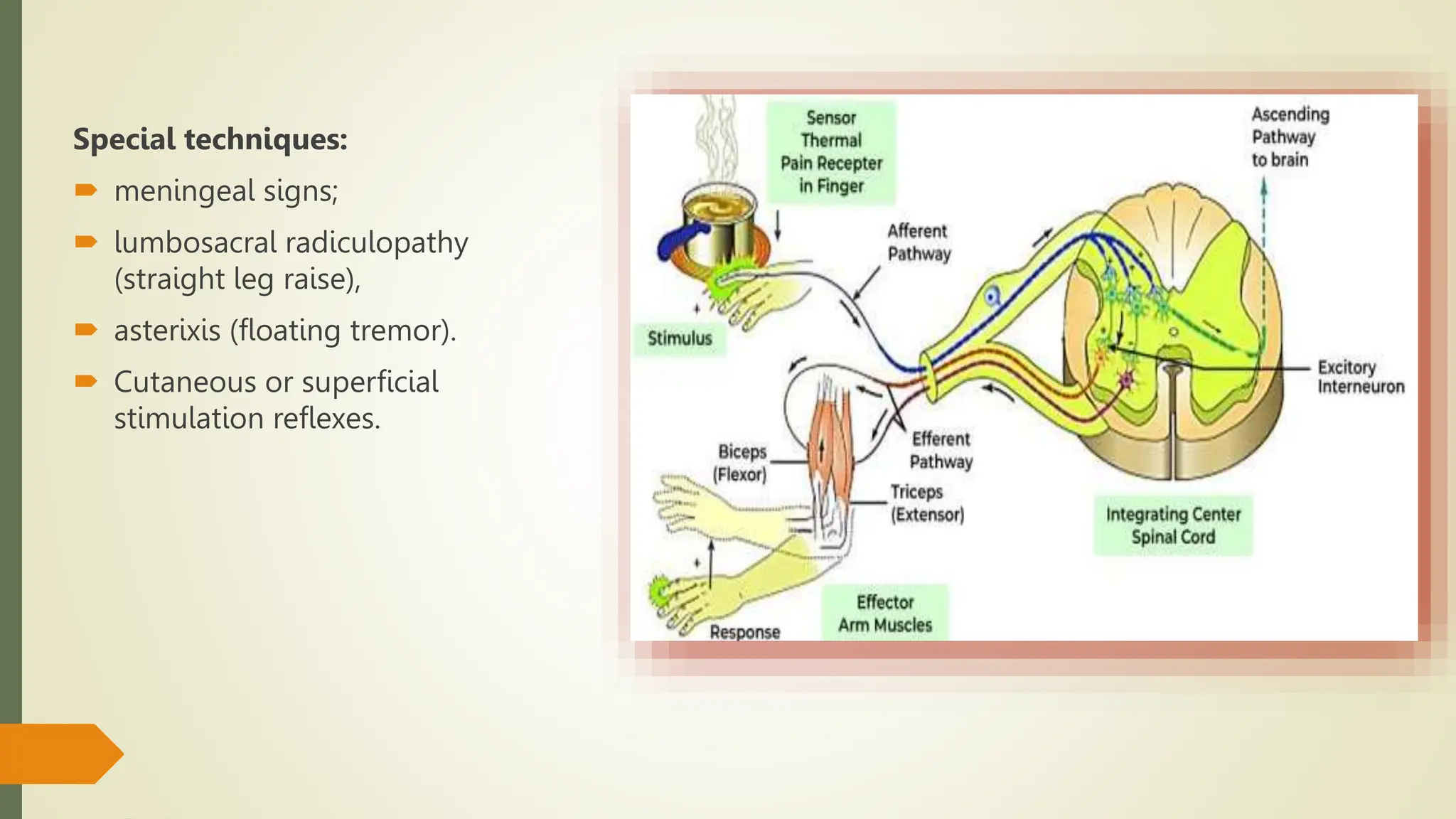
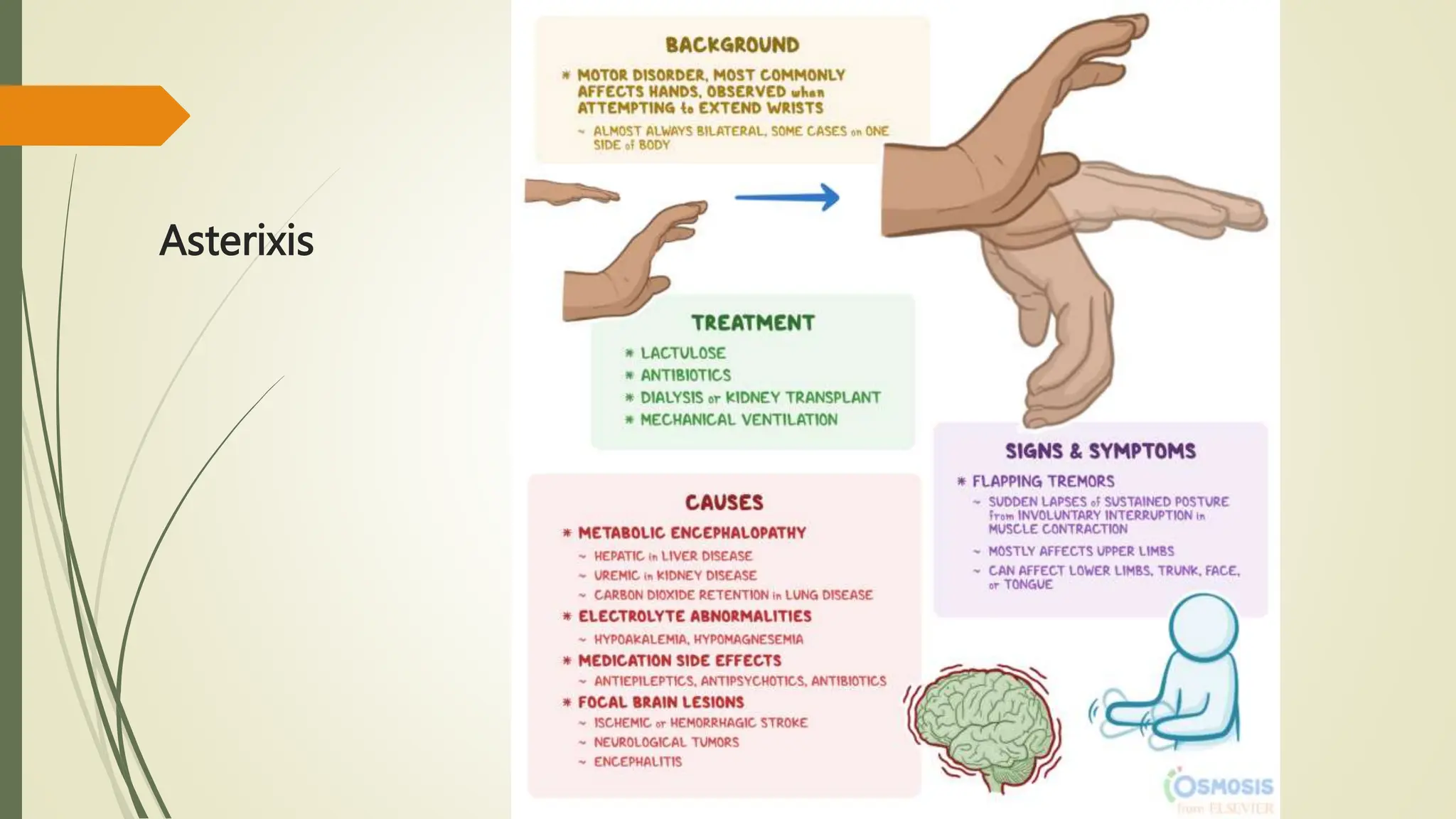
This document describes various neurological examination techniques including:
1) Meningeal signs like neck stiffness, Brudzinski's sign, and Kernig's sign which test for meningeal inflammation.
2) Asterixis which identifies metabolic encephalopathy.
3) Lumbosacral tests like the straight leg raise test which check for radiculopathy.
4) Superficial reflexes and deep tendon reflexes including their locations, testing procedures, and root innervations.