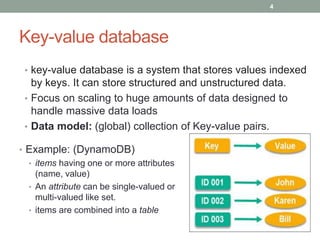
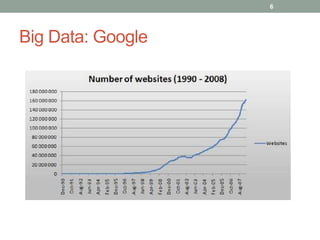
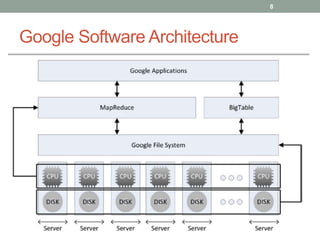
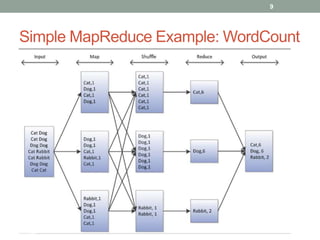
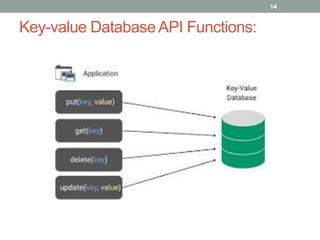
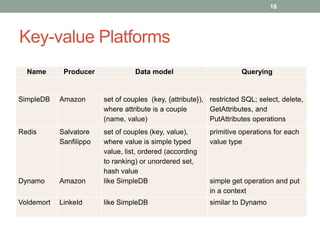
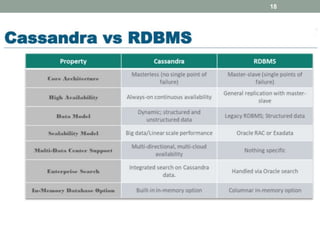
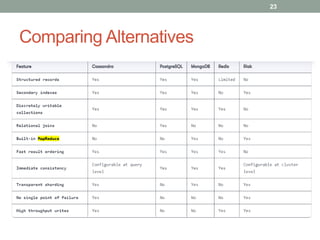
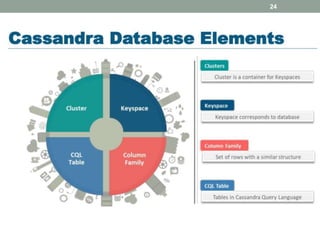
1. The document discusses key-value databases and provides an overview of Apache Cassandra. It describes Cassandra's data model, advantages like scalability and fault tolerance, and disadvantages like lack of aggregations.
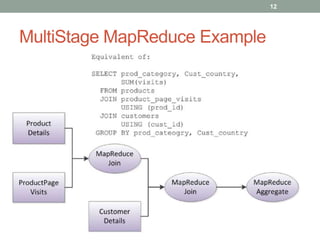
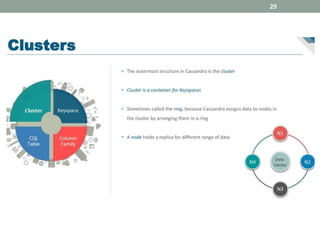
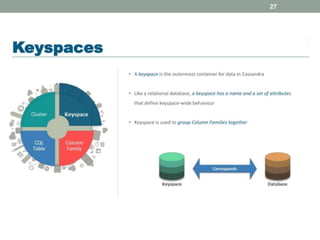
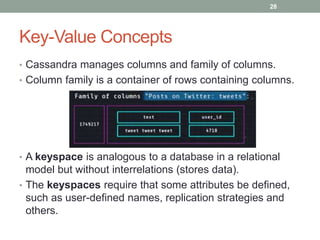
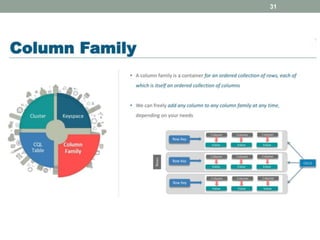
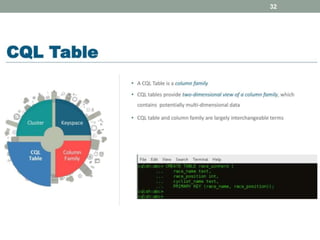
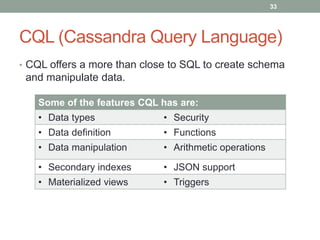
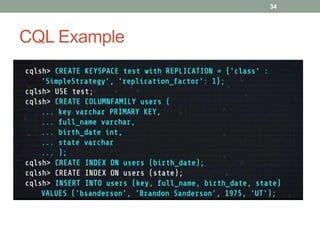
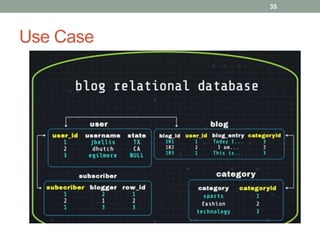
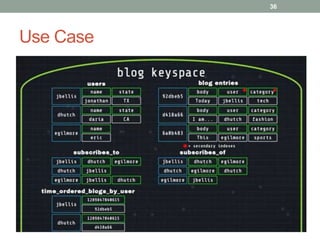
2. It also covers Cassandra's gossip protocol for consistency, use of column families and keyspaces, and CQL for querying. An example use case presented is for user profile data in a social network.
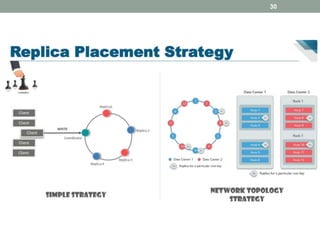
3. Key concepts discussed include Cassandra's distributed architecture, replication factor, data distribution strategies, and CQL features for schema definition and data manipulation.