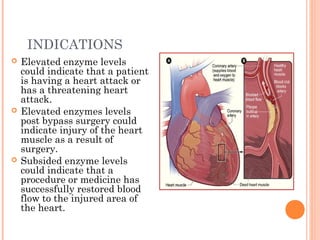
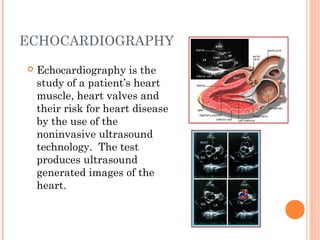
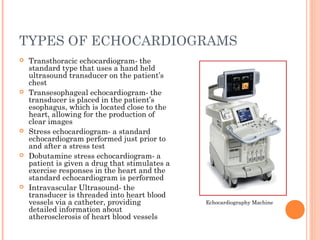
Cardiovascular diagnostic procedures explore the function and health of the heart and blood vessels. The three procedures discussed are cardiac enzymes, stress testing, and echocardiography. Cardiac enzymes measure levels of specific enzymes in the blood related to heart injury. Stress testing evaluates heart function and stress tolerance using exercise. Echocardiography uses ultrasound to create images of the heart and assess function, heart disease, and treatment effectiveness. These procedures provide crucial information for diagnosing and treating cardiovascular abnormalities and disease.