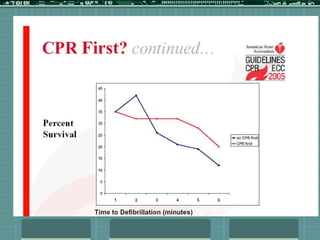
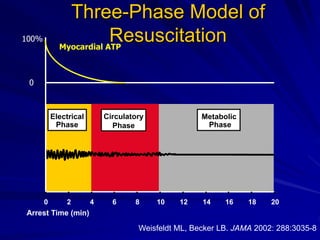
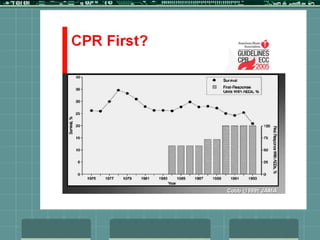
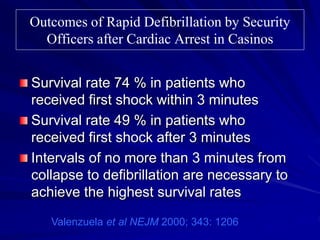
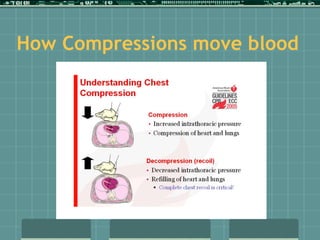
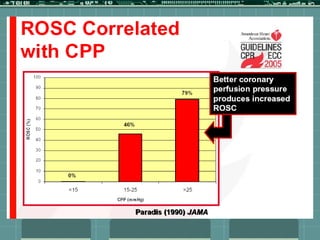
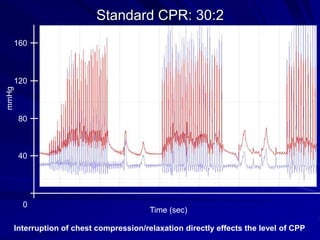
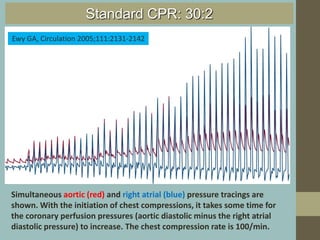
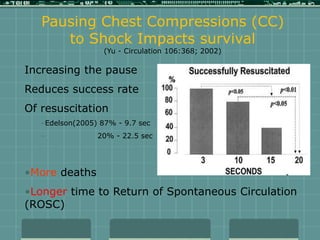
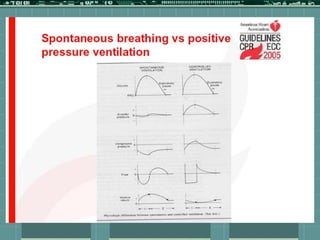
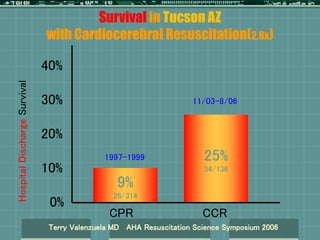
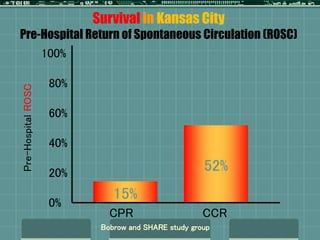
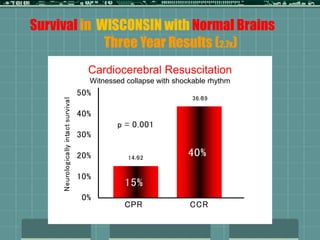
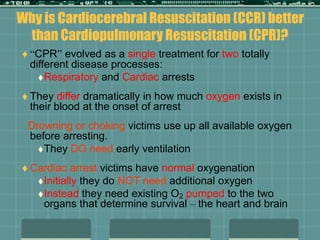
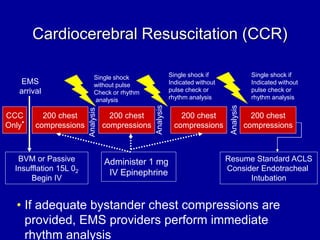
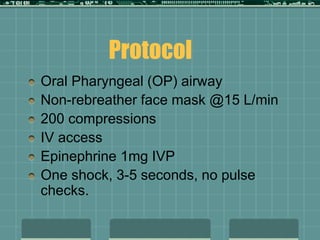
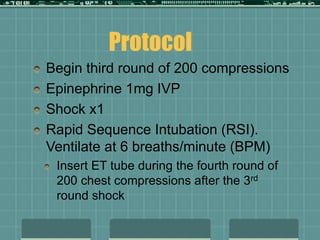
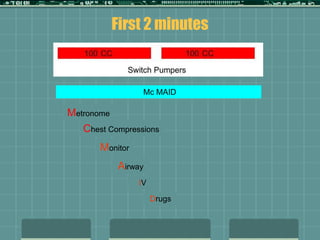
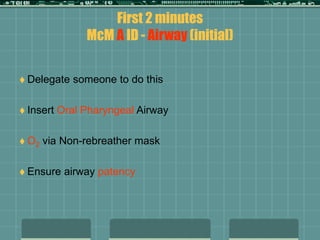
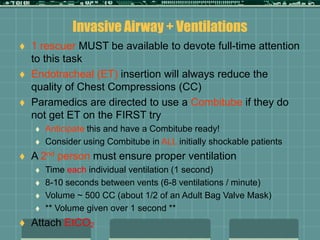
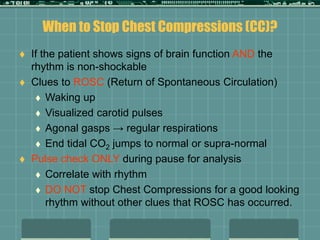
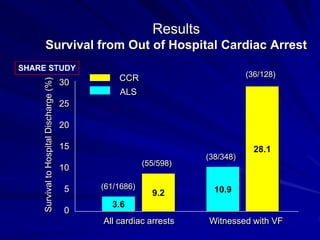
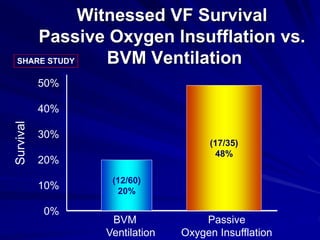
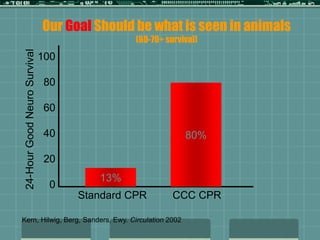
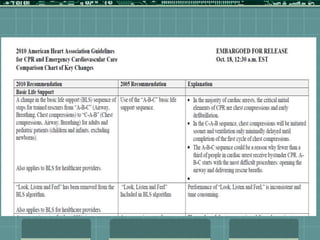
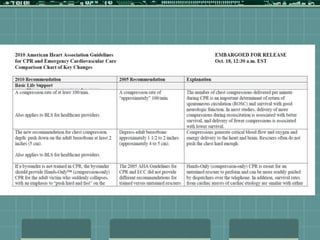
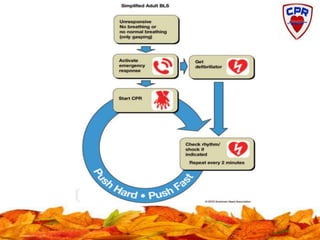
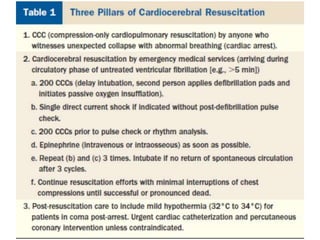
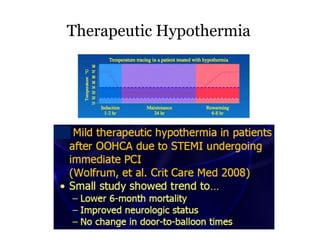
Cardiocerebral resuscitation (CCR) provides a better outcome than cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) with fewer interruptions in chest compressions and delayed ventilation. CCR focuses on continuous chest compressions, early defibrillation, and limiting pauses. Studies show higher rates of survival to hospital discharge and neurological intact survival with CCR compared to CPR. The key elements of CCR are minimizing interruptions in chest compressions through avoiding pulse checks and shorter analysis periods.