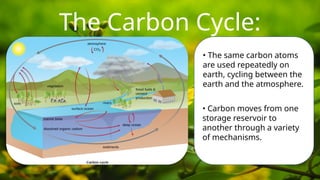
Carbon is essential for life on Earth, found in all living things and regulating temperature and energy. The carbon cycle involves the continuous movement of carbon between storage reservoirs through processes like photosynthesis in plants and consumption by animals. Human activities, particularly in various industrial sectors, significantly impact this natural cycle by emitting carbon dioxide.