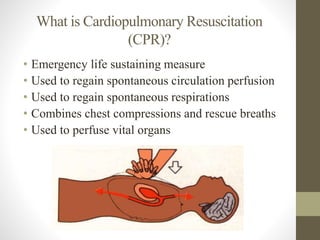
CPR is an emergency procedure that combines chest compressions and rescue breaths to manually circulate blood and provide oxygen to vital organs until emergency medical personnel arrive. It should be performed on an unconscious adult victim by first calling for help, then kneeling beside the victim and placing your hands on their chest to push down firmly and quickly at a rate of 100 times per minute until help arrives. While trained personnel should perform full CPR including rescue breaths, untrained individuals should focus only on chest compressions as this can still significantly increase the victim's chances of survival.