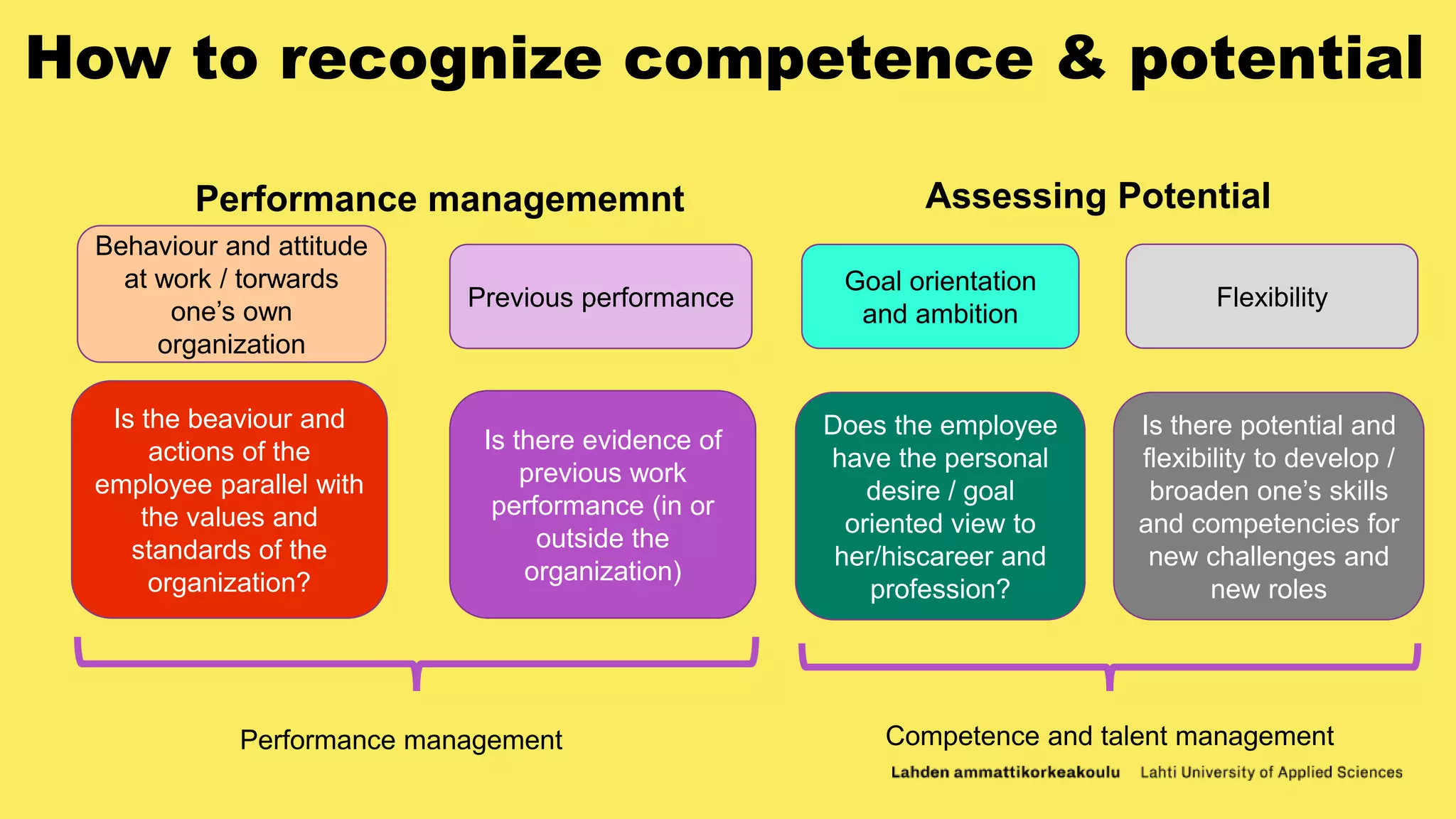
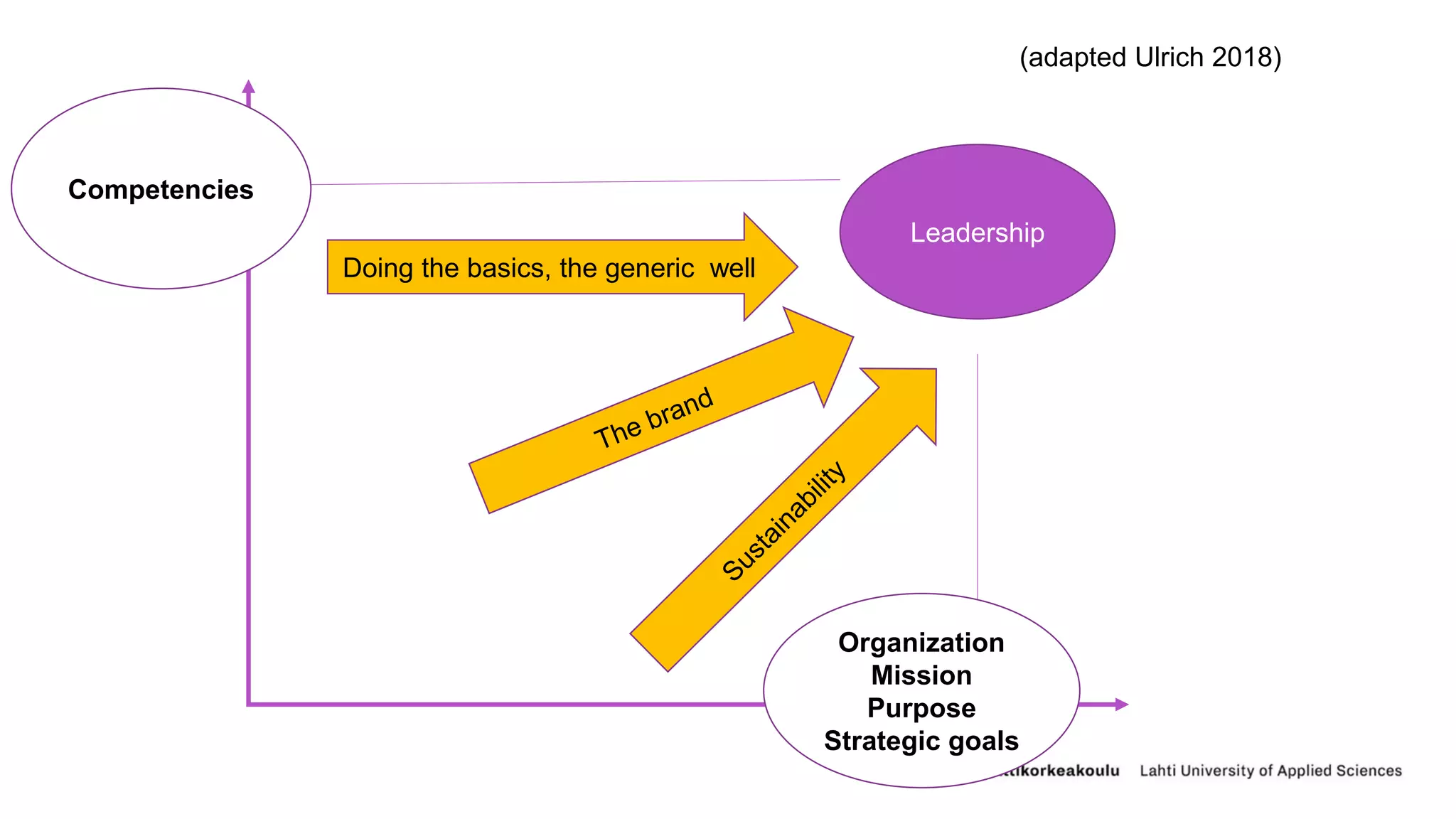
The document discusses capacity building and competence management in organizations. It defines capacity building as actions to strengthen an organization's ability to achieve its mission and objectives. This involves developing knowledge, skills, leadership, and systems. Competence management is about maximizing the potential of employees and helping people utilize their collective knowledge. The document recommends that organizations foster adaptation, embrace disequilibrium during change, generate leadership at all levels, and distribute leadership responsibility. It also emphasizes that competence management involves treating people as the most valuable resource and allowing them to develop to their full potential.