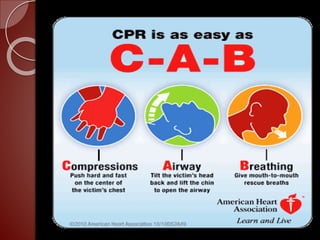
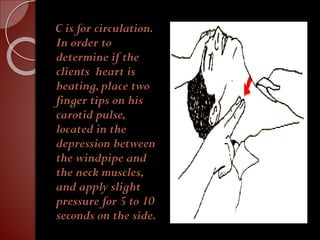
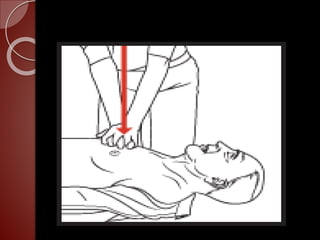
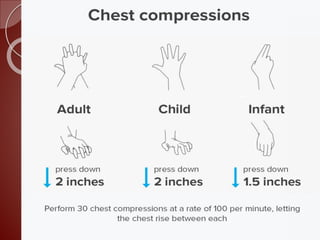
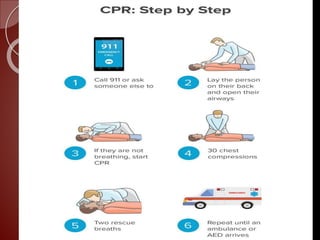
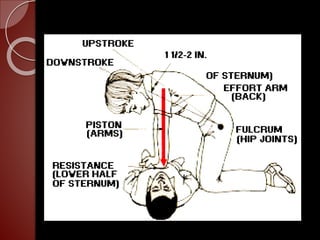
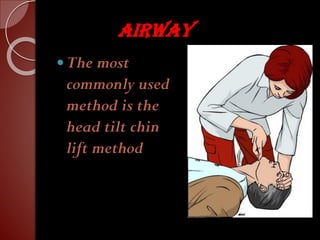
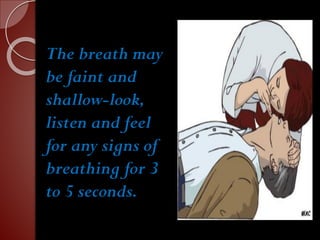
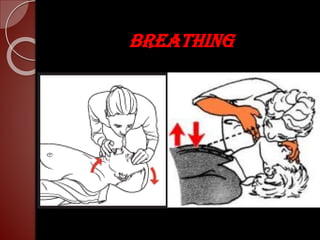
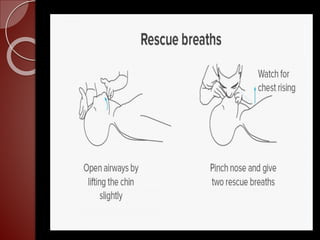
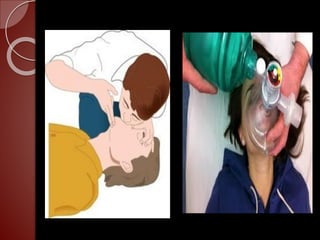
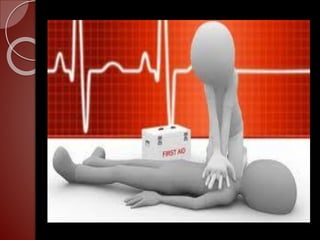
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a technique used to artificially maintain circulation and ventilation when the heart and lungs stop functioning normally. CPR involves performing chest compressions to pump the heart and rescue breaths to oxygenate the lungs until emergency medical services can restore normal heart function. The basic steps of CPR include checking for responsiveness, calling for help, opening the airway, administering 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths, and repeating until help arrives or signs of life return. CPR is used to keep oxygenated blood flowing to the brain and other vital organs when someone is unresponsive and not breathing or breathing abnormally.