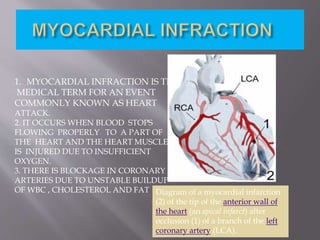
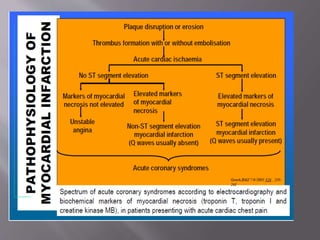
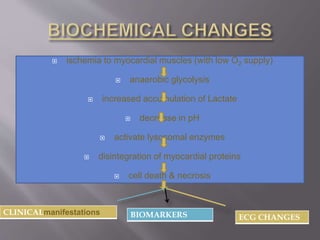
This document discusses acute myocardial infarction (AMI), also known as a heart attack. AMI occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, injuring the heart muscle due to lack of oxygen. It is caused by a buildup of cholesterol, fat, and white blood cells in the coronary arteries. AMI can be diagnosed if a patient experiences chest pain for over 20 minutes and has changes on their electrocardiogram (ECG) and increasing and decreasing levels of cardiac biomarkers. Common biomarkers for AMI include creatine kinase, creatine kinase-MB, cardiac troponins, and myoglobin. These biomarkers are detectable in blood and can help determine the extent and timing of the heart injury.