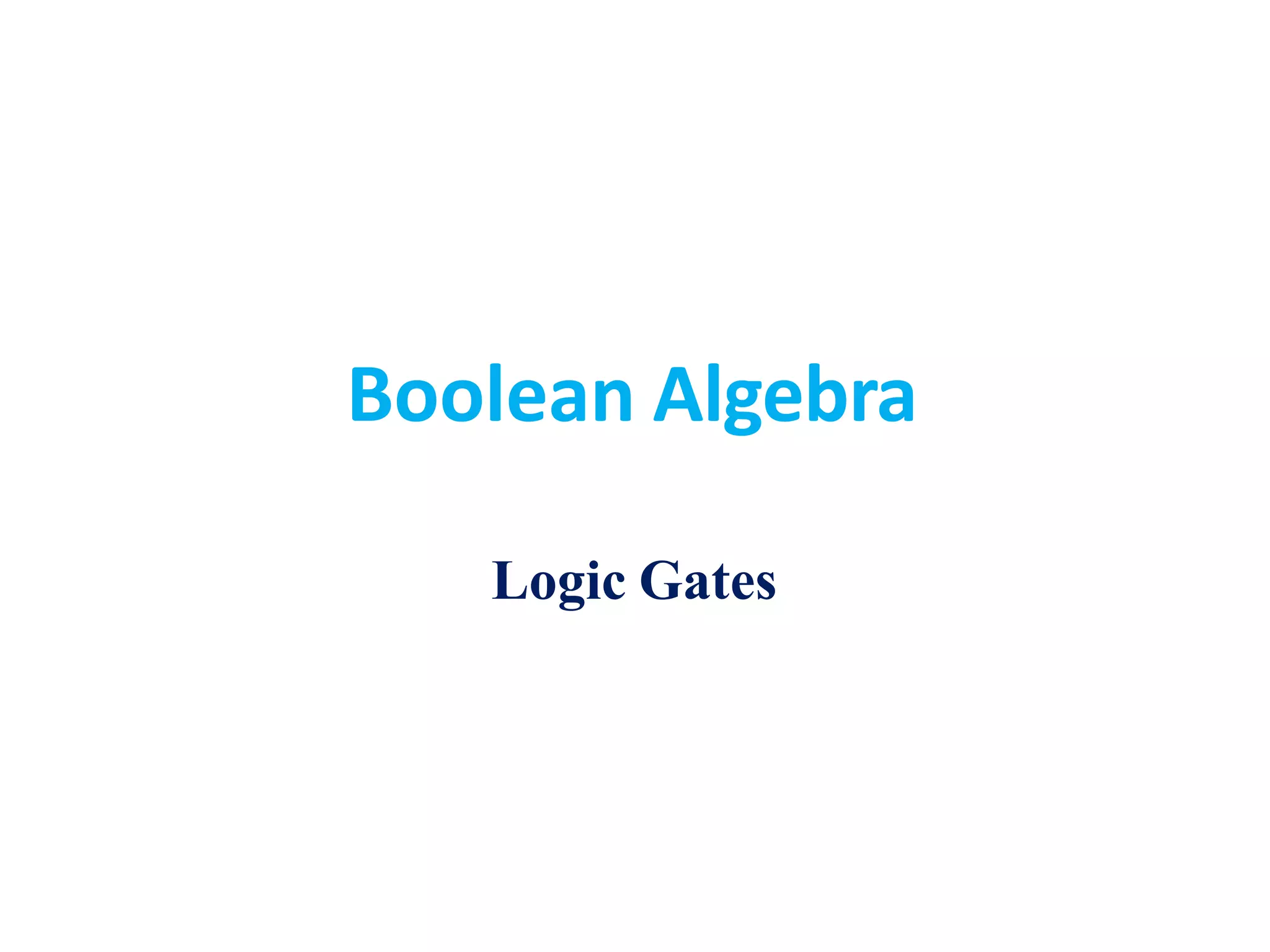
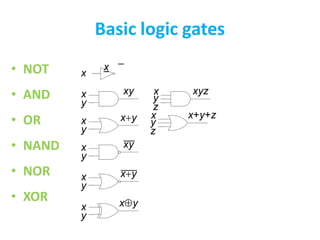
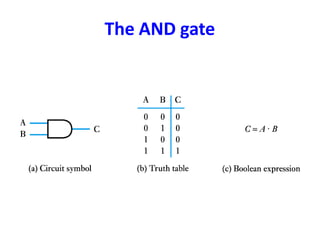
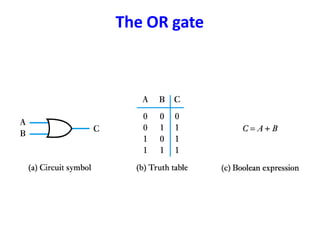
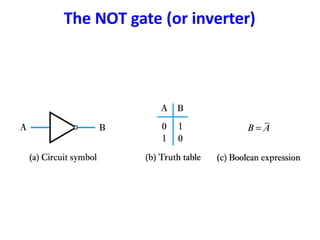
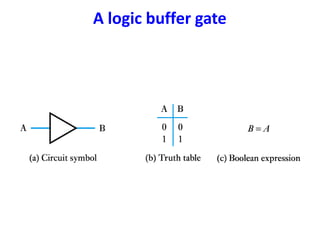
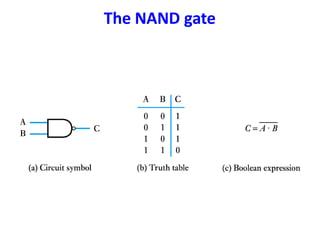
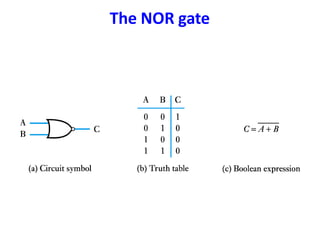
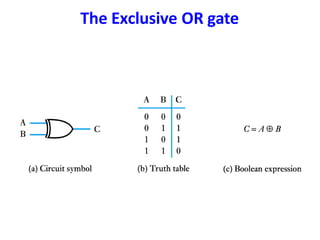
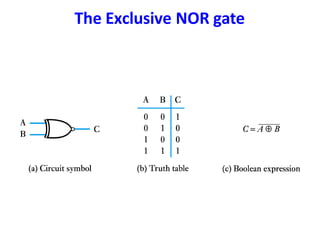
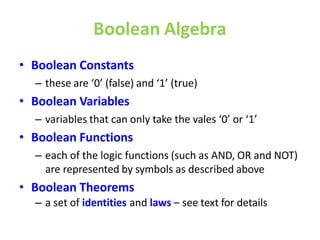
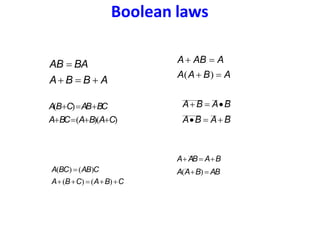
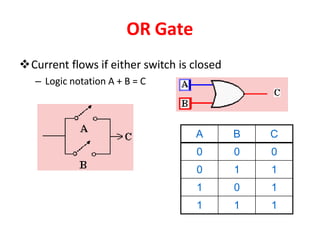
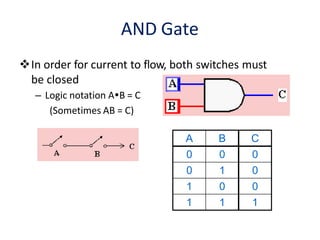
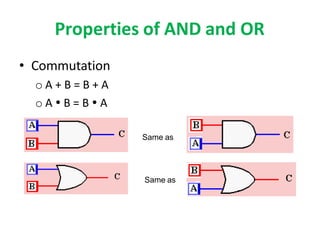
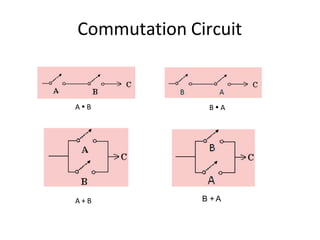
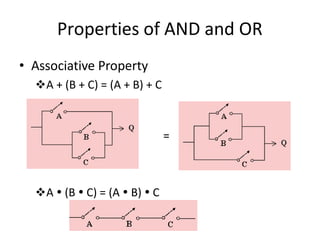
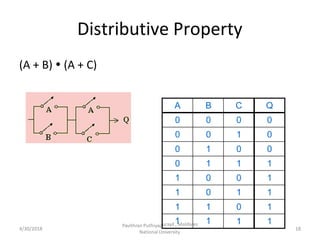
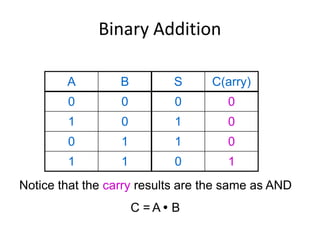
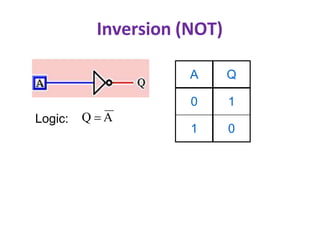
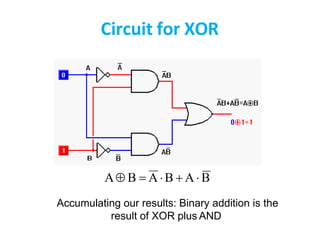
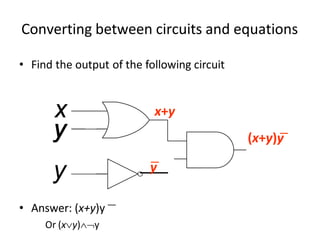
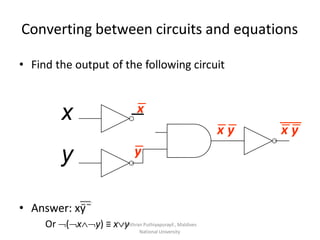
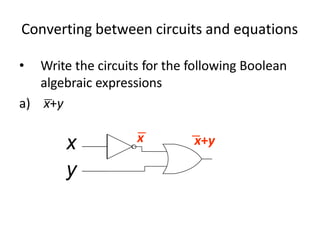
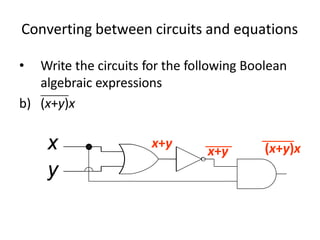
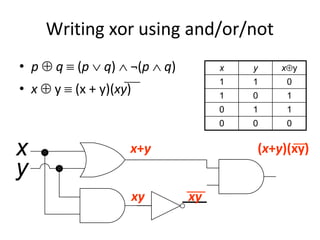
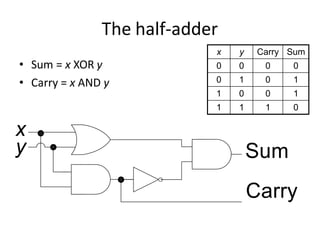
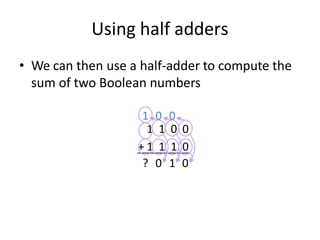
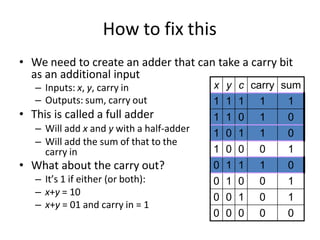
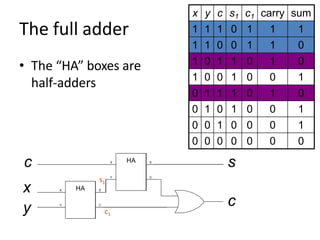
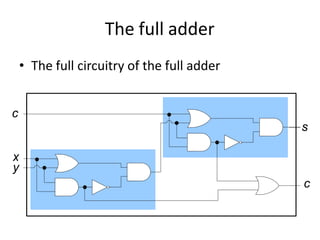
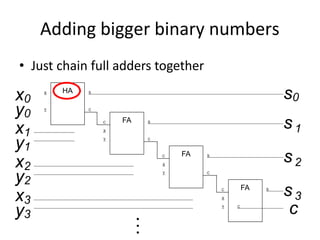
Boolean algebra uses logic gates and binary numbers to represent logical operations in circuits. The basic logic gates are NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. Binary addition can be performed using half adders and full adders built from these basic gates. A half adder adds two bits and outputs their sum and carry, while a full adder also takes a carry in bit to output the final sum and carry out. Larger binary numbers can be added by chaining together full adders.