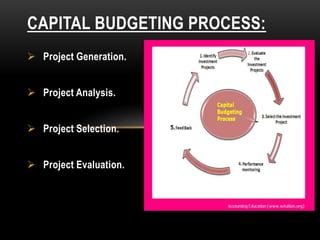
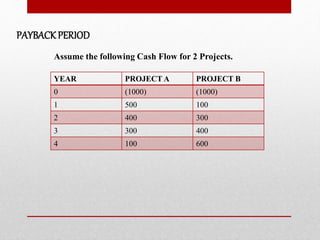
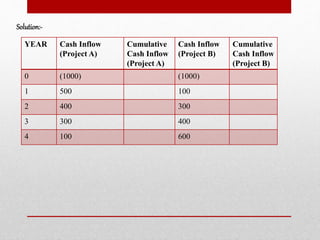
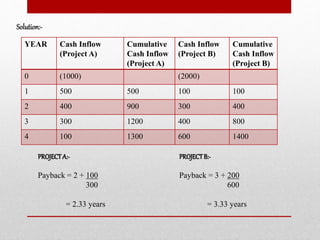
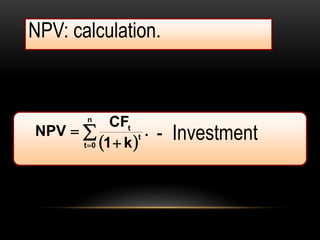
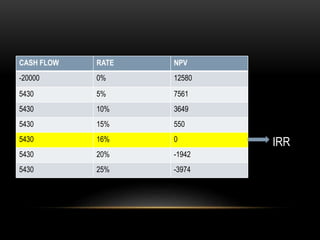
The document discusses capital budgeting, which involves planning and justifying large expenditures for long-term projects, including project classification, objectives, importance, advantages, and disadvantages. It details various techniques for capital budgeting analysis, such as payback period, net present value, and internal rate of return, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations. The capital budgeting process includes project generation, analysis, selection, and evaluation, emphasizing the need for informed and judicious decision-making in investments.