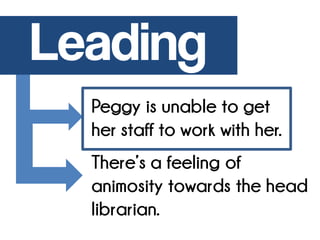
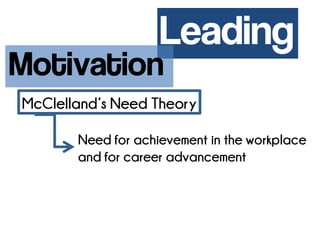
The case study discusses the challenges faced by Peggy, a new head librarian, as her staff refuses to cooperate and lacks the necessary credentials for promotion. It explores concepts of motivation and leadership, emphasizing the need for proper staffing, training, and communication to improve organizational effectiveness. Recommendations include hiring qualified assistants, encouraging further education, and fostering a supportive environment to reduce high turnover rates and enhance teamwork.