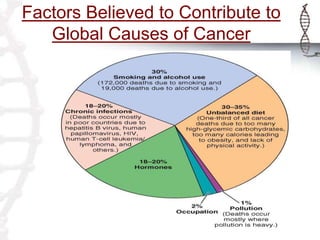
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation that has transformed from normal cells. Several screening methods are used to test potential cancer treatments in vitro and in vivo. In vitro methods include tetrazolium salt assays, sulphorhodamine B assays, and thymidine uptake assays to test cell viability. In vivo methods include inducing tumors in mice and rats through chemicals like DMBA and testing whether treatments reduce tumor incidence and size. DMBA is used to induce skin papillomas in mice and mammary gland carcinomas in rats, with the drug's efficacy measured by decreased tumor rates compared to controls. Various assays then measure cell viability and proliferation after treatment to screen for potential anti-cancer effects.