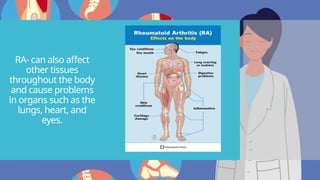
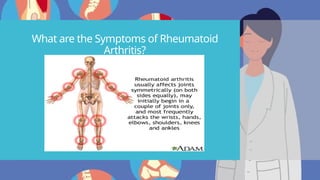
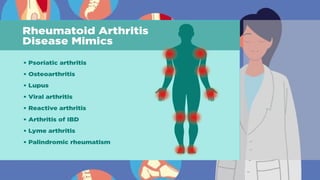
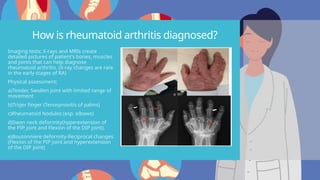
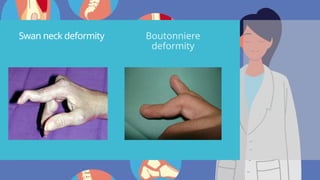
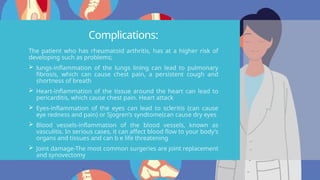
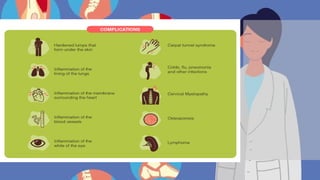
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential damage to other organs. The exact cause is unknown but may involve genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors, with common symptoms including joint stiffness, swelling, and fatigue. Diagnosis is made through patient symptoms, physical examination, and various tests, while treatment options include painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and disease-modifying medications.