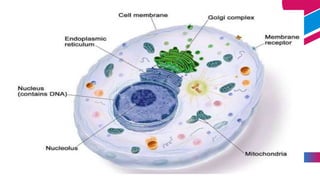
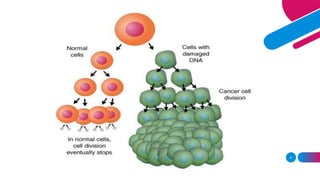
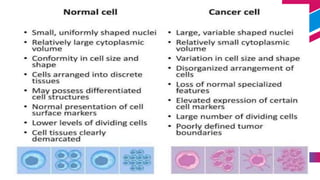
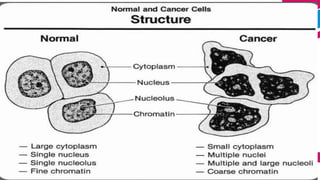
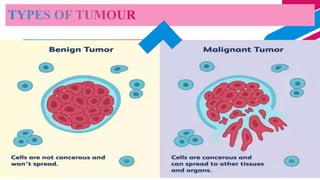
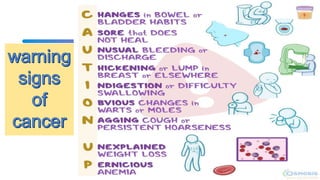
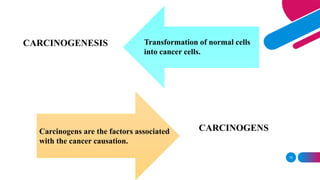
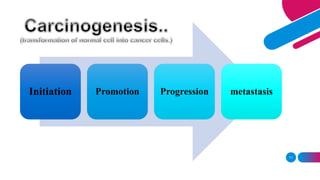
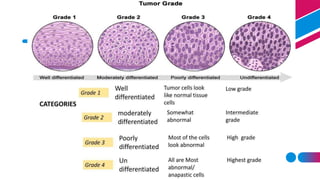
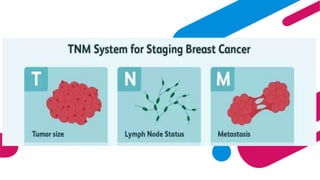
This document discusses cancer and its stages. It defines cancer as uncontrolled cell growth that can spread to other parts of the body. The World Health Organization defines cancer as abnormal cells that grow beyond their usual boundaries and invade other tissues or spread to other organs. The document then discusses carcinogenesis, the process by which normal cells are transformed into cancerous cells, as well as the stages of cancer including initiation, promotion, progression, and metastasis. It concludes by explaining the TNM staging system used to describe the extent of solid tumors.











![Cancer [medical surgical nursing] basic information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-240402020405-0a62f4f6/85/Cancer-medical-surgical-nursing-basic-information-26-320.jpg)