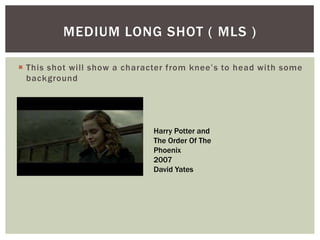
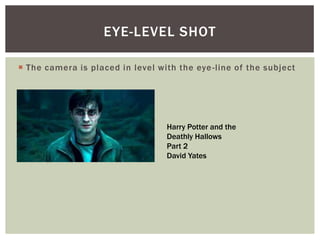
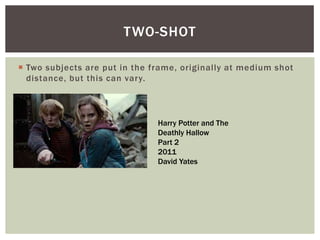
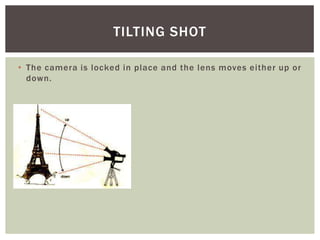
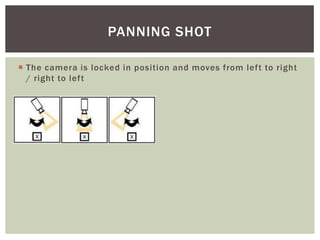
The document defines and provides examples of various camera shots and techniques used in filmmaking. It discusses long shots, establishing shots, wide shots, medium long shots, medium shots, medium close ups, close ups, big close ups, extreme close ups, aerial shots, overhead shots, high-angle shots, eye-level shots, low-angle shots, two-shots, over the shoulder shots, tracking shots, tilting shots, static shots, panning shots, zooms, zoom in/track outs, focus, foreground focus, and deep focus. Examples are provided from various Harry Potter films to illustrate each technique.