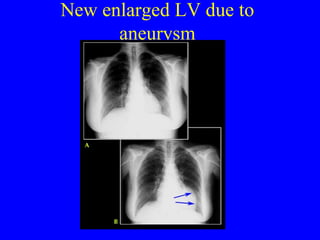
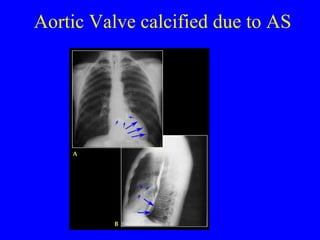
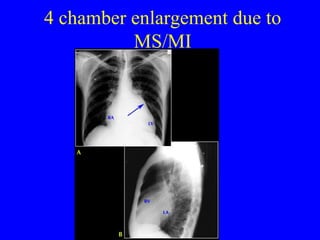
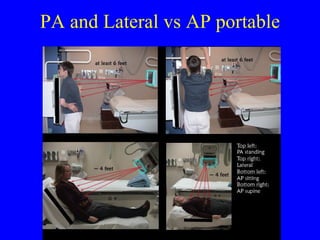
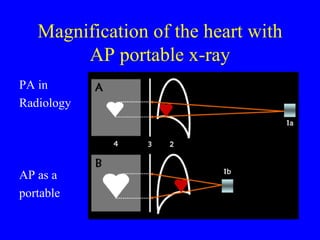
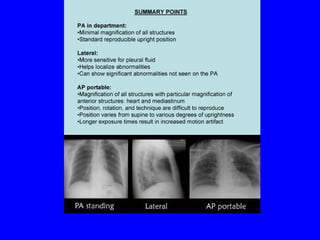
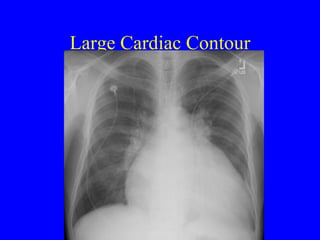
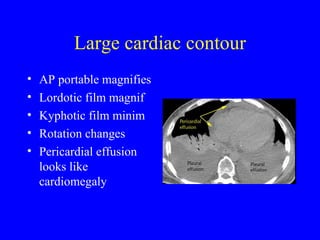
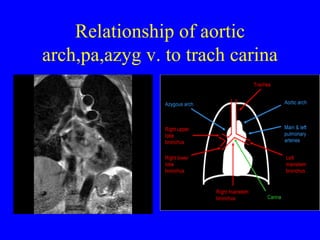
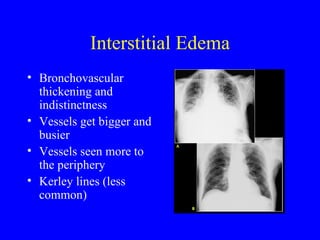
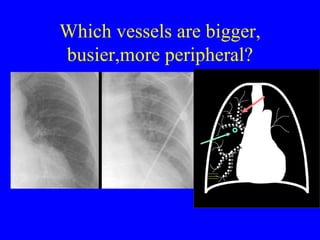
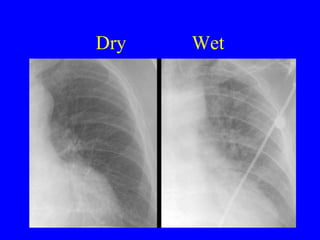
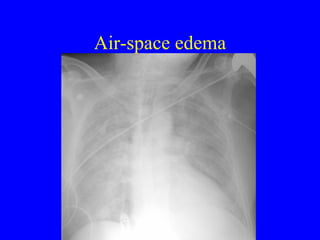
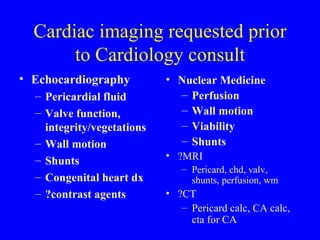
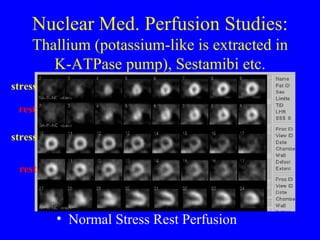
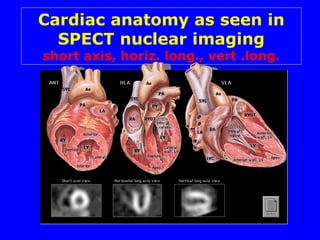
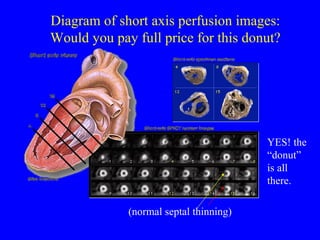
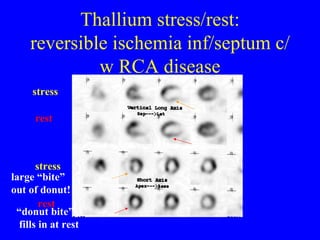
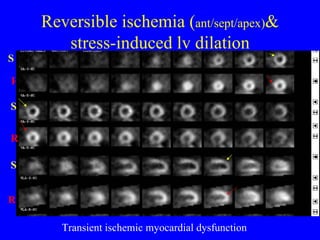
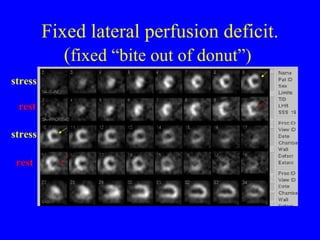
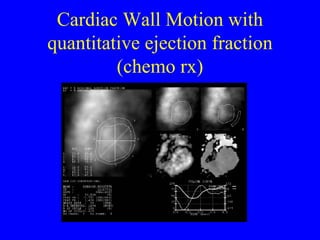
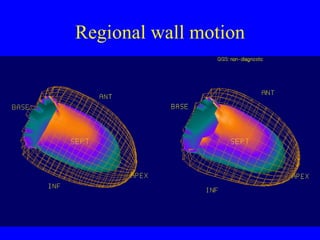
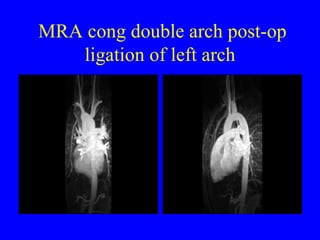
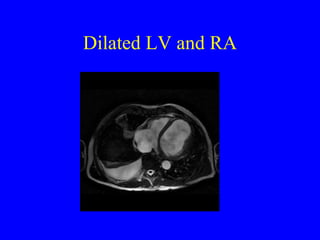
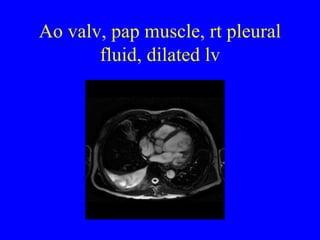
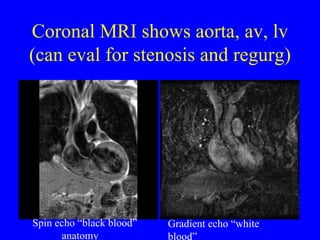
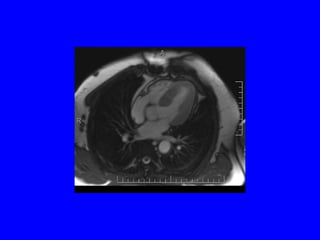
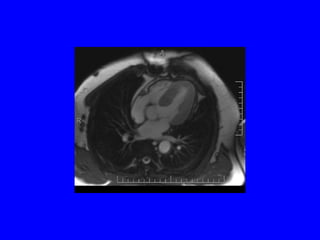
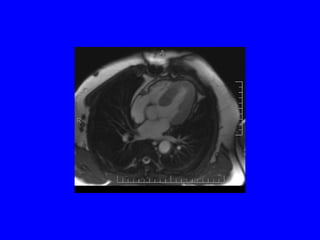
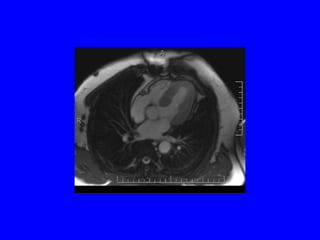
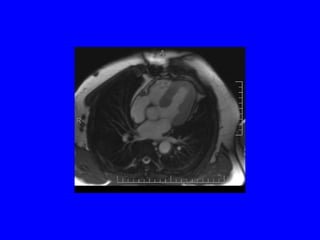
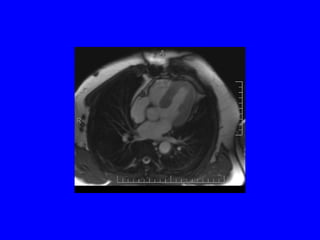
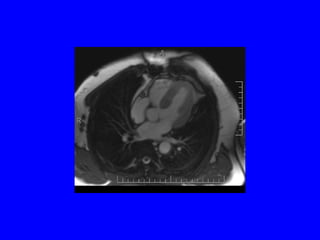
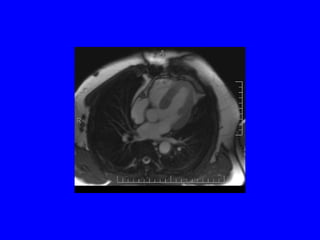
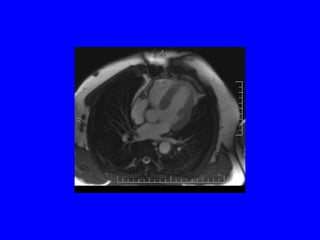
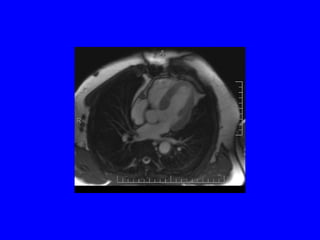
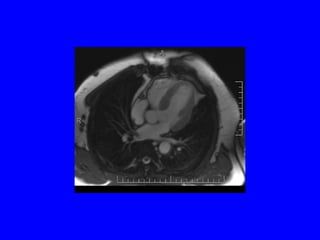
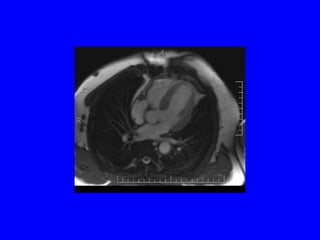
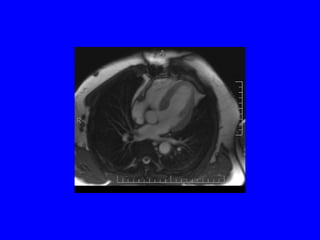
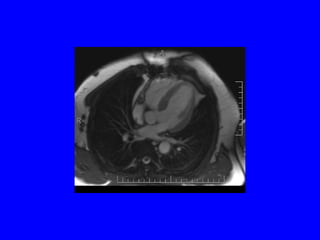
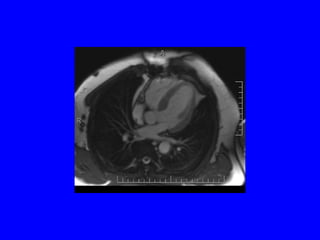
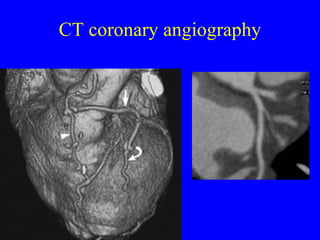
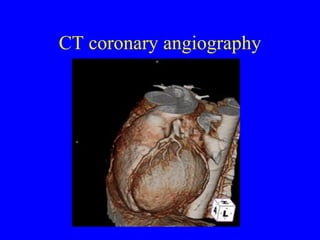
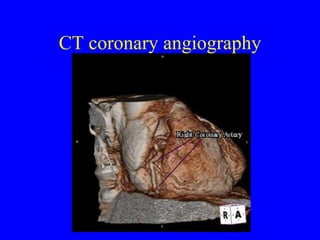
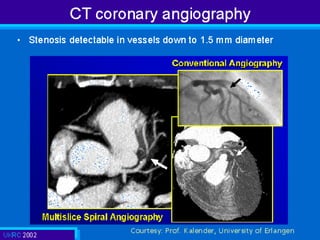
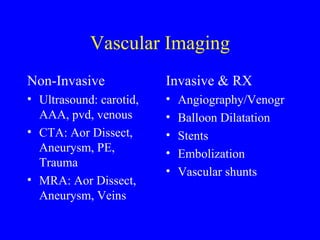
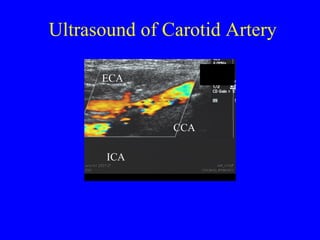
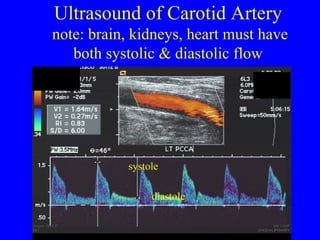
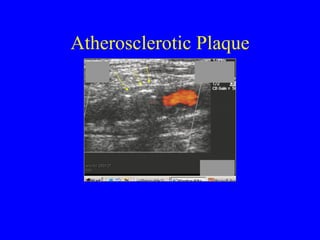
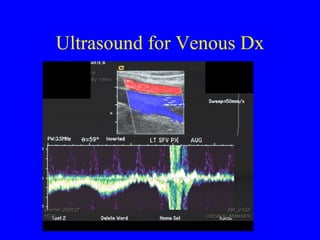
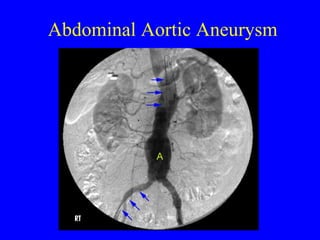
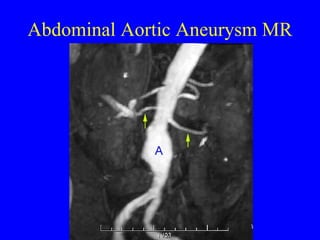
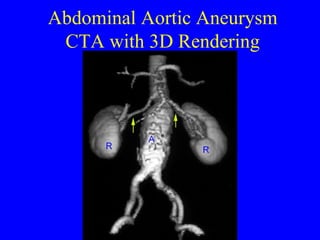
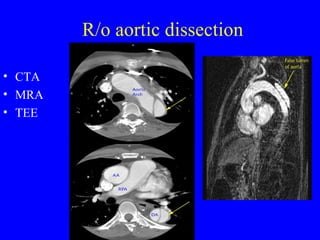
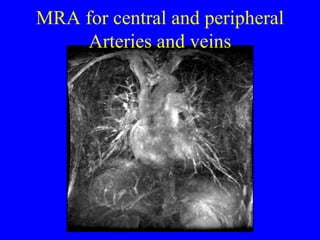
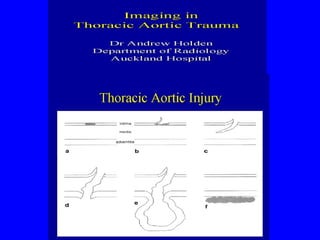
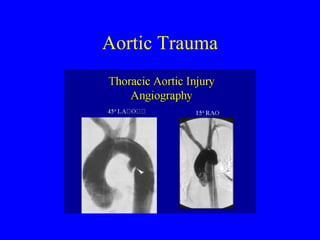
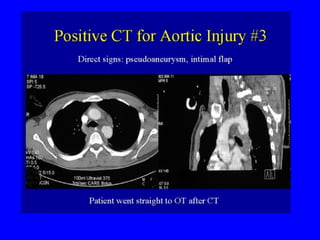
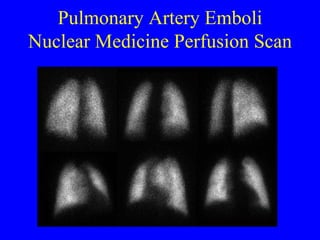
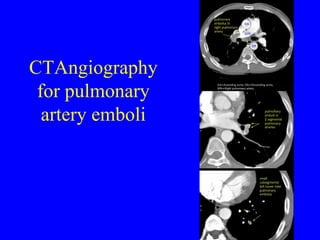
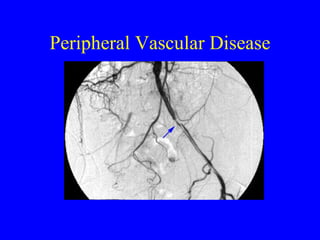
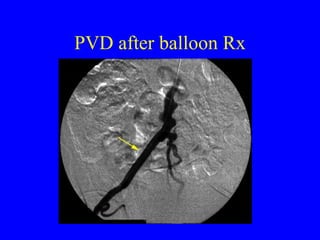
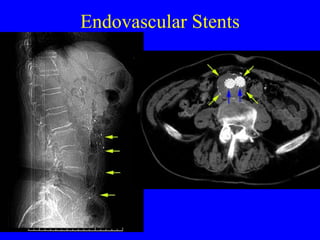
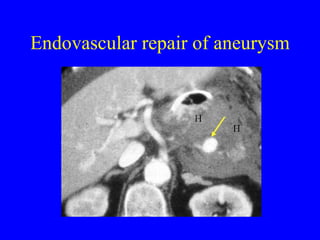
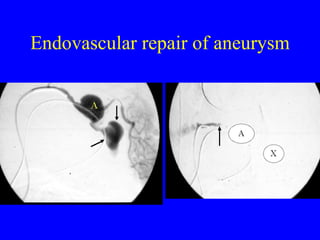
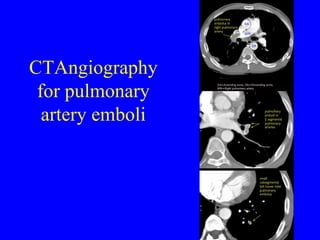
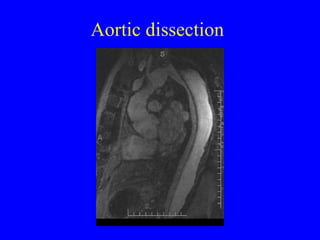
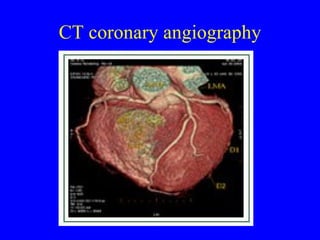
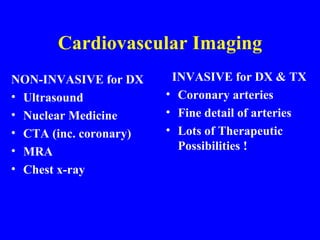
This document discusses various cardiovascular imaging modalities including their uses, strengths, and limitations. It covers modalities such as chest x-ray, echocardiography, nuclear medicine studies, MRI, CT, ultrasound, and invasive angiography. For each modality, it provides examples of what cardiovascular structures or conditions they can best evaluate such as valve function, wall motion, perfusion, coronary arteries, aneurysms, and more. It also notes some modalities may be used for both diagnostic and interventional purposes.