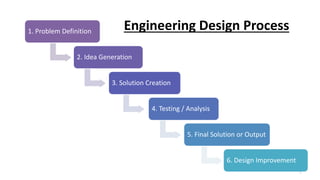
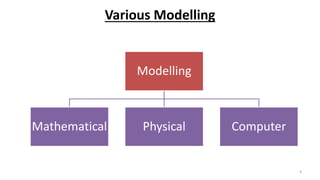
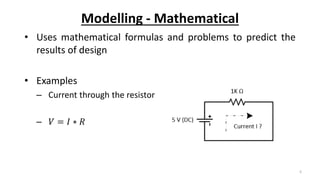
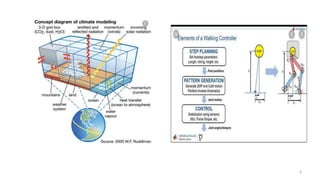
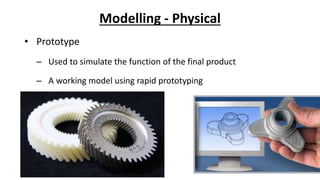
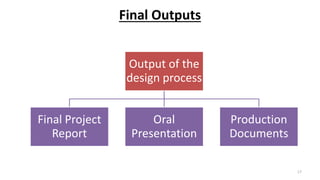
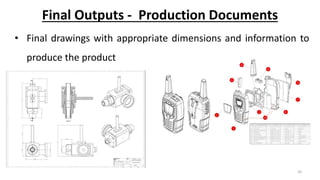
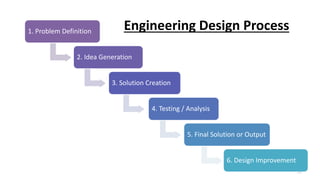
This document outlines the engineering design process, including modelling, testing, and final outputs. It discusses the steps of defining the problem, generating ideas, creating a solution, testing and analysis, and improving the final design. Modelling can be mathematical, physical, or computer-based. Physical modelling includes mock-ups and prototypes. Testing criteria ensure the design functions properly, fits requirements, is aesthetically pleasing, safe, and environmentally sound. Final outputs are a project report, presentation, and production documents. The design process concludes by identifying opportunities to improve the final solution.