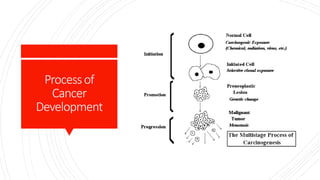
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cancer, covering its definition, prevalence, causes, and the importance of screening and prevention. Globally, cancer is the second leading cause of death with significant numbers arising from lifestyle-related risks, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. In India, breast and cervical cancers are notably prevalent, with high mortality rates associated with tobacco use and lack of early detection measures.