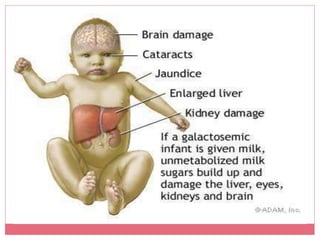
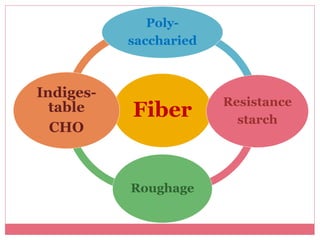
This document discusses carbohydrates, which are compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that serve as an important energy source. It defines simple carbohydrates like glucose, fructose, and galactose as well as complex carbohydrates like fiber. Glucose is a key source of energy for cells and the brain. Fructose provides energy to the liver while galactose aids in lactose digestion. Complex carbohydrates include fiber, which has many health benefits such as regulating blood sugar, promoting digestive and heart health, and reducing cancer risk. The document outlines food sources and daily requirements for various carbohydrates.