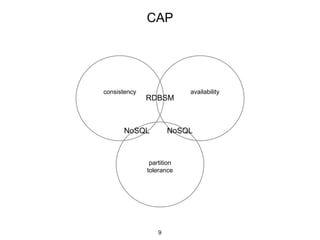
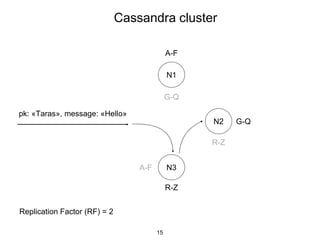
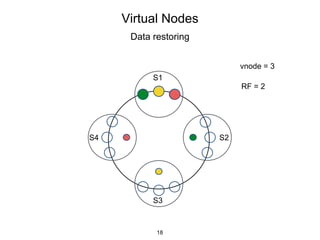
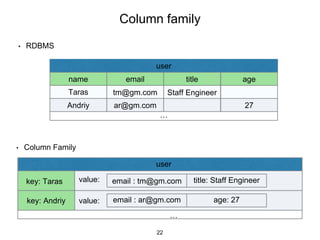
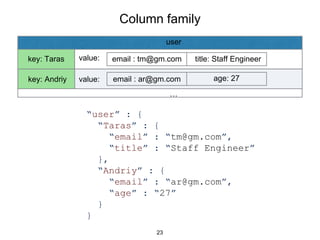
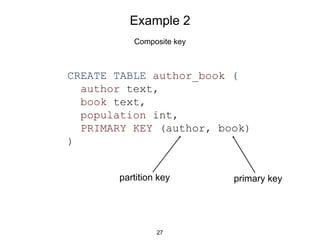
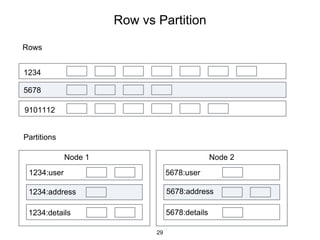
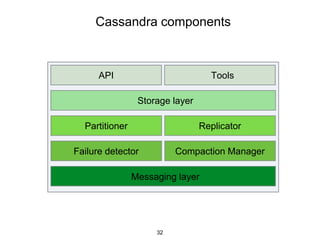
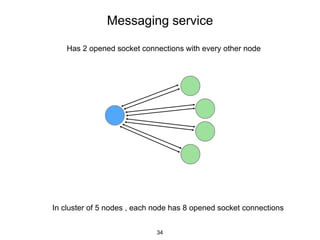
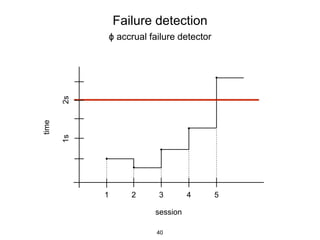
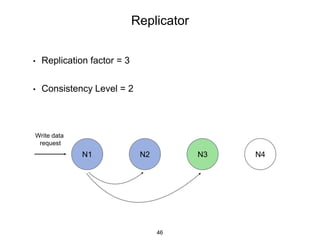
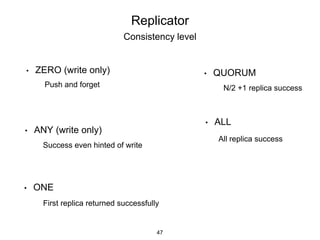
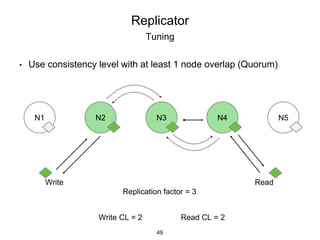
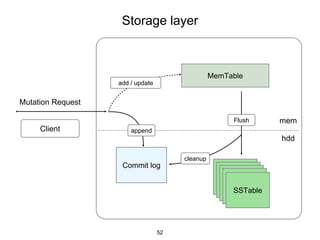
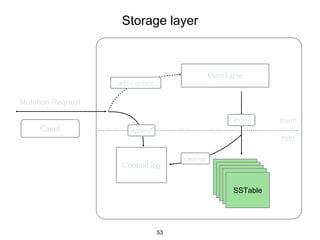
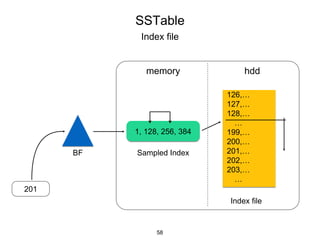
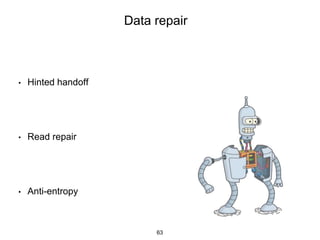
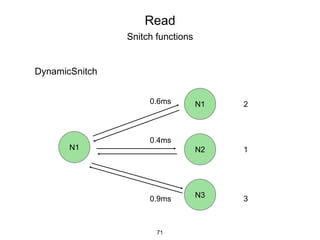
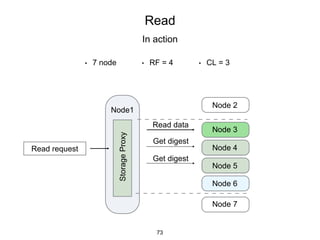
This document provides an in-depth overview of Apache Cassandra, including its architecture, data model, and operations, while contrasting it with traditional RDBMS systems. It covers key concepts such as clusters, tokens, and replication factors, along with detailed explanations of read and write operations, including consistency levels and partitioners. The presentation concludes with references to additional resources for further learning about Cassandra.