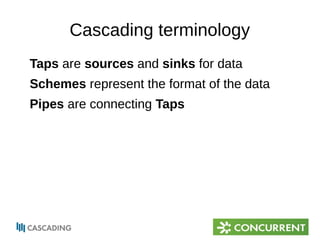
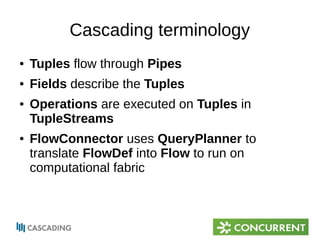
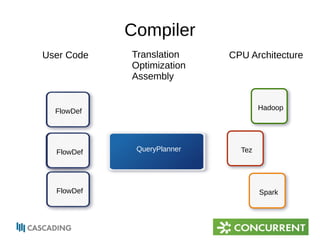
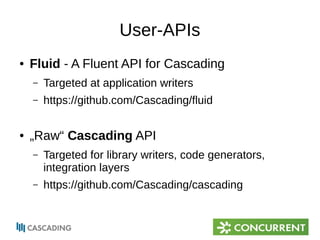
The document provides an overview of Cascading, an Apache-licensed Java framework for creating data-oriented applications, focusing on enhancing developer productivity and robustness in production-quality applications. It describes key components and terminology used in Cascading, such as taps, pipes, and flows, alongside highlighting various operations and integration points with other data sources. Additionally, it mentions the current status and development of Cascading versions, and provides resources for further exploration.





![Counting words
// configuration
String docPath = args[ 0 ];
String wcPath = args[ 1 ];
Properties properties = new Properties();
AppProps.setApplicationJarClass( properties, Main.class );
FlowConnector flowConnector = new Hadoop2MR1FlowConnector( properties );
// create source and sink taps
Tap docTap = new Hfs( new TextDelimited( true, "t" ), docPath );
Tap wcTap = new Hfs( new TextDelimited( true, "t" ), wcPath );
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cascading-andre-kelpe-hugfr-november-2014-141125173942-conversion-gate01/85/The-Cascading-big-data-application-framework-Andre-Keple-Sr-Engineer-Concurrent-11-320.jpg)
![Counting words (cont.)
// specify a regex operation to split the "document" text lines into a
token stream
Fields token = new Fields( "token" );
Fields text = new Fields( "text" );
RegexSplitGenerator splitter =
new RegexSplitGenerator( token, "[ [](),.]" );
// only returns "token"
Pipe docPipe = new Each( "token", text, splitter, Fields.RESULTS );
// determine the word counts
Pipe wcPipe = new Pipe( "wc", docPipe );
wcPipe = new GroupBy( wcPipe, token );
wcPipe = new Every( wcPipe, Fields.ALL, new Count(), Fields.ALL );
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cascading-andre-kelpe-hugfr-november-2014-141125173942-conversion-gate01/85/The-Cascading-big-data-application-framework-Andre-Keple-Sr-Engineer-Concurrent-12-320.jpg)