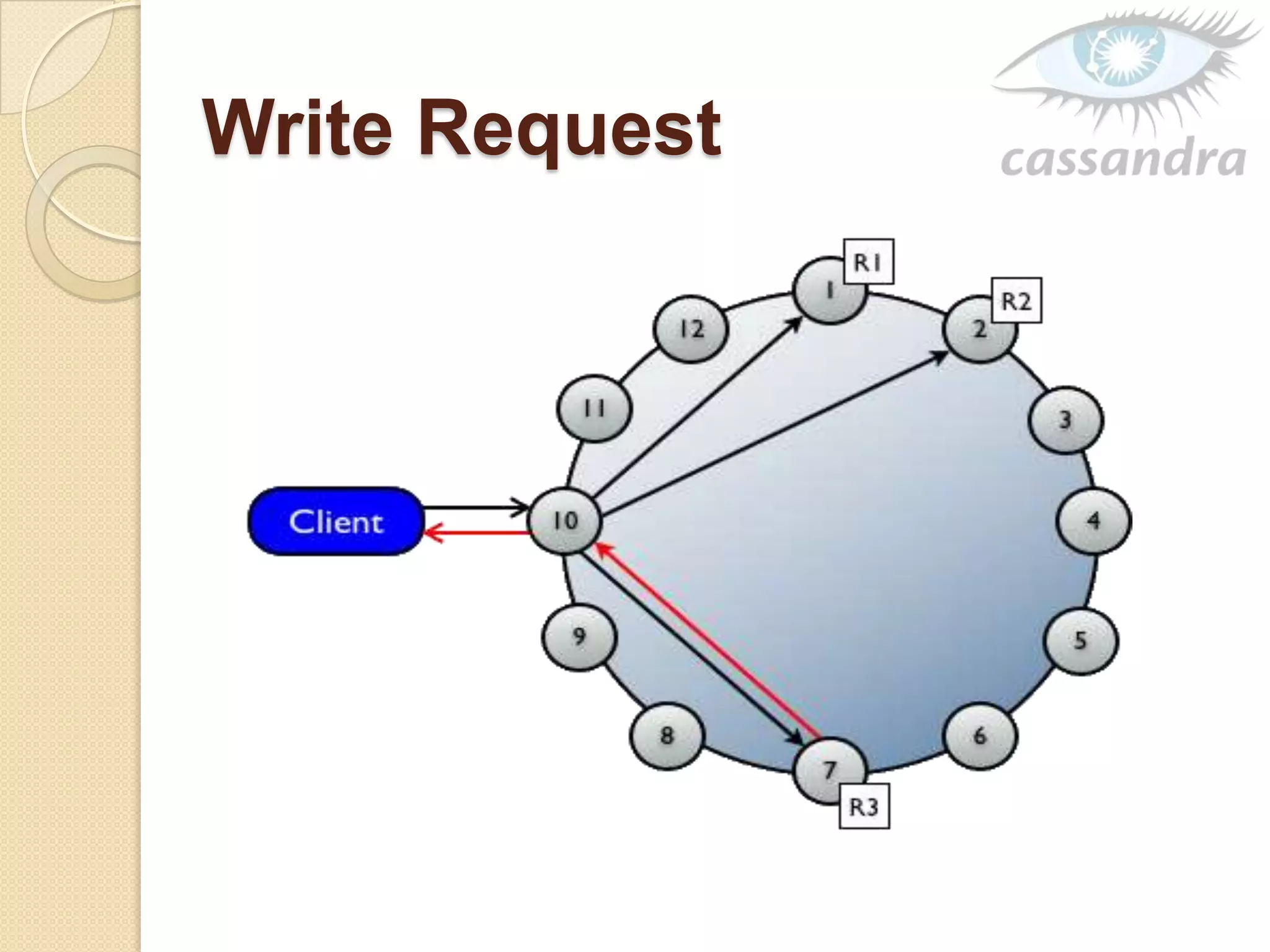
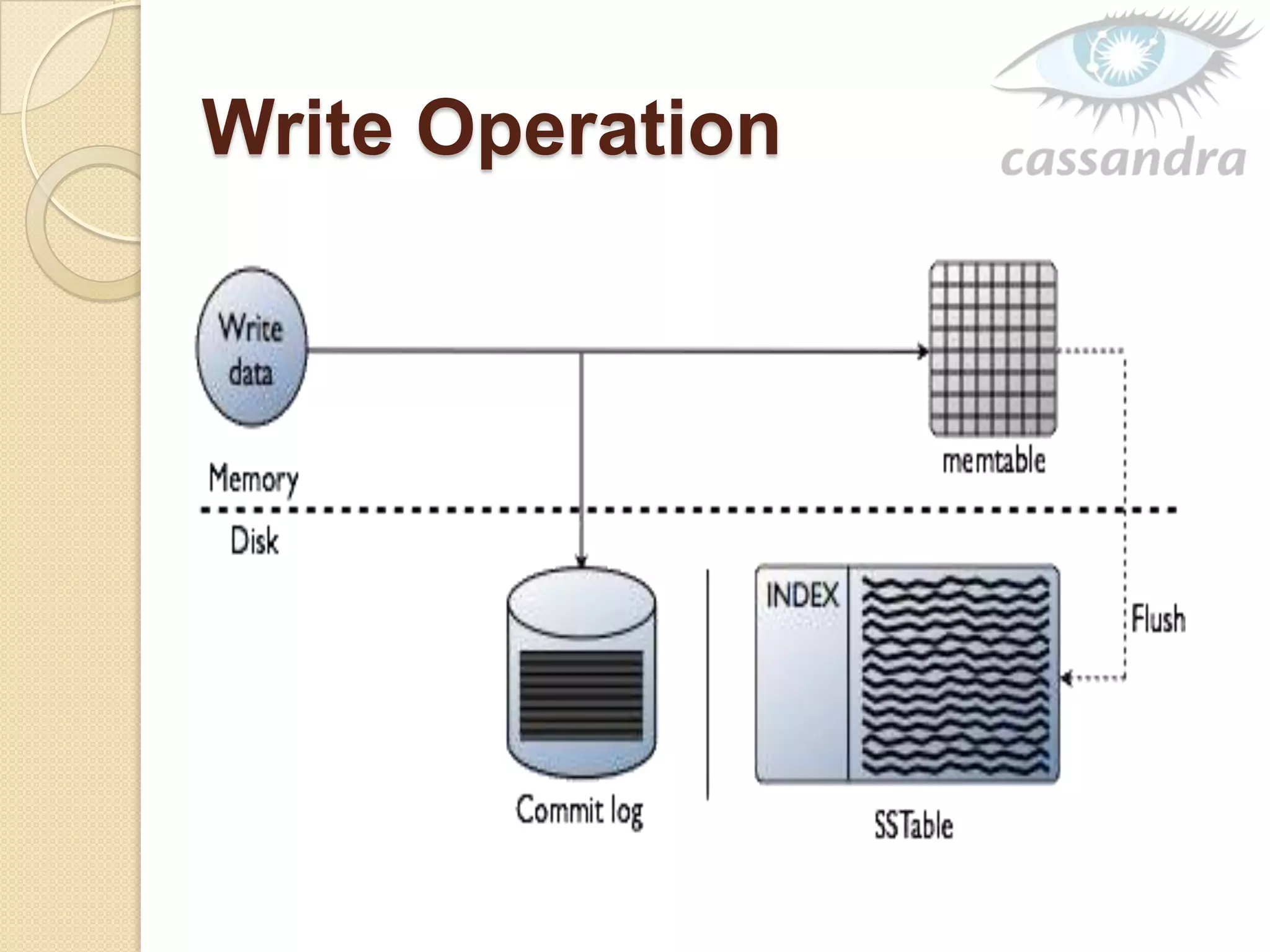
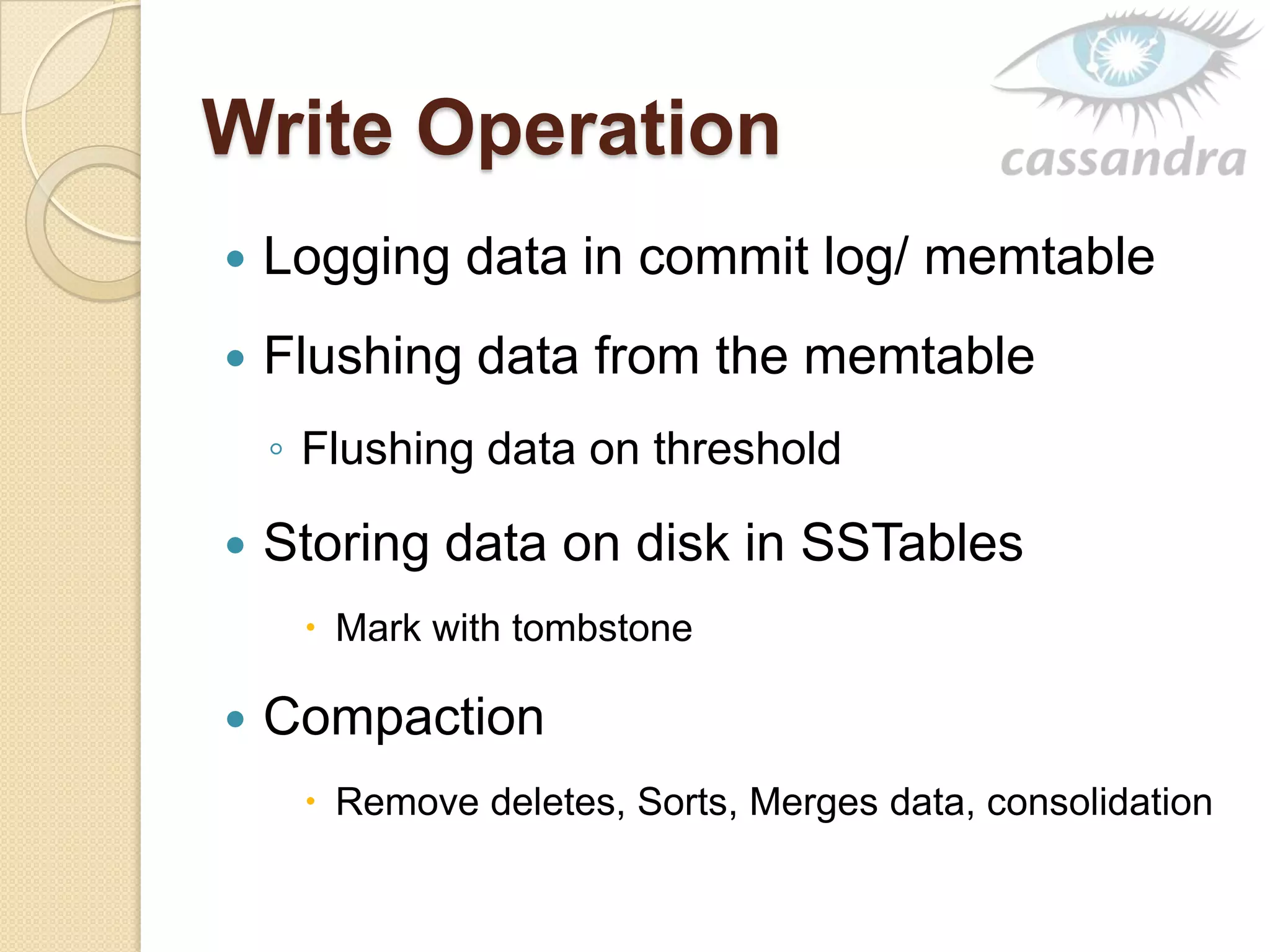
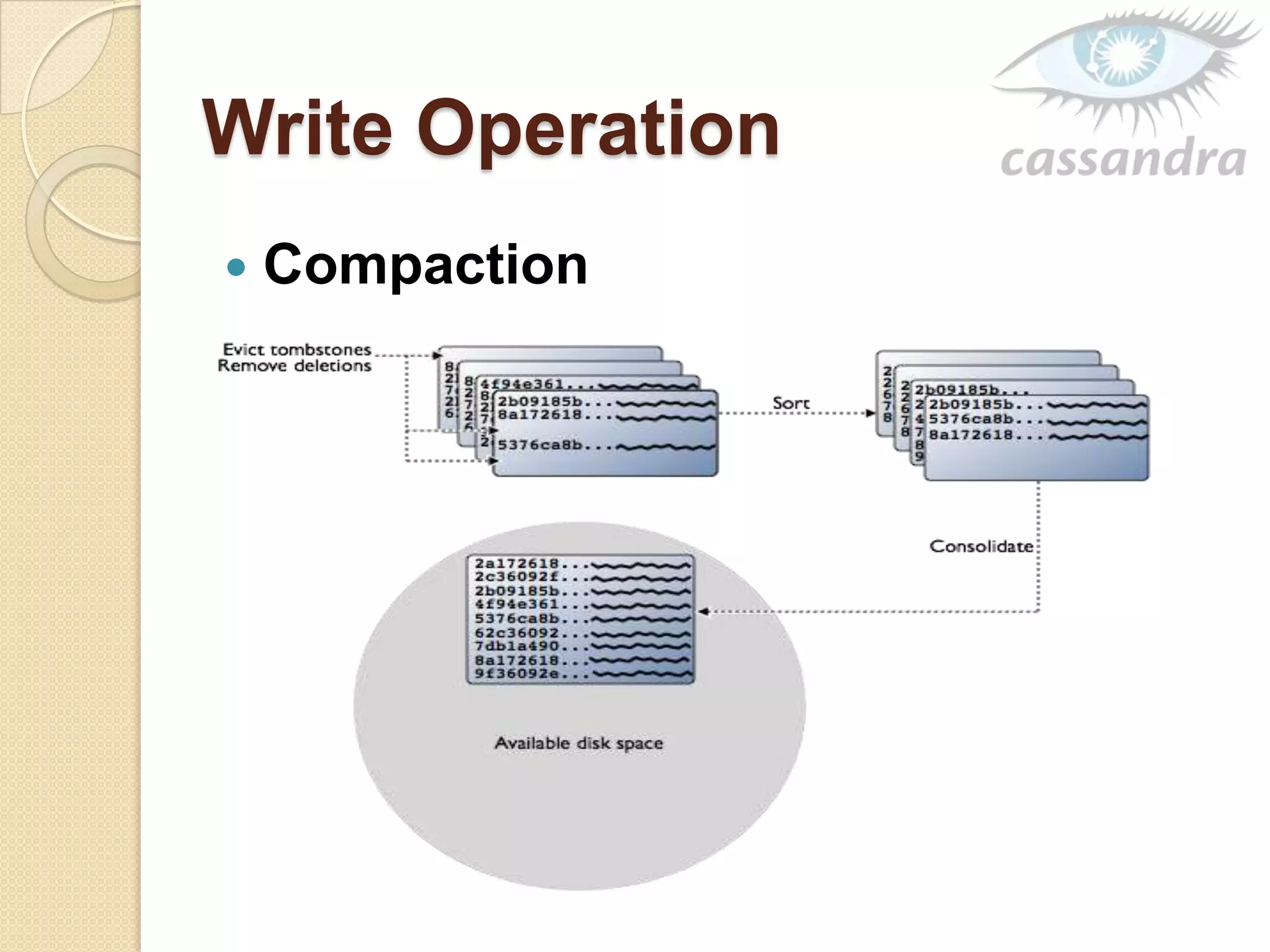
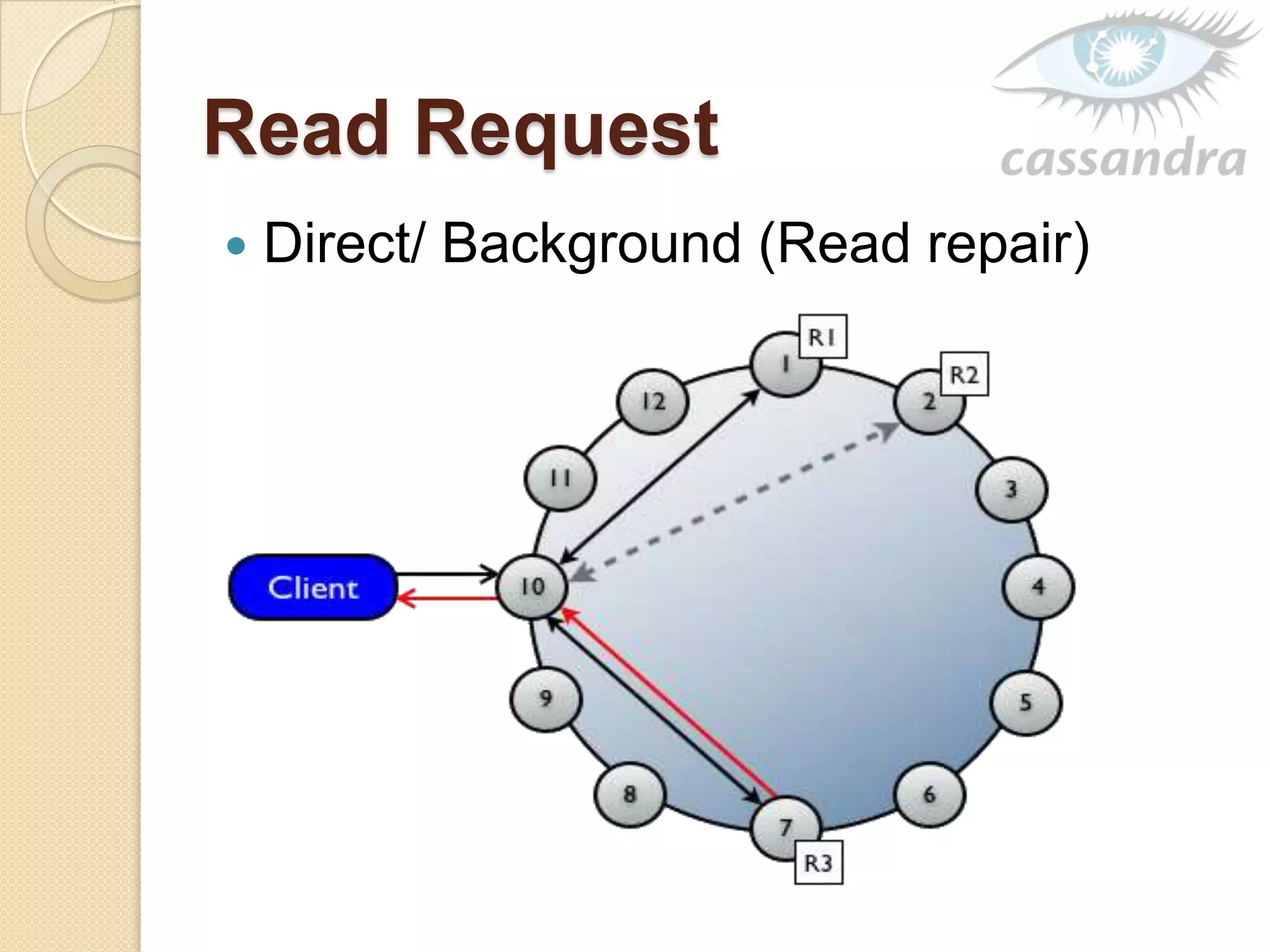
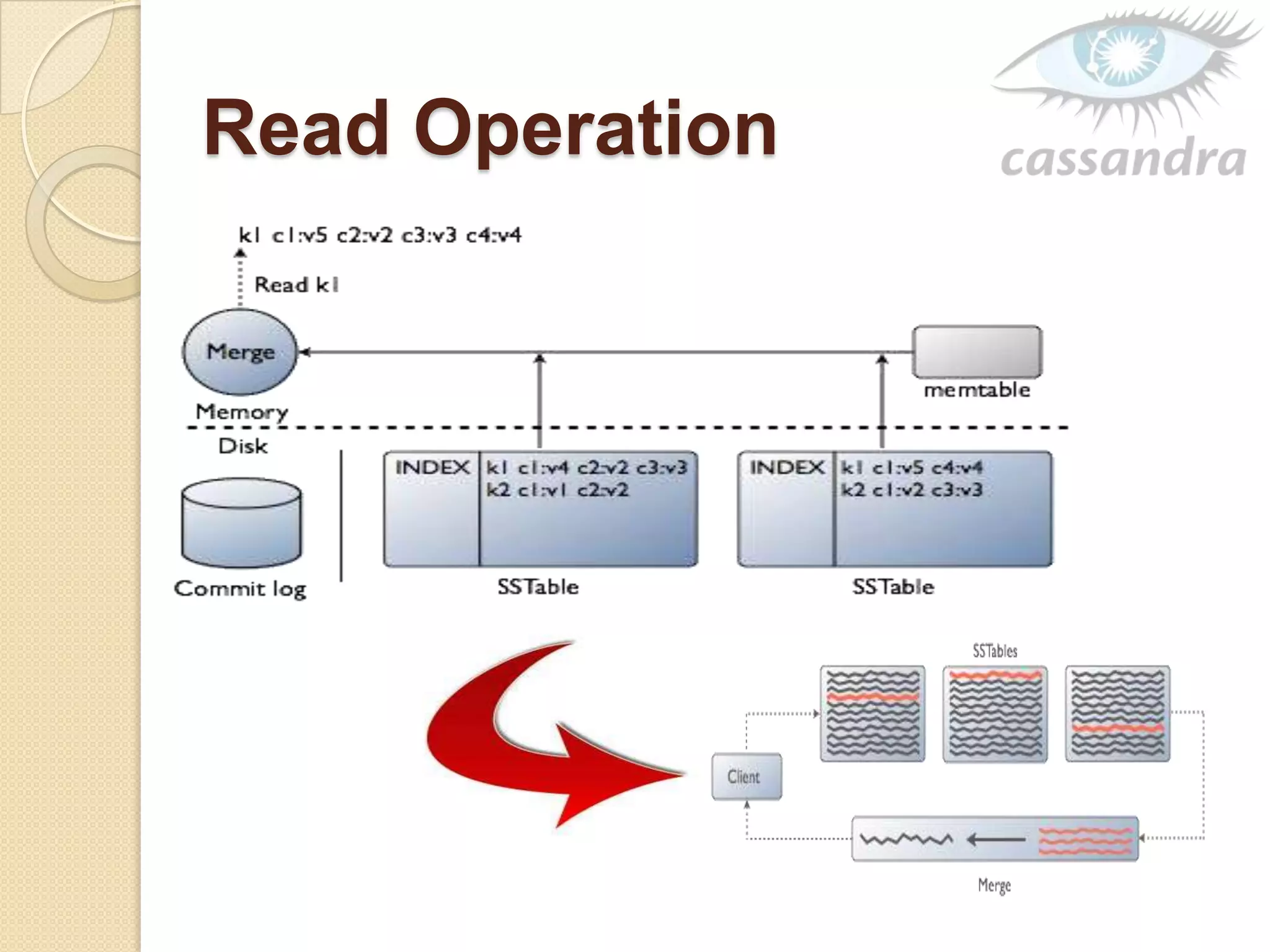
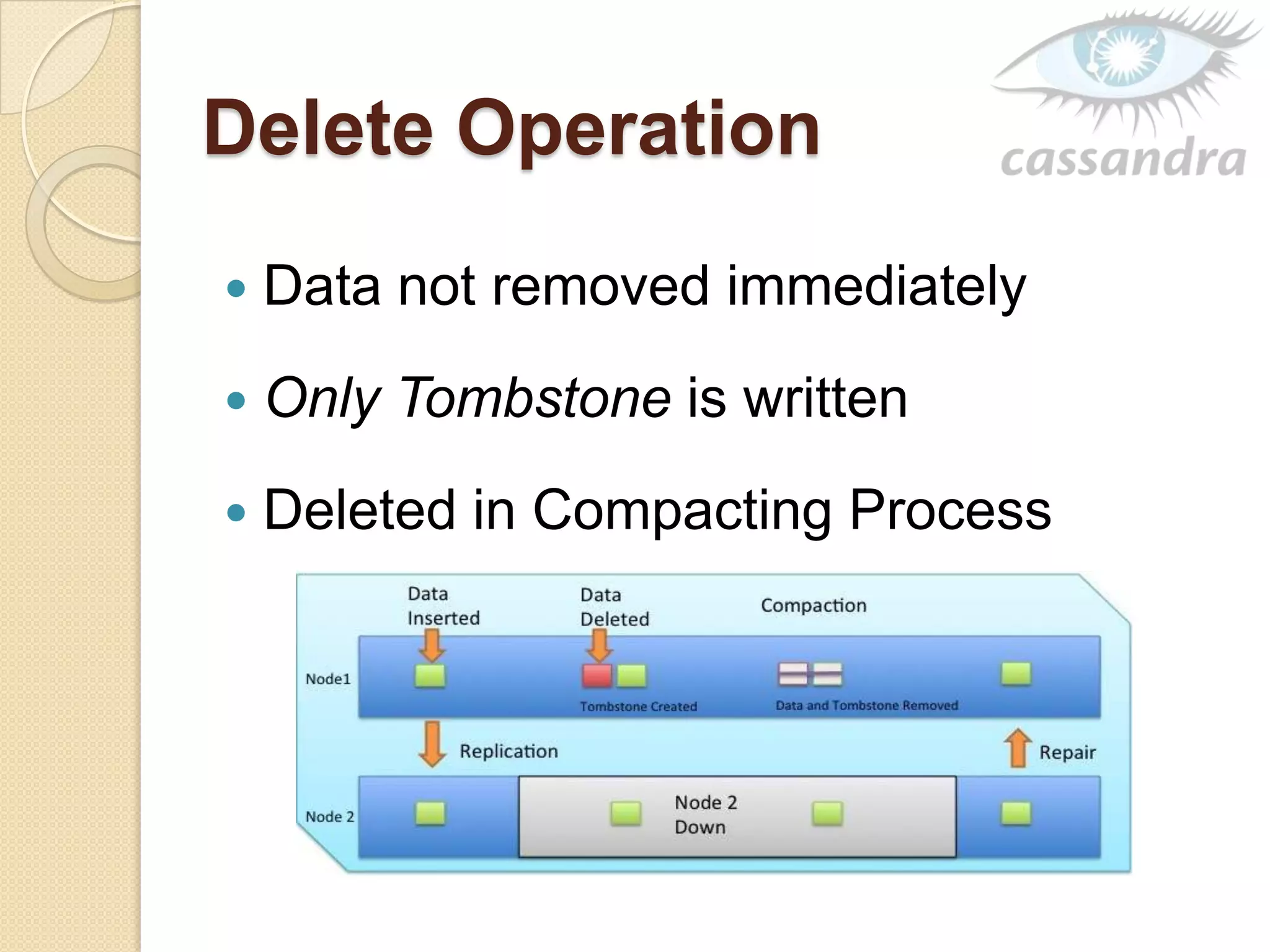
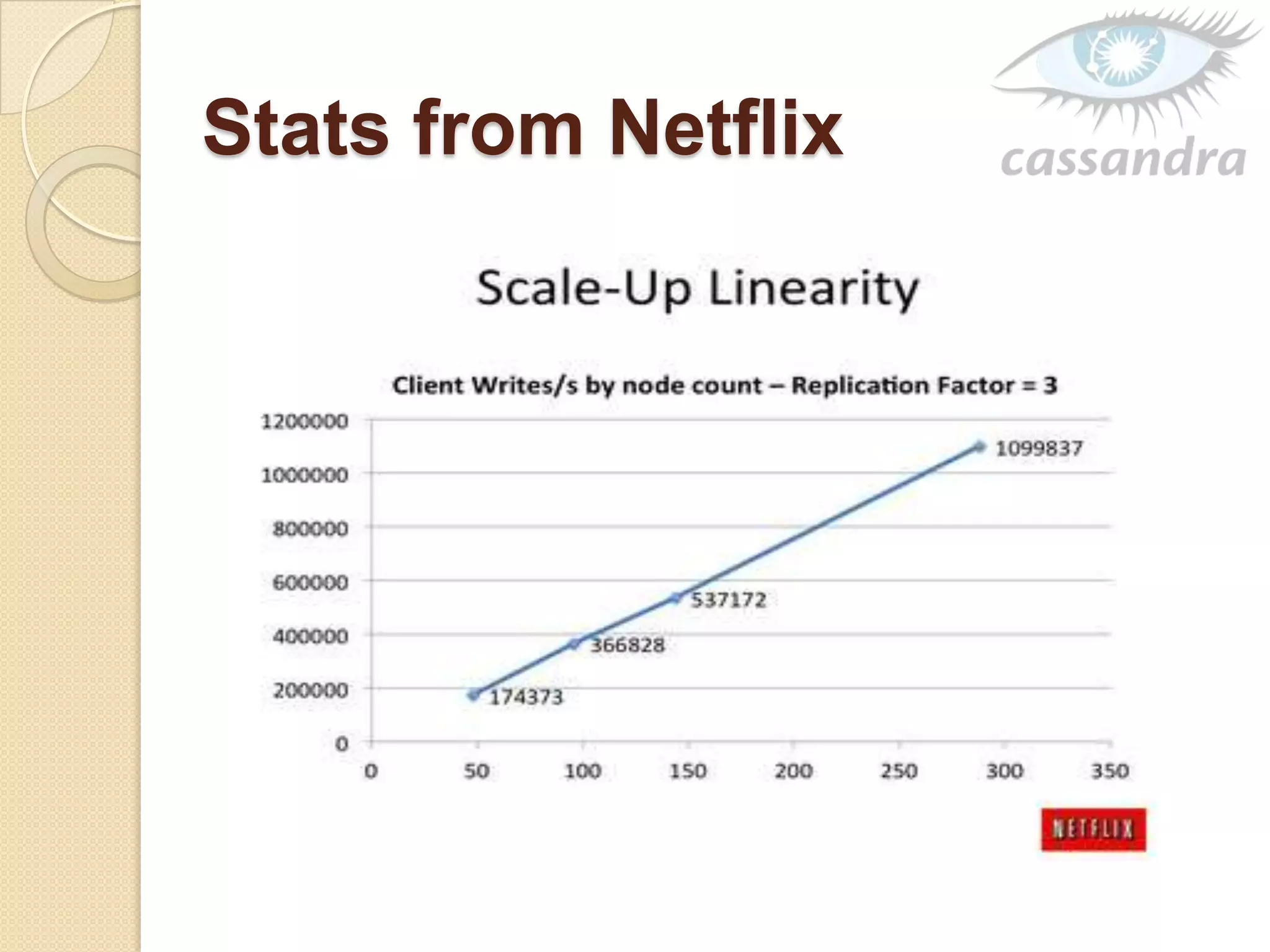
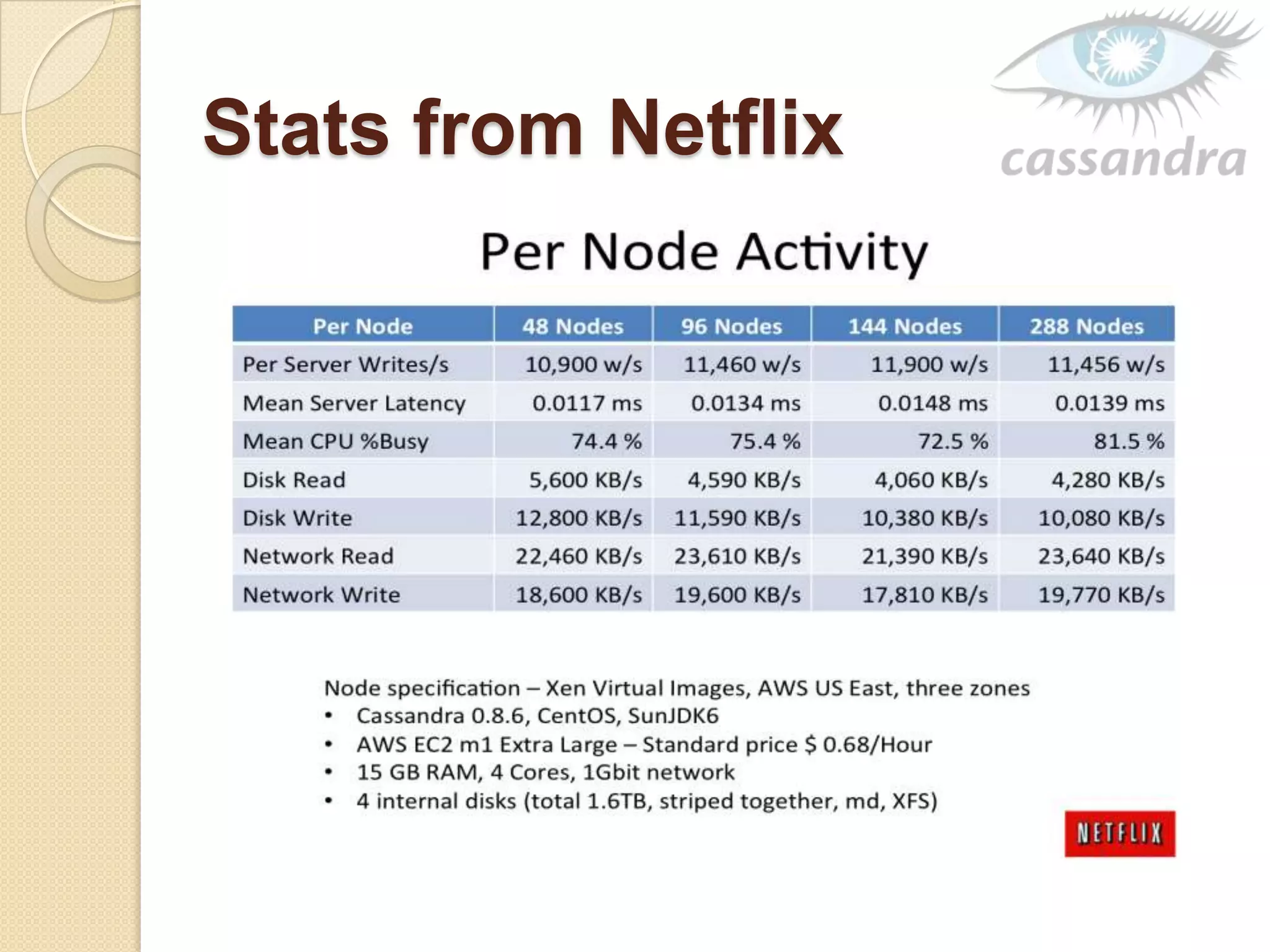
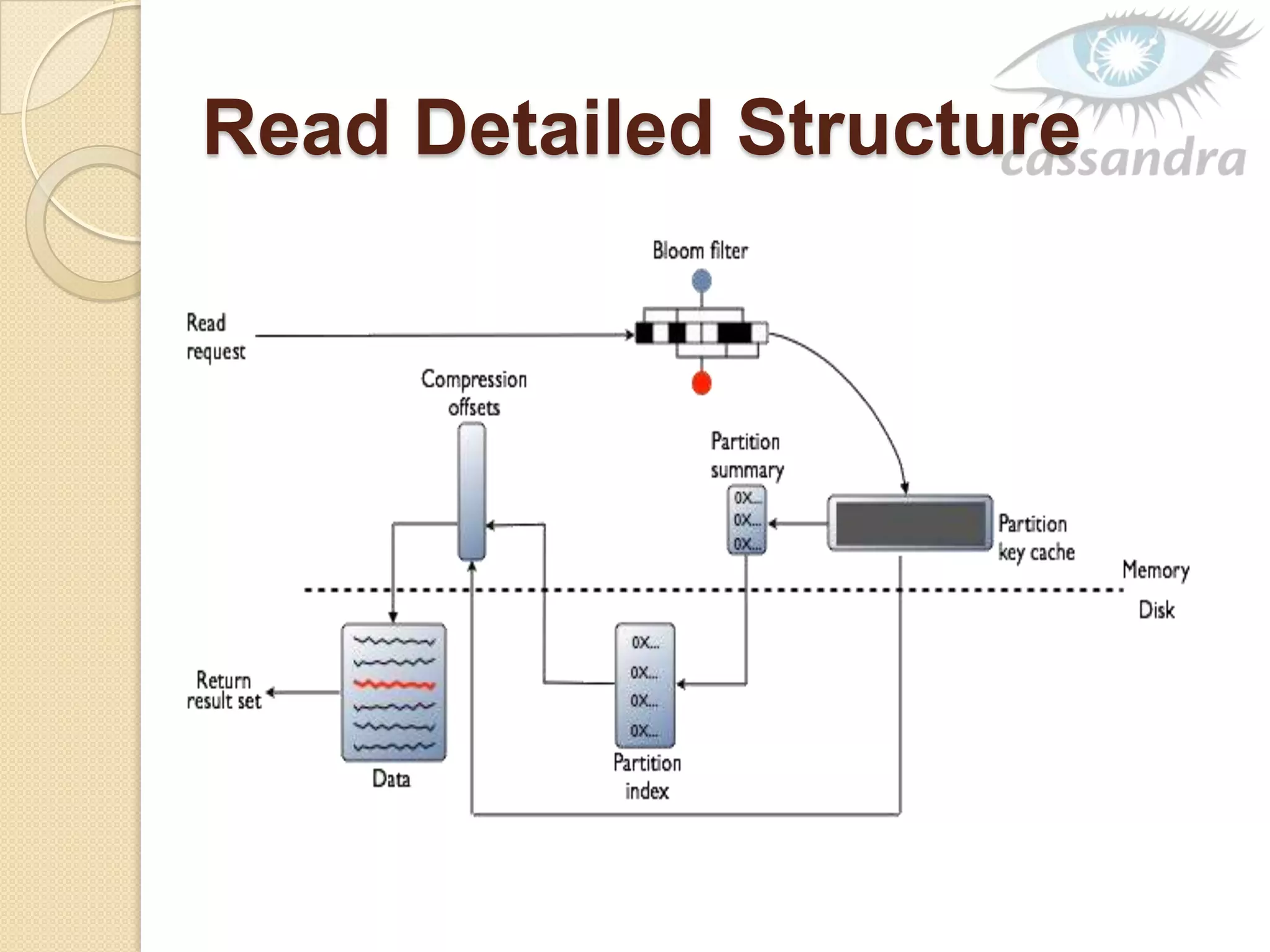
This document provides an overview of Cassandra, a decentralized structured storage system. It describes Cassandra as a distributed system that manages structured data with high availability and no single point of failure. The document outlines Cassandra's data model, system architecture including partitioning, replication and failure detection, local data persistence, and performance characteristics. It also provides examples of companies using Cassandra at scale.