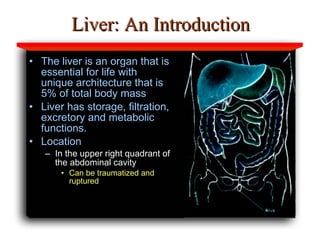
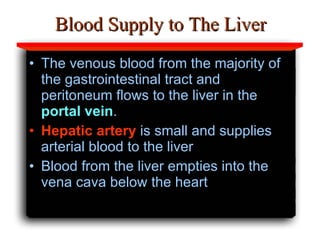
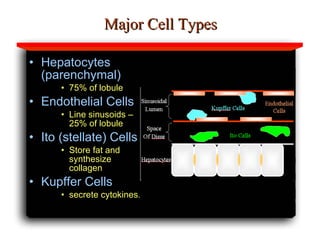
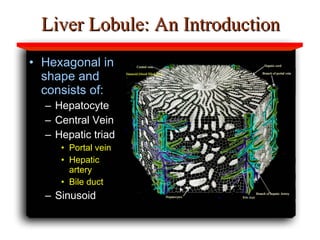
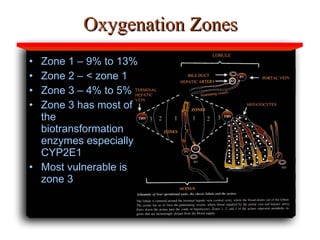
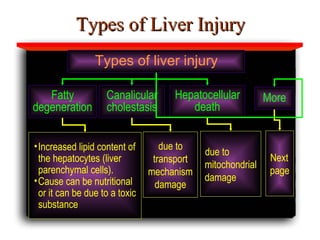
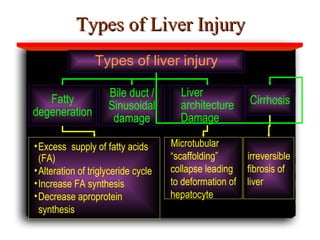
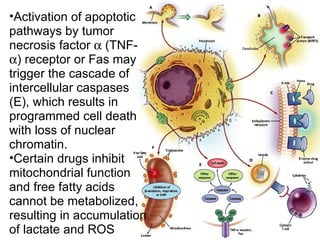
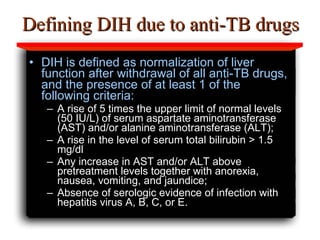
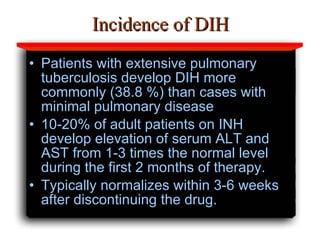
Hepatotoxicity, or liver toxicity, can result from anti-tuberculosis (TB) drugs and is known as drug-induced hepatitis (DIH). Patients at high risk include those with pre-existing liver conditions, alcohol use, and advanced TB. Monitoring of liver enzymes is important for high risk patients during TB treatment. Symptoms of DIH include fatigue, nausea, and jaundice. Diagnosis involves abnormal liver enzymes and symptom resolution after stopping anti-TB drugs. Management consists of gradual dose escalation while monitoring for toxicity.






![Risks for DIH Higher risk of hepatotoxicity to the first-line antitubercular agents [DIH] has been reported in Indian patients; Risk of DIH is 4 times in alcohol drinkers than non-drinkers; INH hepatotoxicity is more common in females than males; Other risk factors include pre-existing liver disease, and advanced TB.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepatotoxicity-111115213821-phpapp01/85/Hepatotoxicity-17-320.jpg)








![Diagnosis of DIH due to anti-TB drugs Hepatotoxicity due to antitubercular agents [DIH] is revealed by clinical examination and abnormal liver function test results During periodic consultations in the course of anti-TB therapy, all pts. must be monitored clinically for S/S suggestive of DIH. Routine laboratory monitoring for DIH is not recommended in all but in high-risk cas es, where it must be performed monthly in the initial phase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepatotoxicity-111115213821-phpapp01/85/Hepatotoxicity-26-320.jpg)



