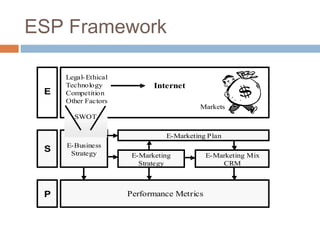
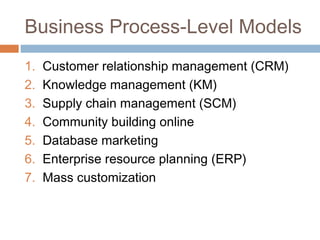
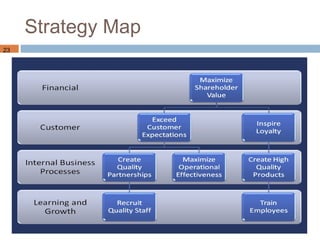
This document discusses Amazon's e-marketing strategy. It summarizes that Amazon was founded in 1995 as an online retailer, leveraged its competencies into different e-business models, and its success is based on broad selection, lower prices, availability, technology, and product information. Amazon's core competencies of selection, prices, availability, and technology will likely drive its future strategy.