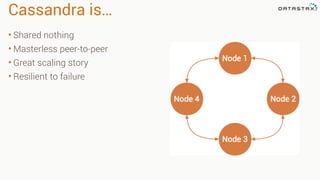
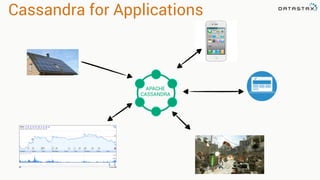
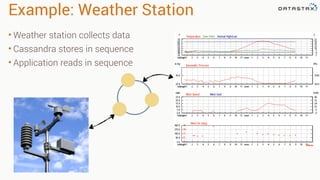
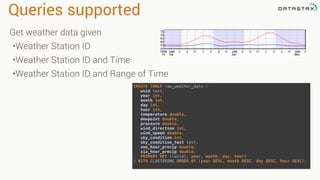
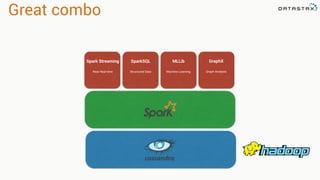
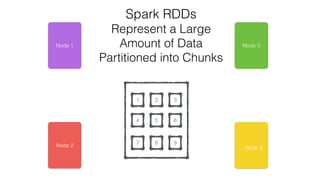
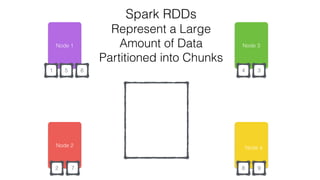
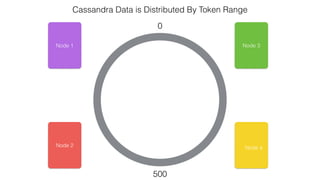
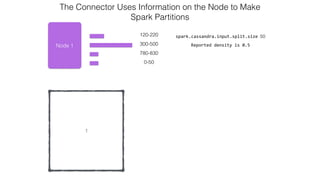
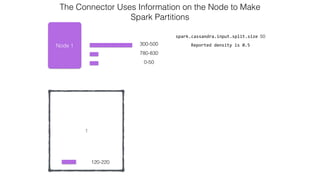
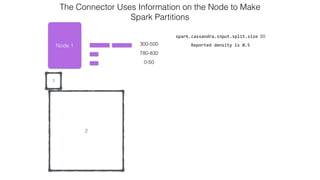
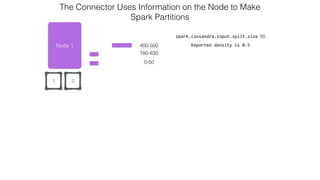
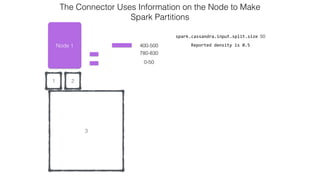
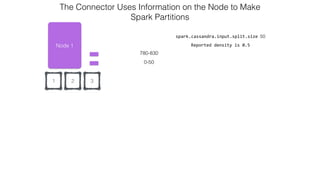
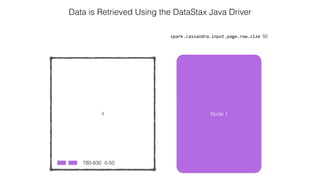
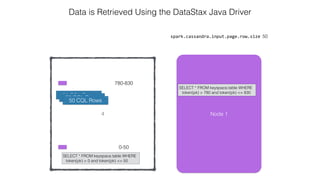
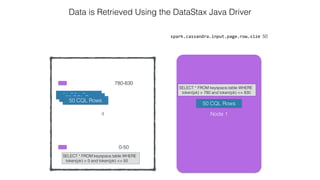
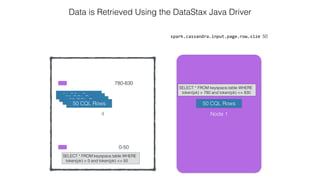
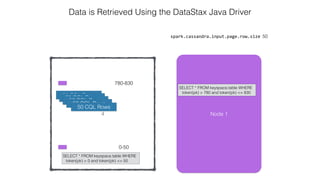
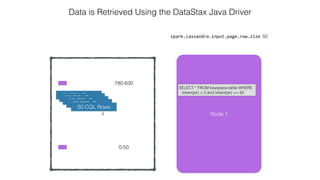
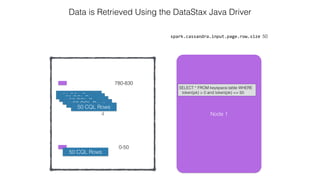
This document discusses Apache Spark and Cassandra. It provides an overview of Cassandra as a shared-nothing, masterless, peer-to-peer database with great scaling. It then discusses how Spark can be used to analyze large amounts of data stored in Cassandra in parallel across a cluster. The Spark Cassandra connector allows Spark to create partitions that align with the token ranges in Cassandra, enabling efficient distributed queries across the cluster.











![RDD
Tranformations
•Produces new RDD
•Calls: filter, flatmap, map,
distinct, groupBy, union, zip,
reduceByKey, subtract
Are
•Immutable
•Partitioned
•Reusable
Actions
•Start cluster computing operations
•Calls: collect: Array[T], count,
fold, reduce..
and Have](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyzingtimeseriesdatawithapachesparkandcassandra-yahoojapan-150908111200-lva1-app6892/85/Cassandra-and-Spark-16-320.jpg)


































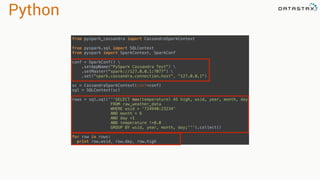
![Attaching to Spark and Cassandra
// Import Cassandra-specific functions on SparkContext and RDD objects
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import com.datastax.spark.connector._
/** The setMaster("local") lets us run & test the job right in our IDE */
val conf = new SparkConf(true)
.set("spark.cassandra.connection.host", "127.0.0.1")
.setMaster(“local[*]")
.setAppName(getClass.getName)
// Optionally
.set("cassandra.username", "cassandra")
.set("cassandra.password", “cassandra")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyzingtimeseriesdatawithapachesparkandcassandra-yahoojapan-150908111200-lva1-app6892/85/Cassandra-and-Spark-70-320.jpg)




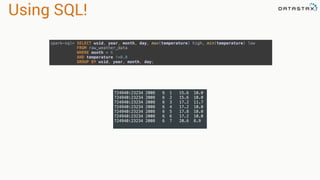
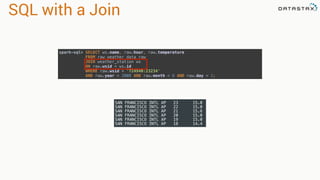

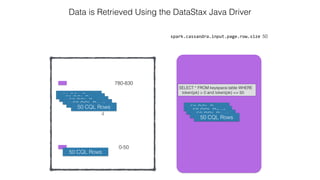
.select("temperature")
.where("wsid = ? AND year = ? AND month = ? AND DAY = ?",
"724940:23234", "2008", "12", "1").spanBy(row => (row.getString("wsid")))
•Specify partition grouping
•Use with large partitions
•Perfect for time series](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyzingtimeseriesdatawithapachesparkandcassandra-yahoojapan-150908111200-lva1-app6892/85/Cassandra-and-Spark-78-320.jpg)