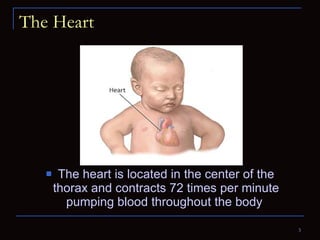
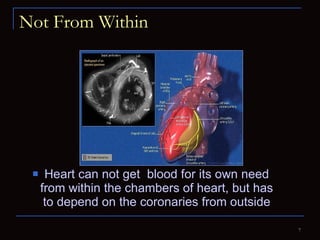
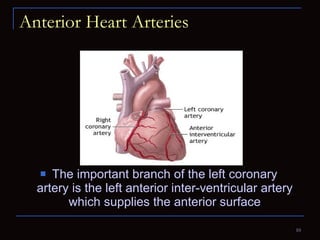
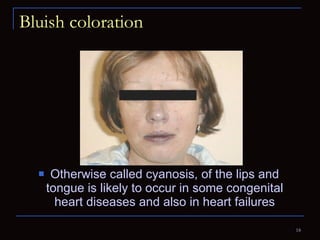
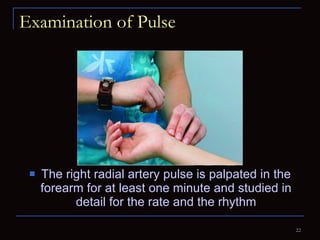
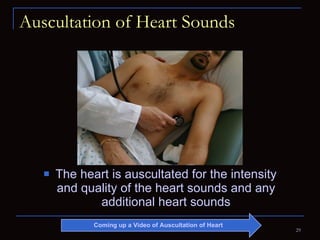
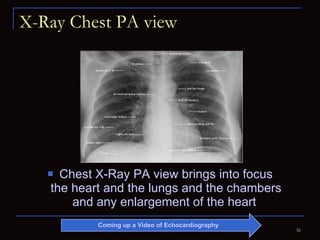
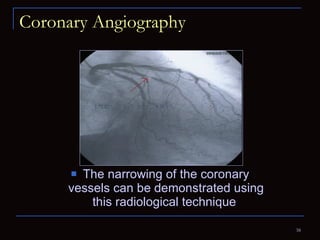
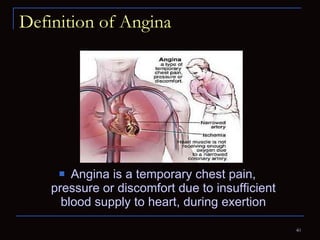
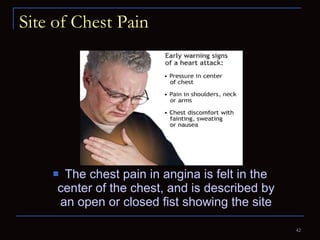
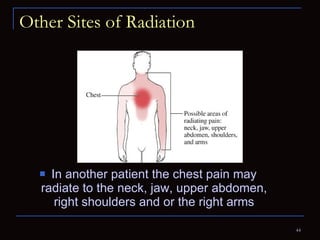
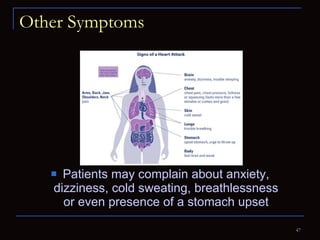
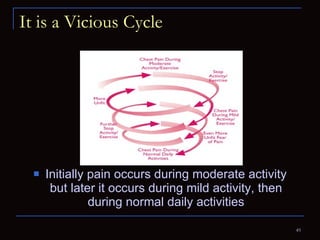
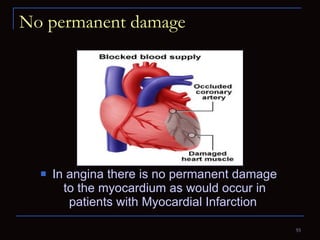
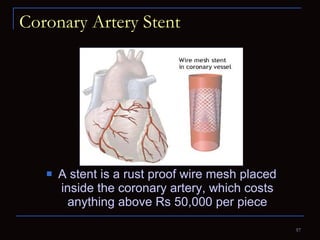
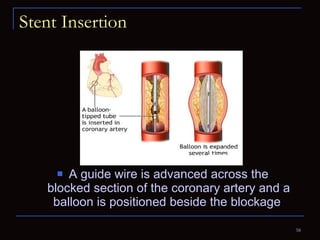
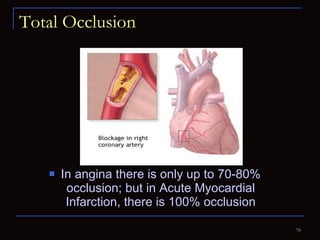
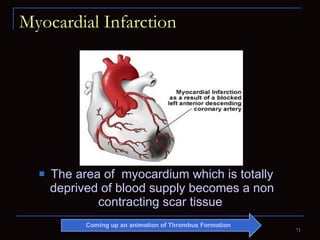
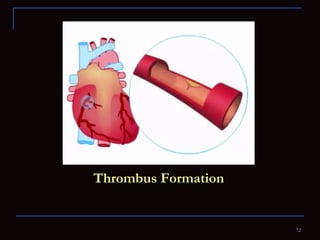
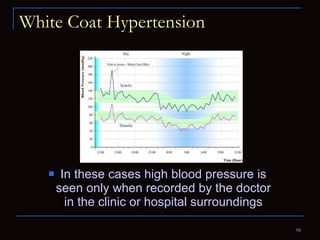
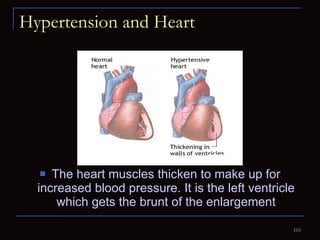
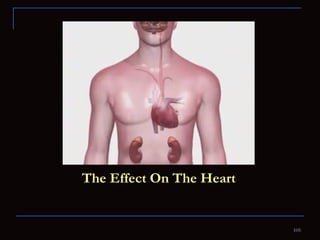
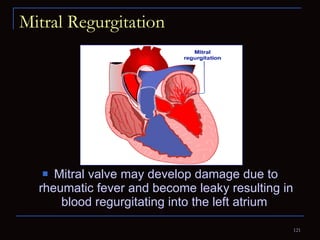
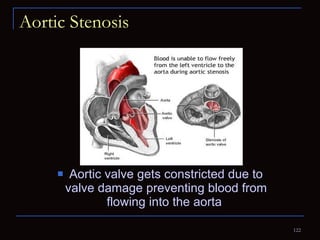
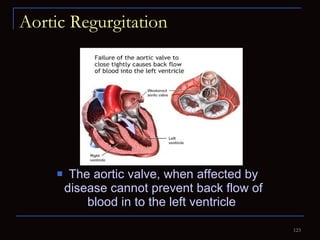
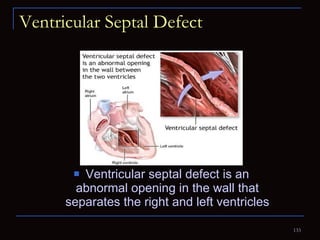
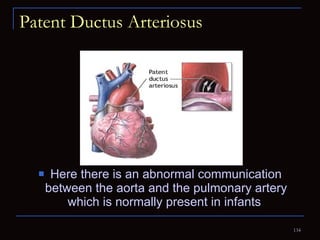
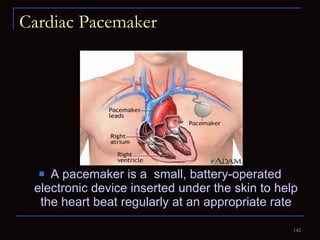
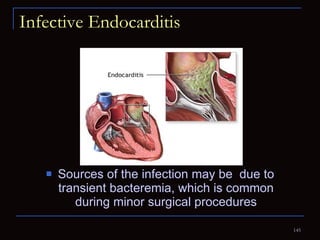
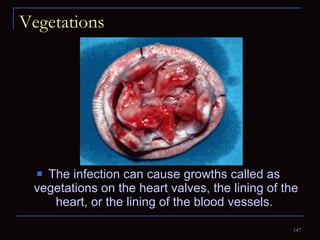
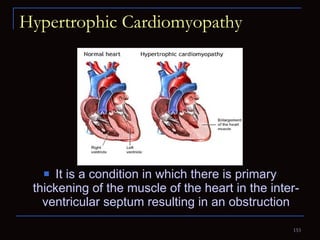
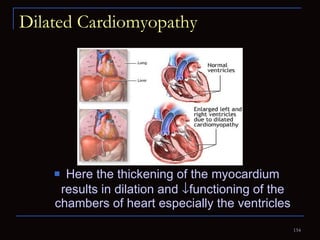
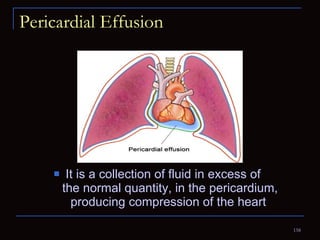
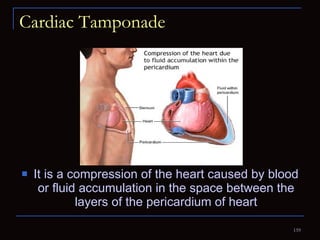
The document provides information about the anatomy and physiology of the heart, as well as various heart diseases. It describes the internal and external structures of the heart, how the heart pumps blood through the body, and how the heart gets its own blood supply. It then covers topics like the symptoms, signs, and investigations of general heart disease. It discusses specific conditions like coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, hypertensive heart disease, valvular heart disease, heart failure, congenital heart diseases, heart rhythm disorders, and infectious endocarditis.