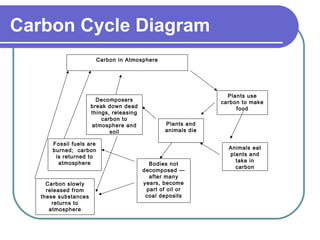
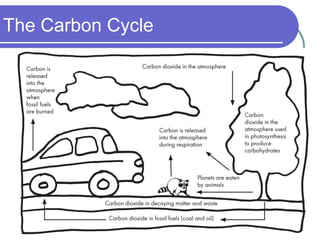
Carbon cycles between the atmosphere, living things, oceans, and land through photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and the burning of fossil fuels. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air and use it to grow, then animals release carbon back to the air by breathing or when they die and decompose. Some carbon gets trapped in oceans, soils, fossil fuels and rocks. Human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.