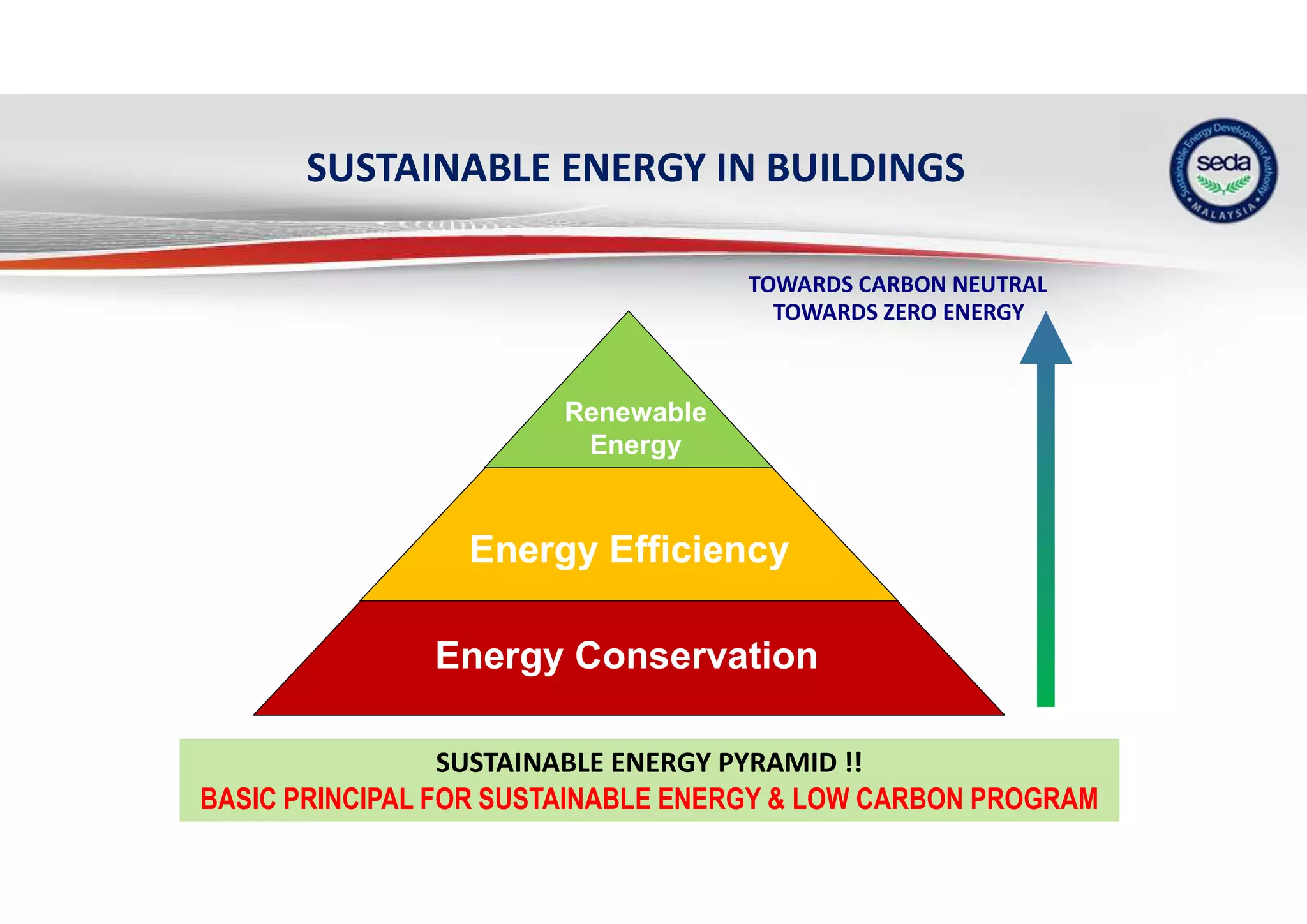
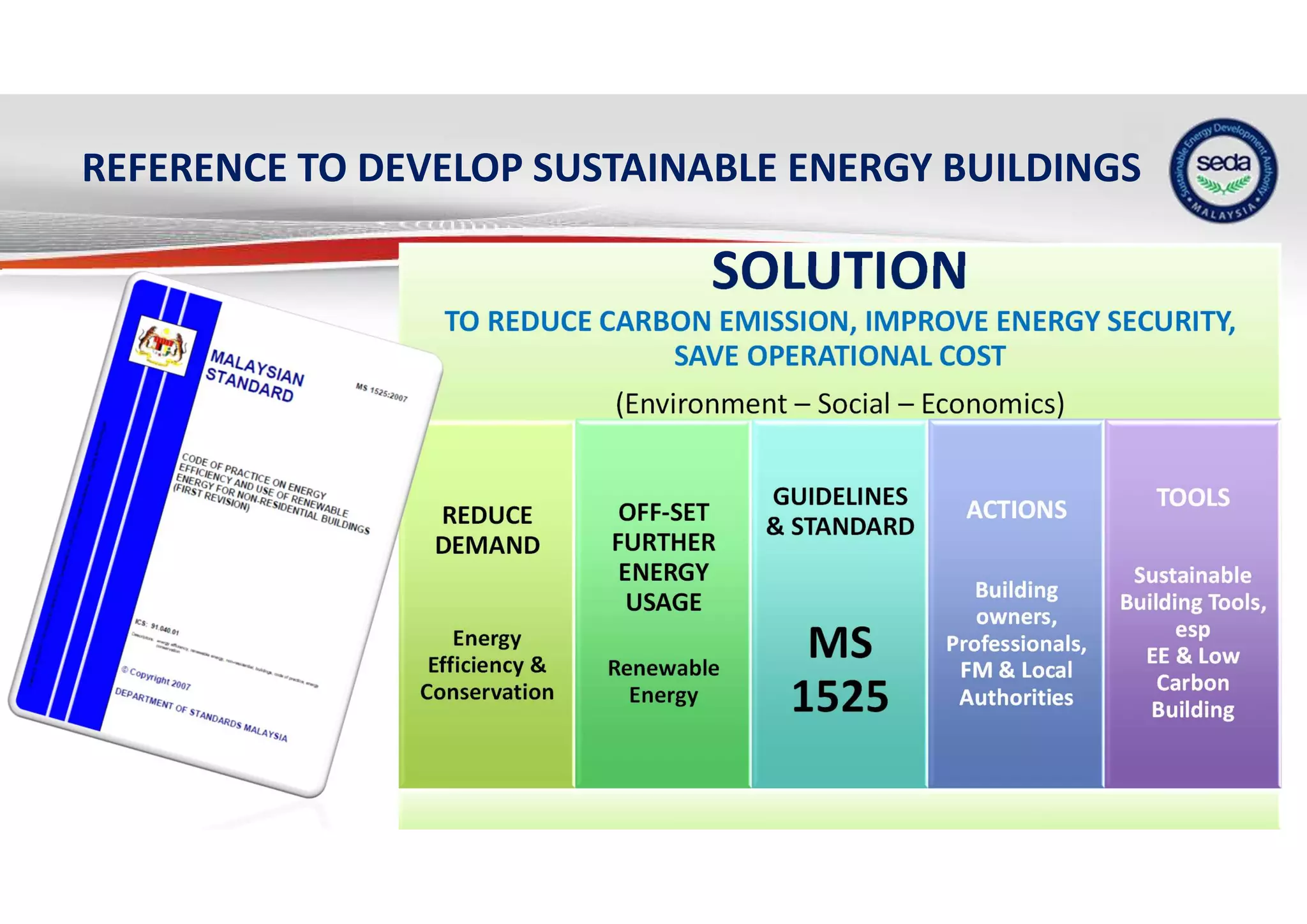
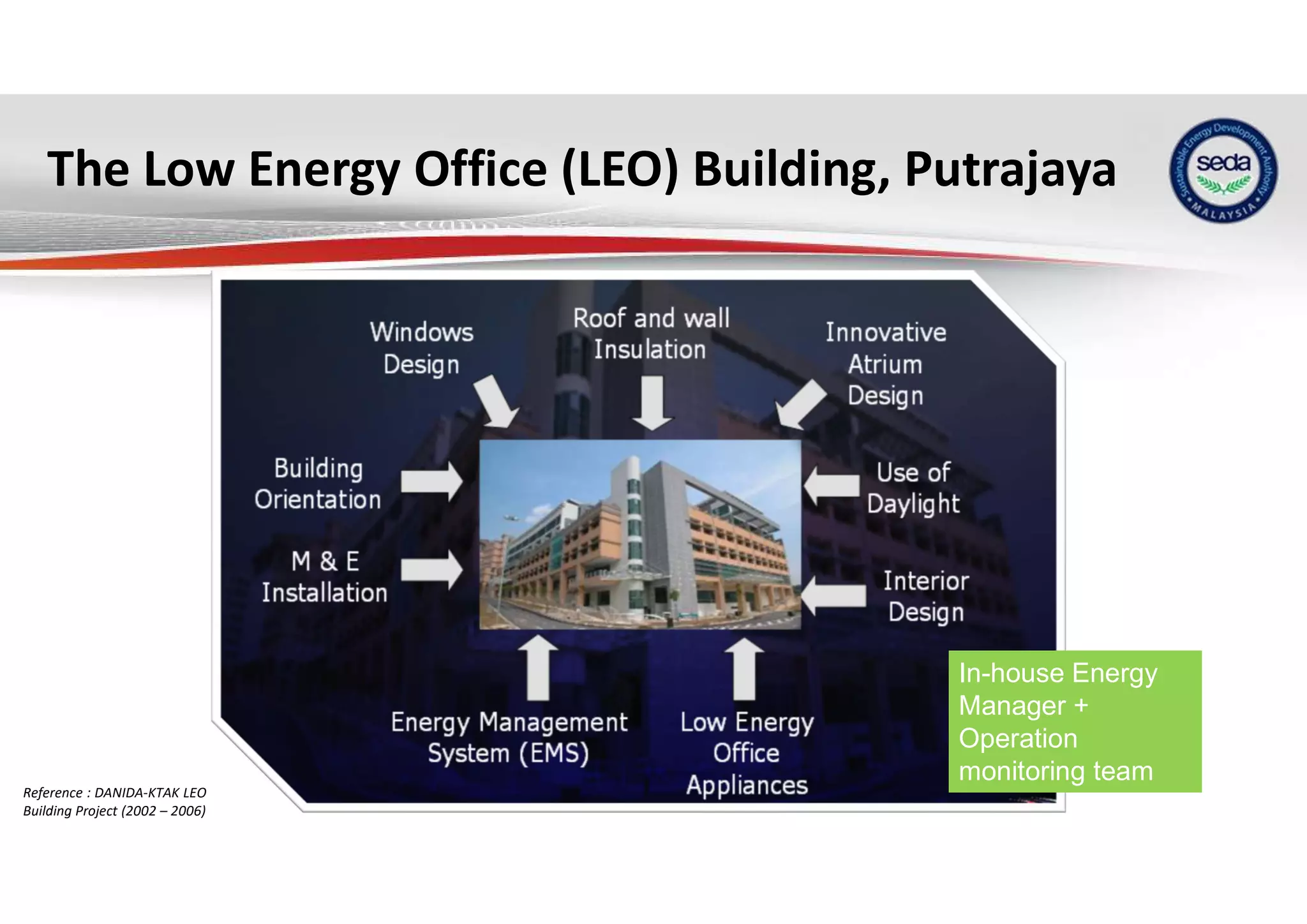
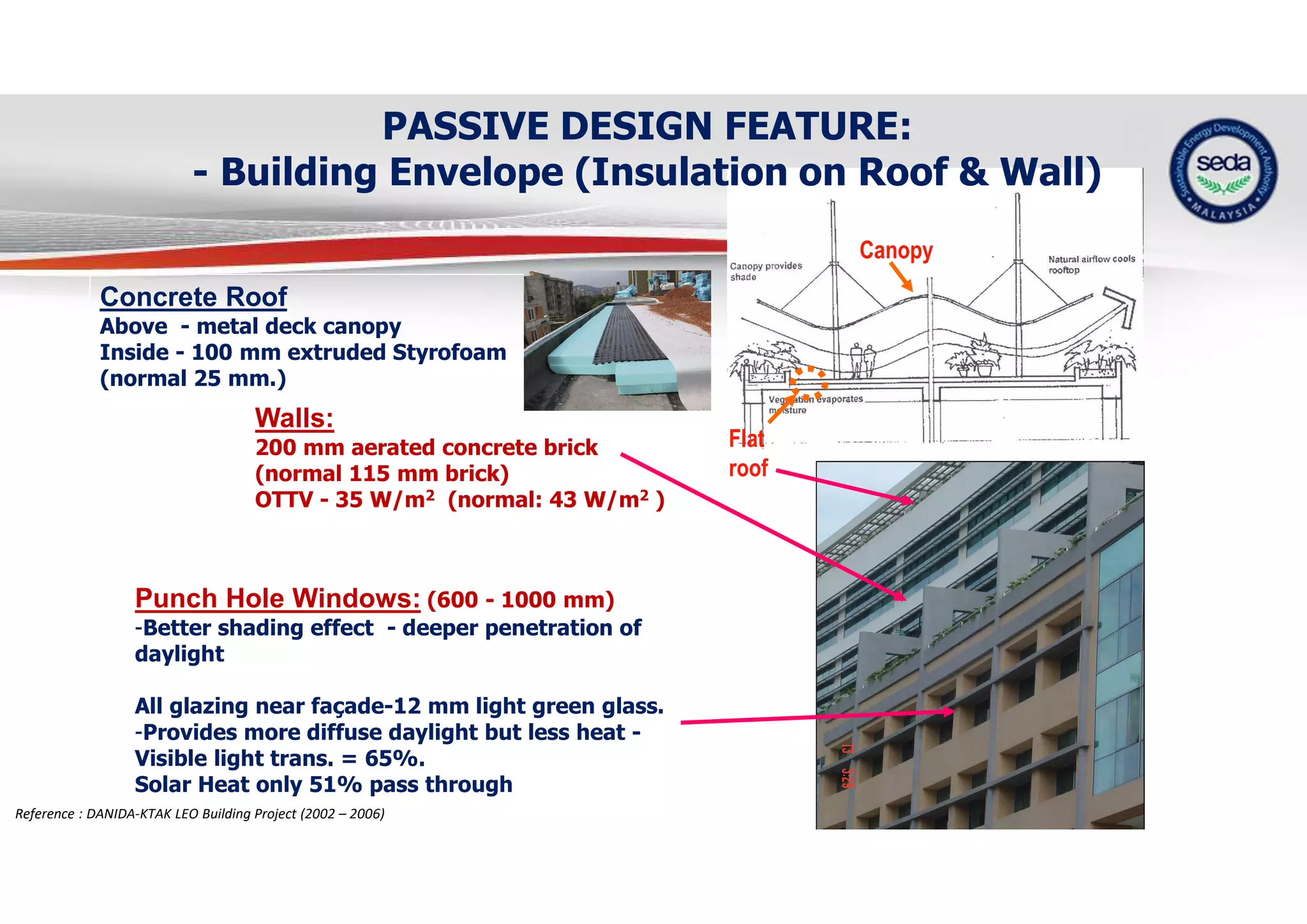
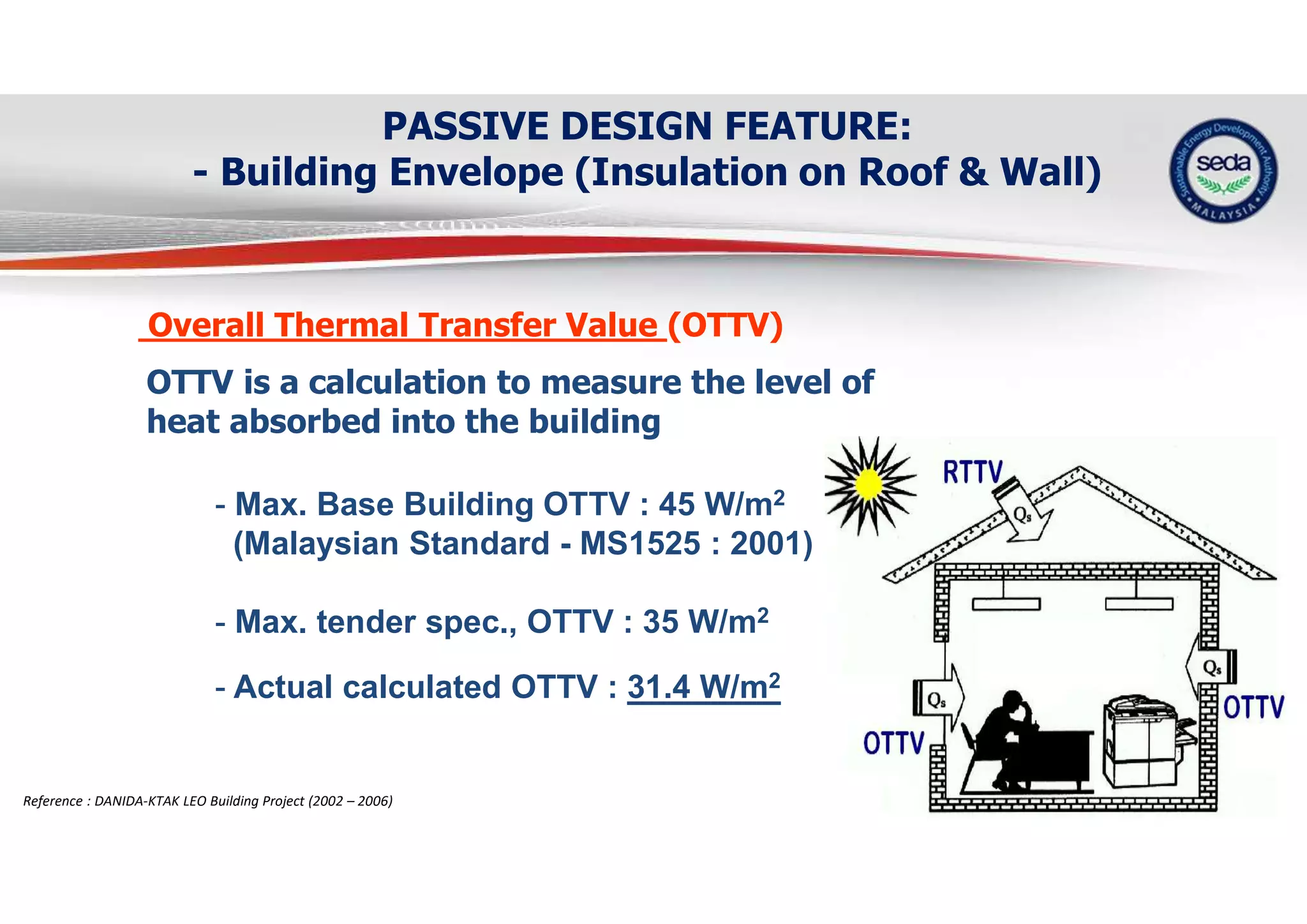
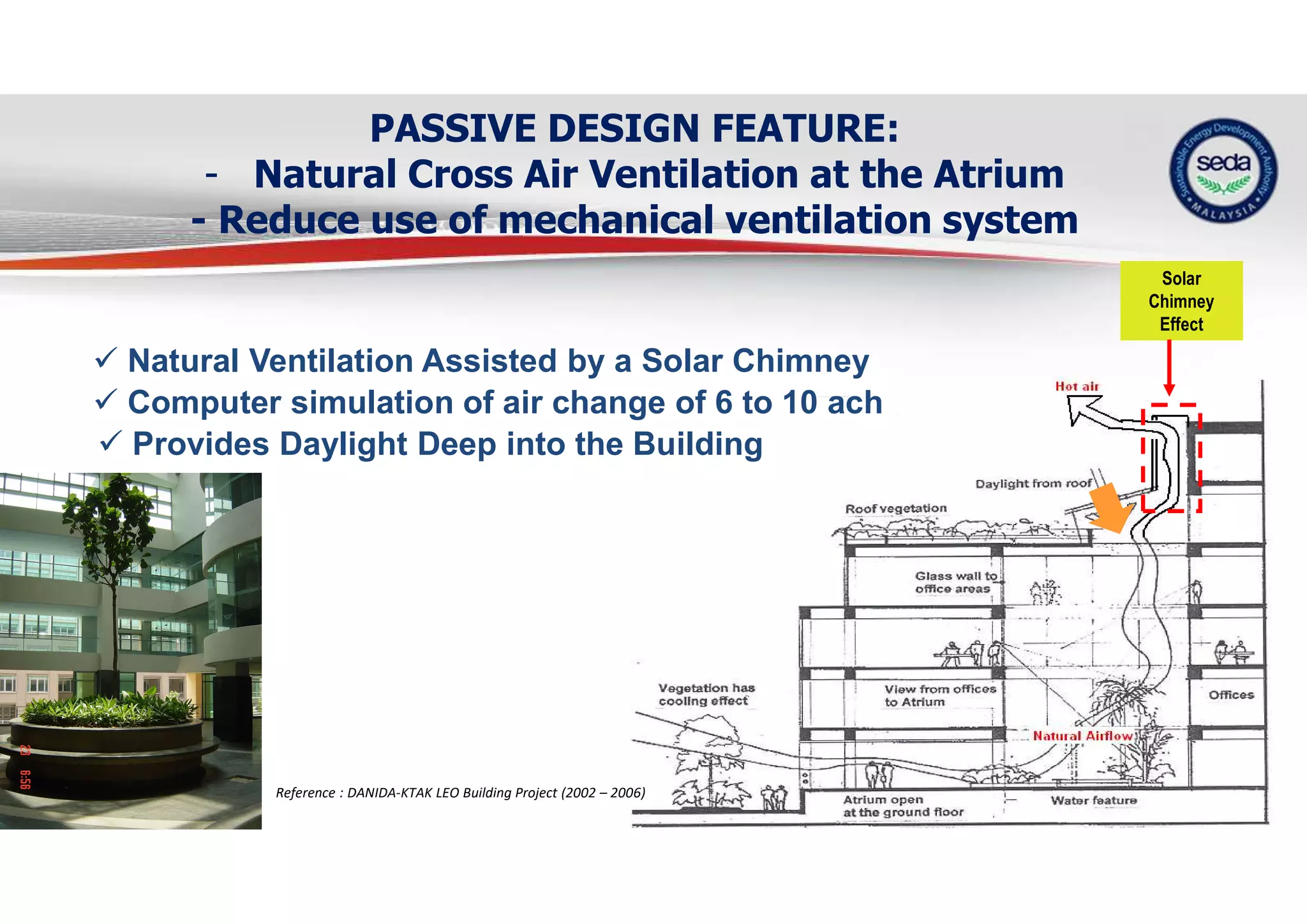
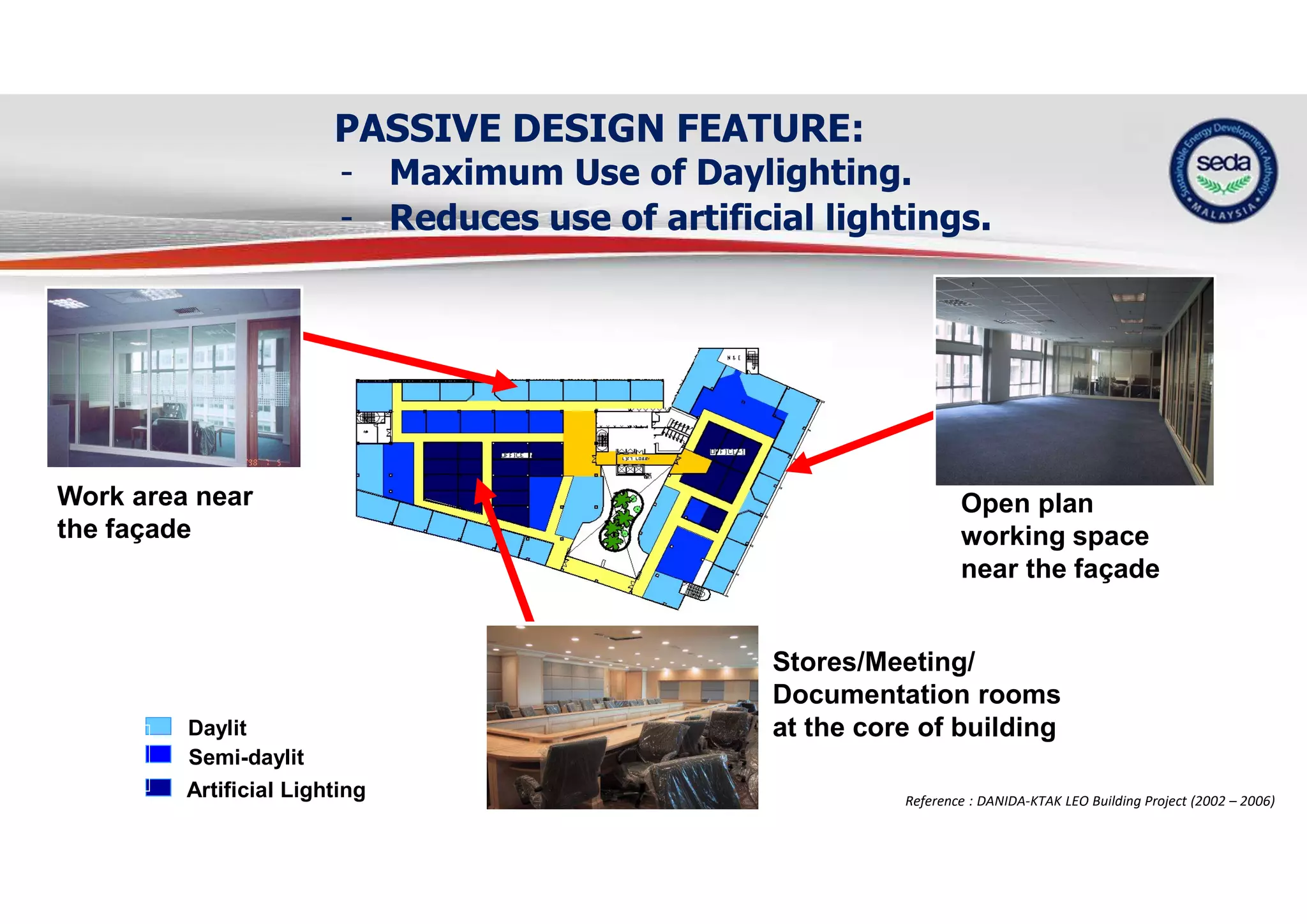
The document provides a case study on the application of the MS1525 code of practice for energy efficiency in non-residential buildings, emphasizing the importance of sustainable energy design and operation. It highlights successful strategies and features from the Low Energy Office (LEO) building in Putrajaya, including passive and active design elements aimed at reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions. Additionally, it discusses the importance of integrating renewable energy systems and monitoring tools to achieve operational efficiency and sustainability goals.






![ENERGY MANAGEMENT IN OPERATIONAL:
- Fine tuning, Optimisation & Maintain Performance.
Building Energy Index
(Based on Energy Bills)
64
38
29
16
38
29
28
27
33
30
31
32
29
24
26
25
23
29
20
32
29
27
31
27
30
26
25
18
35
26
31
30
32
35
33
30
24
26
26
24
24
25
25
30
30
30
34
31
28
32
30
-
28
64
36
111
94
90
78
83
88
90
87
92
87
88
87
79
80
77
78
80
77
73
80
81
79
80
78
74
81
79
76
82
92
90
89
90
95
94
89
85
88
89
93
90
87
93
91
89
94
91
90
92
87
-
86
36
100
149
122
106
116
112
115
117
120
122
118
120
116
103
106
102
100
109
97
105
109
108
110
107
108
99
106
97
111
108
123
121
122
124
128
124
113
110
114
113
116
116
113
122
120
119
128
122
118
124
118
100
115
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Month
[kWh/m2/yr]
Chilled Water-Cooling Index [kWh/m2/yr] Electrical Energy Index [kWh/m2/yr] Building Energy Index [kWh/m2/yr]
LEO Monitoring & PerformanceReference : DANIDA-KTAK LEO
Building Project (2002 – 2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casestudyofms1525-energyefficiencyandrenewableenergycodeofpractice-190912041726/75/Case-study-of-ms1525-energy-efficiency-and-renewable-energy-code-of-practice-22-2048.jpg)
![ENERGY MANAGEMENT IN OPERATIONAL:
- Fine tune, Optimisation & Maintain Performance.
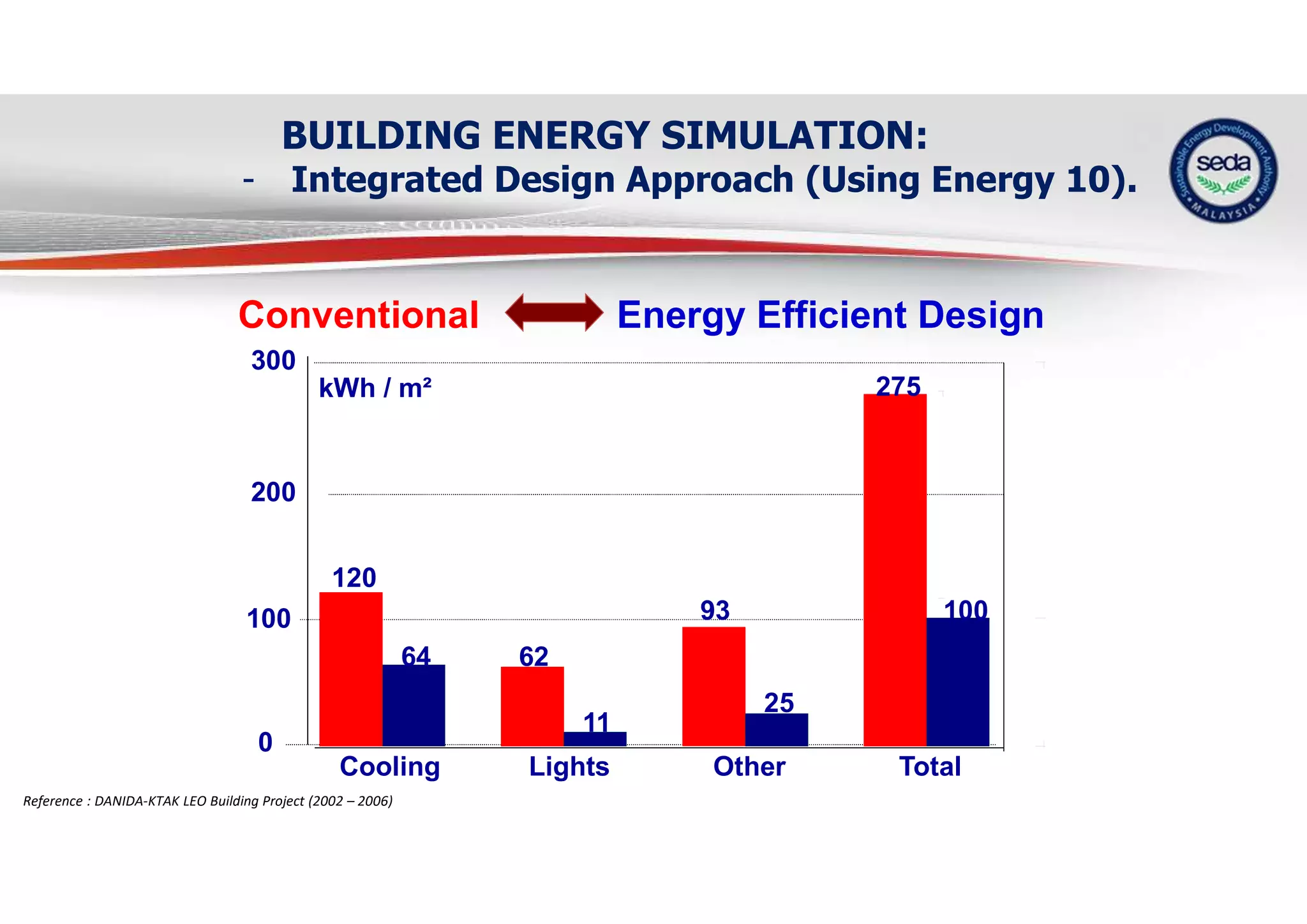
= 3,366,475 kWh/yr
or more than RM 800,000
per year
= 3,366,475 kWh/yr x
0.614 kg CO2/kwh
= 2,067,016 kg/year CO2
= 2,067 tones CO2/year
LEO Building
LEO BEI = 100
(Conventional) BEI = 275
175 kWh/m2year
Tariff C1
28.8 sen/kWh
Savings = 56%
Average Building Energy Index (BEI) in Parcel B
[kWh/m2/yr]
378
315
278
196
233
253
322
349
123
321
268
236
167
198
215
273
296
114
-
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 E4/5
Blocks
[kWh/m2/yr]
AVERAGE (3276 hrs/yr) AVERAGE (Normalised to 2646hrs/yr)
Comparison LEO Building with several
buildings in Putrajaya
Reference : DANIDA-KTAK LEO Building Project (2002 – 2006)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casestudyofms1525-energyefficiencyandrenewableenergycodeofpractice-190912041726/75/Case-study-of-ms1525-energy-efficiency-and-renewable-energy-code-of-practice-23-2048.jpg)