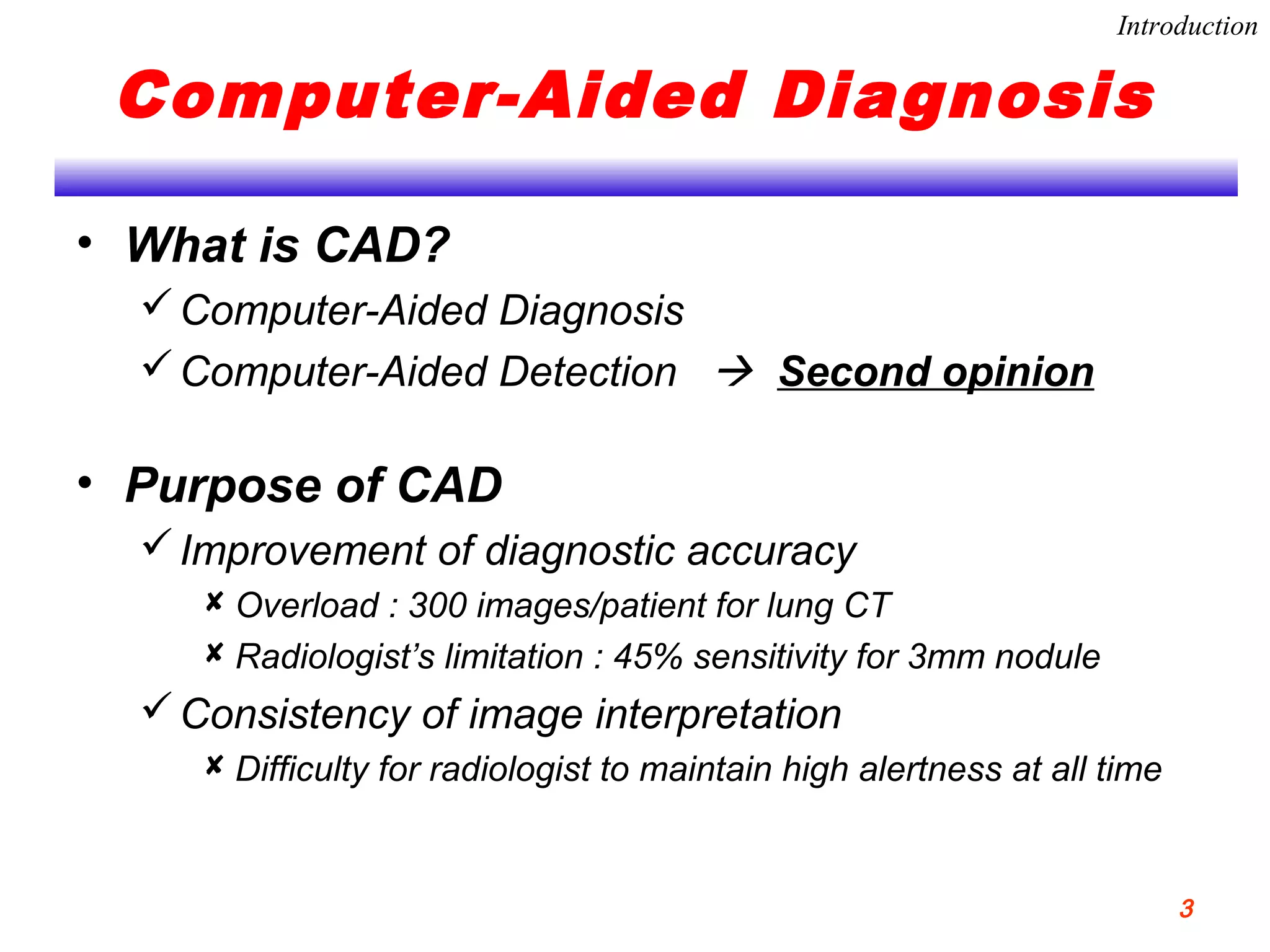
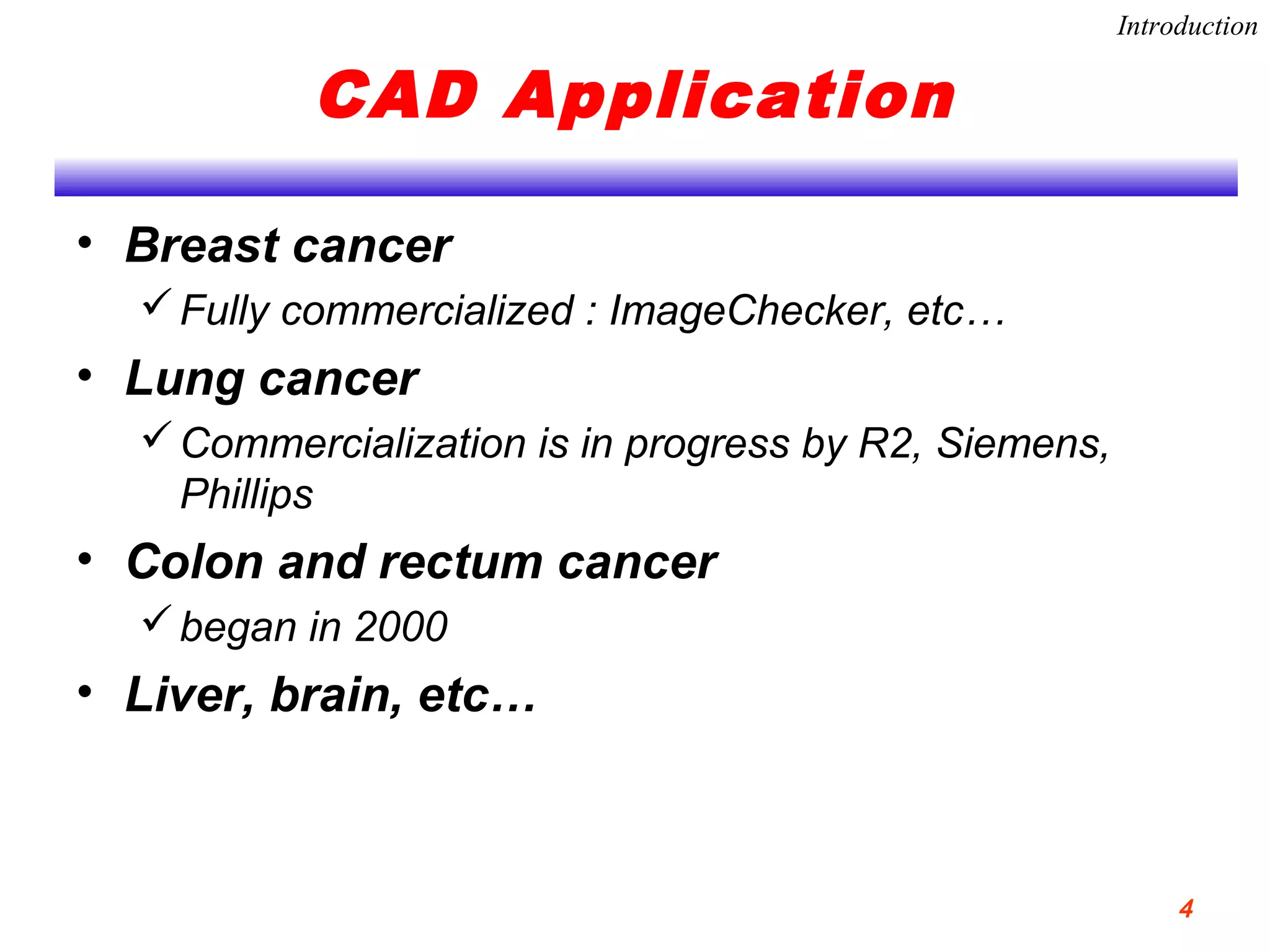
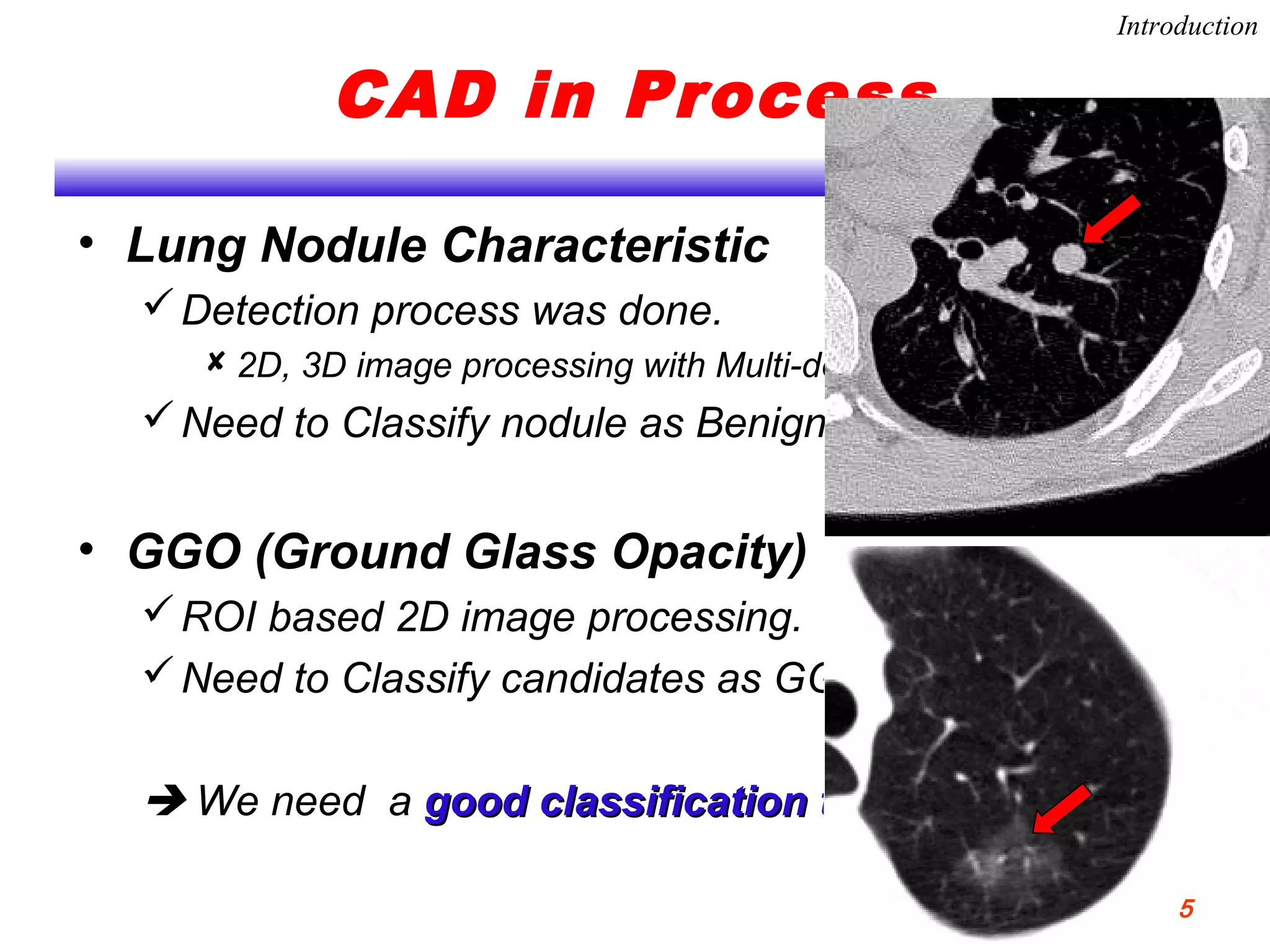
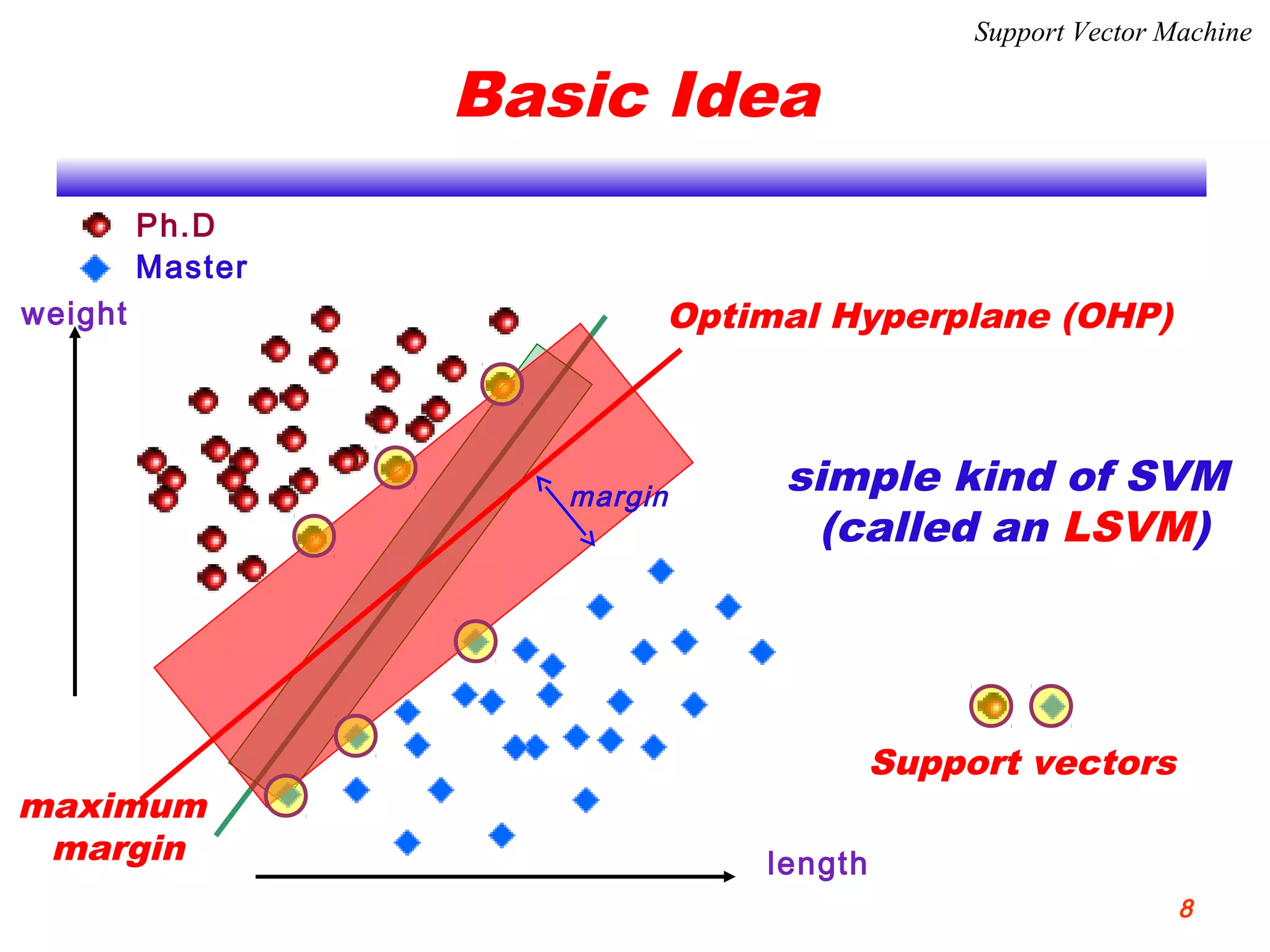
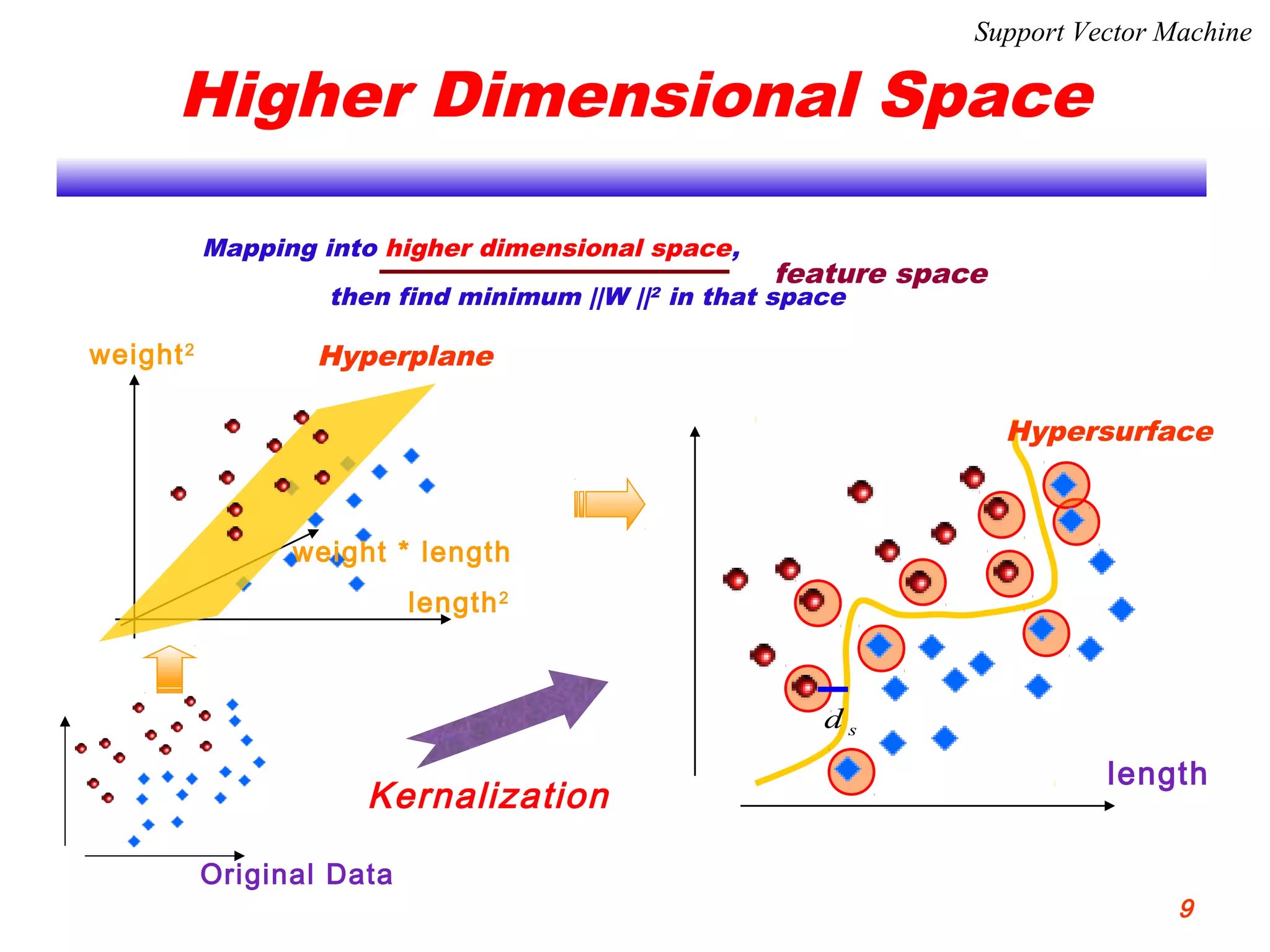
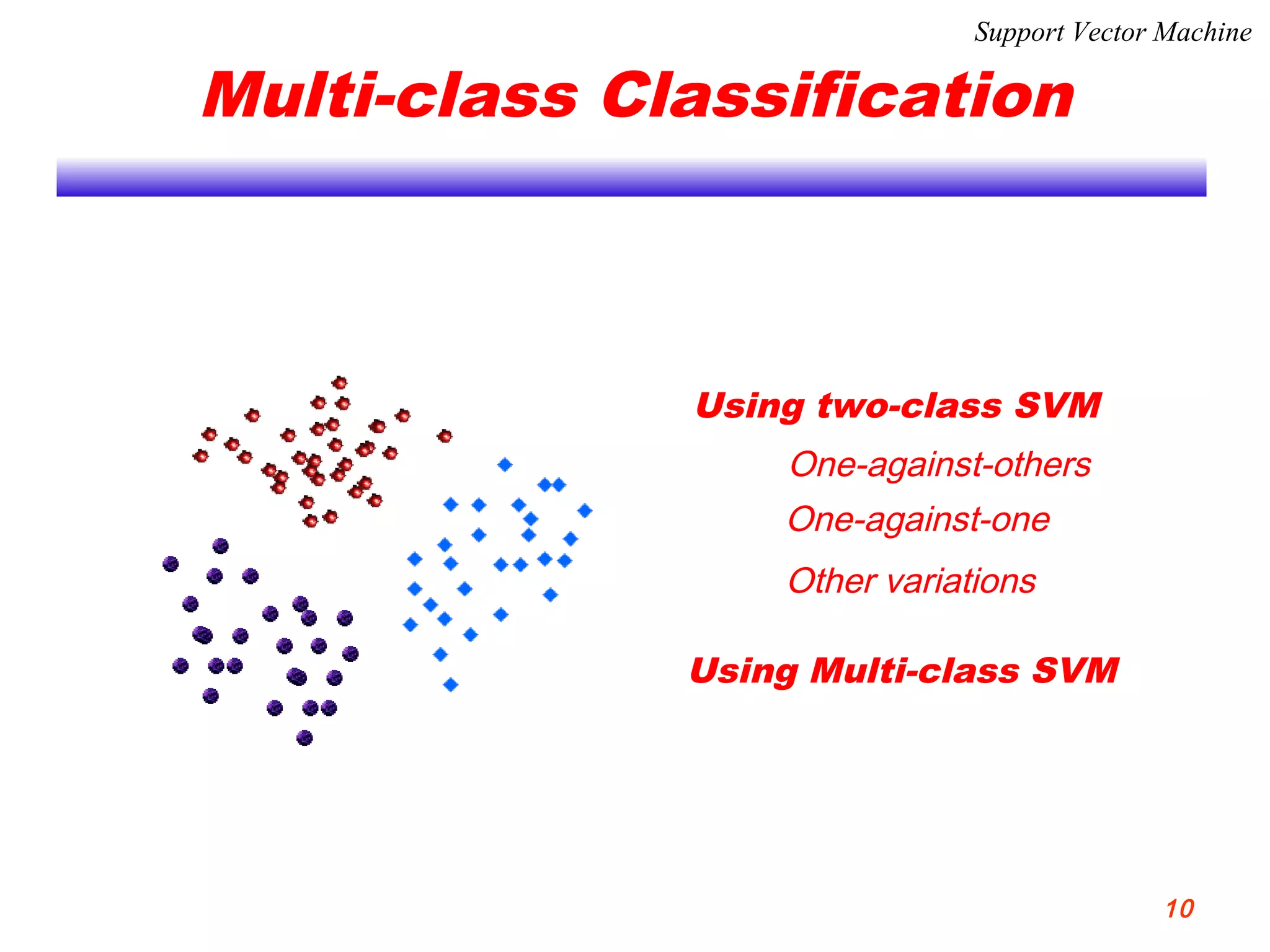
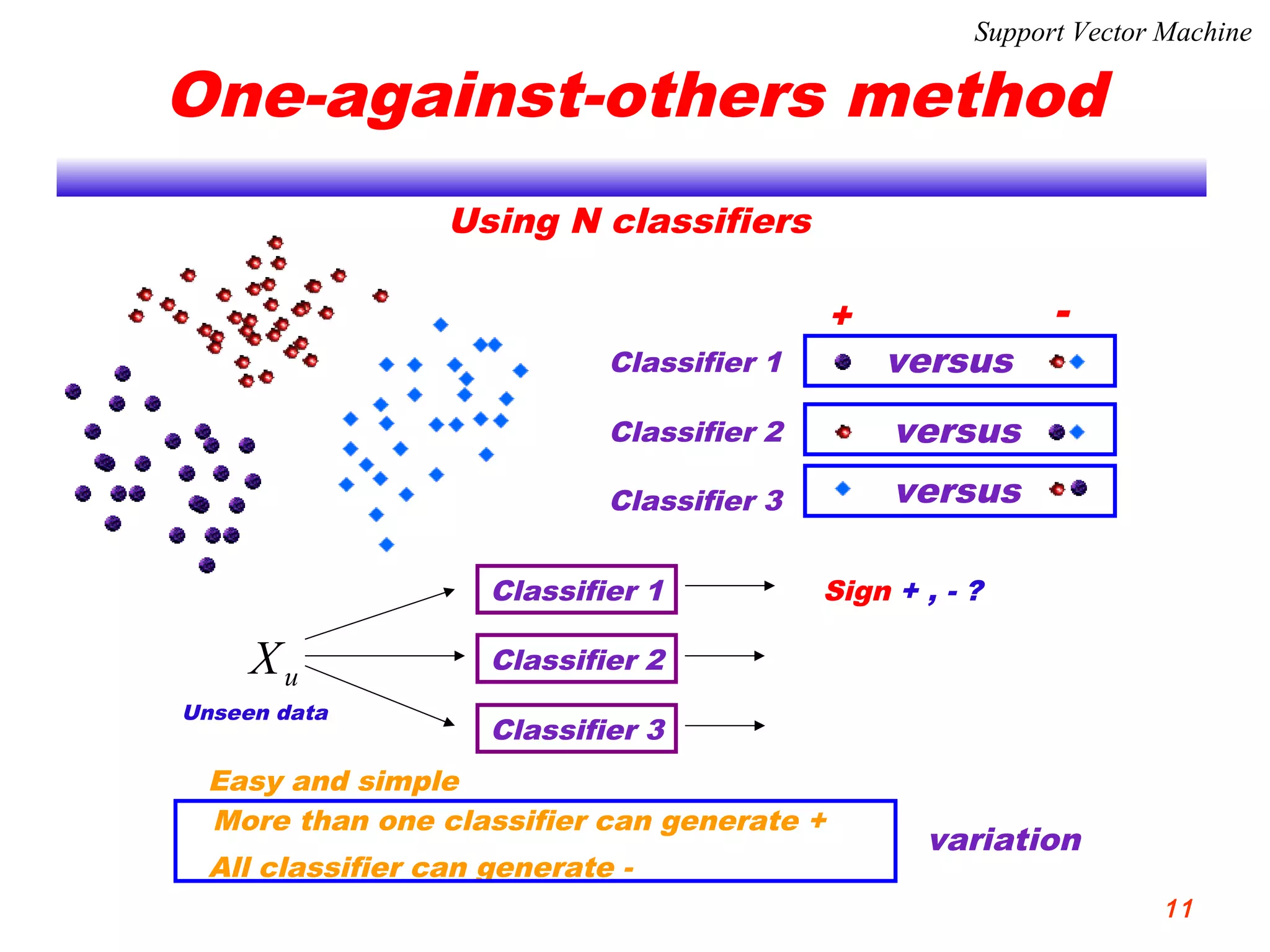
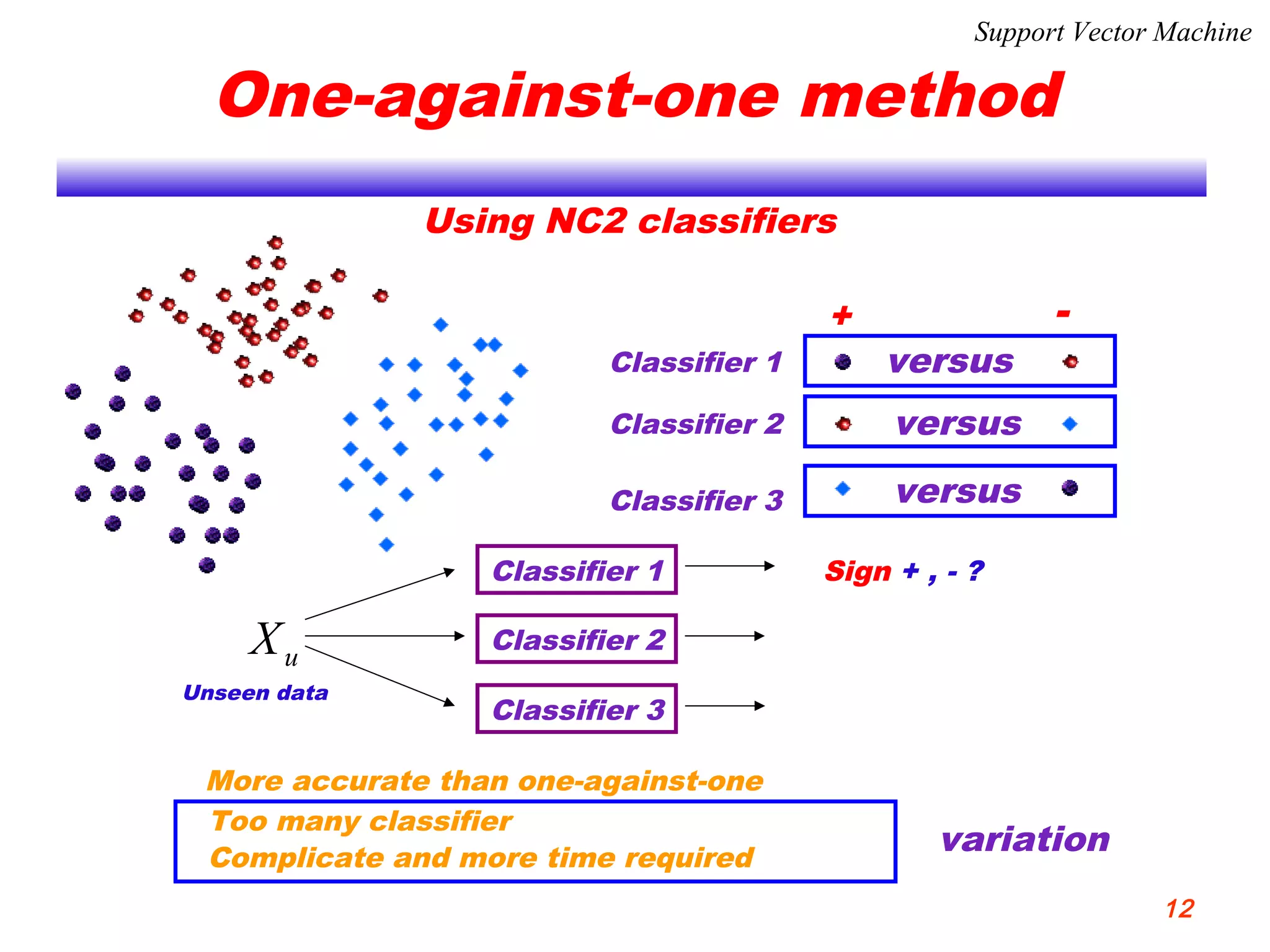
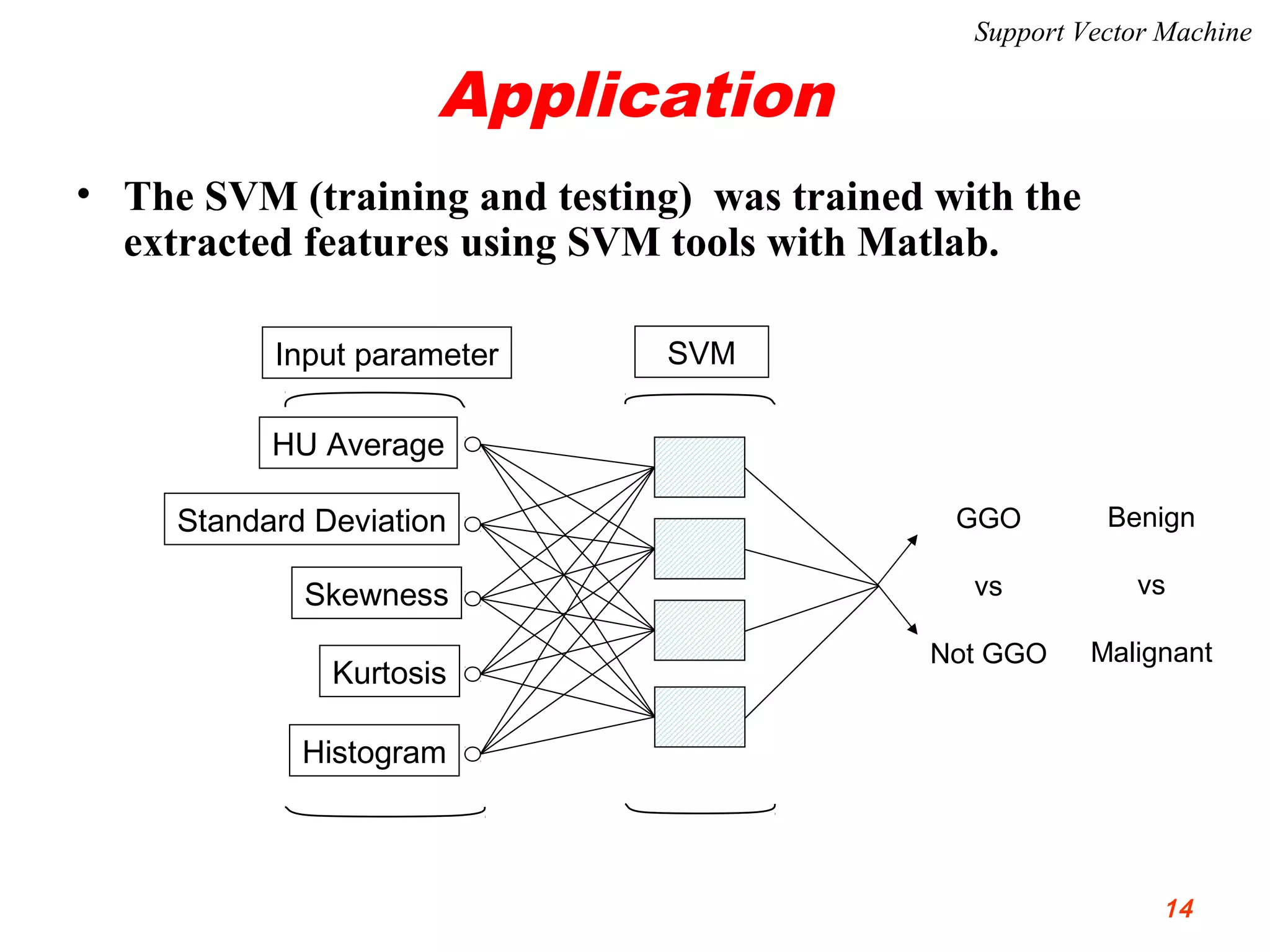
This document discusses using support vector machines for computer-aided diagnosis. It begins with an introduction to computer-aided diagnosis and its purpose of improving diagnostic accuracy for radiologists. It then provides an overview of support vector machines, including their basic ideas, nonlinear separable cases, multi-class classification, and their application in computer-aided diagnosis. Specifically, support vector machines were trained using extracted features from medical images to classify lesions as either benign or malignant, or ground glass opacities versus nodules. The document concludes that support vector machines provide a simple and optimal tool for classification in computer-aided diagnosis systems.