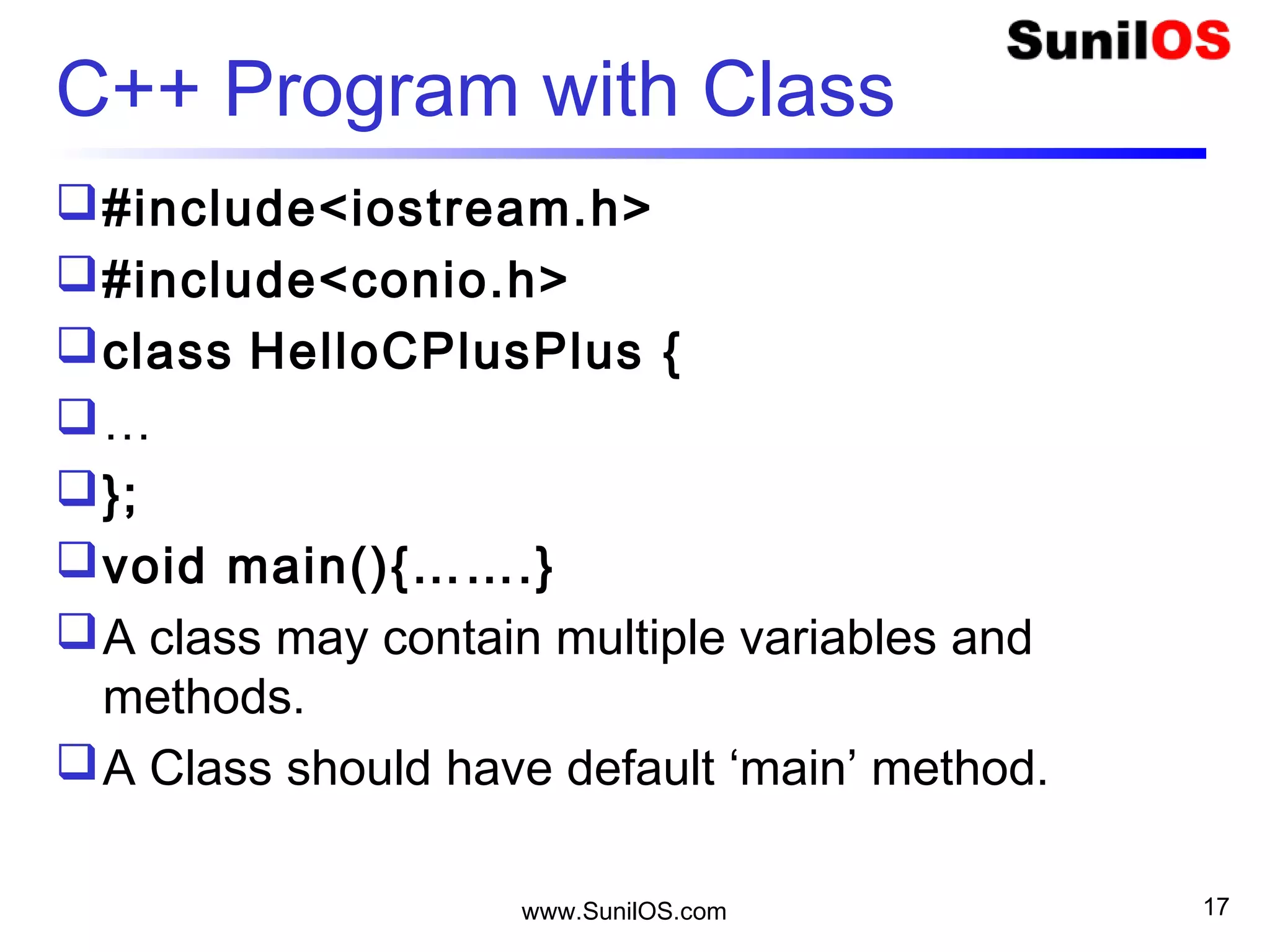
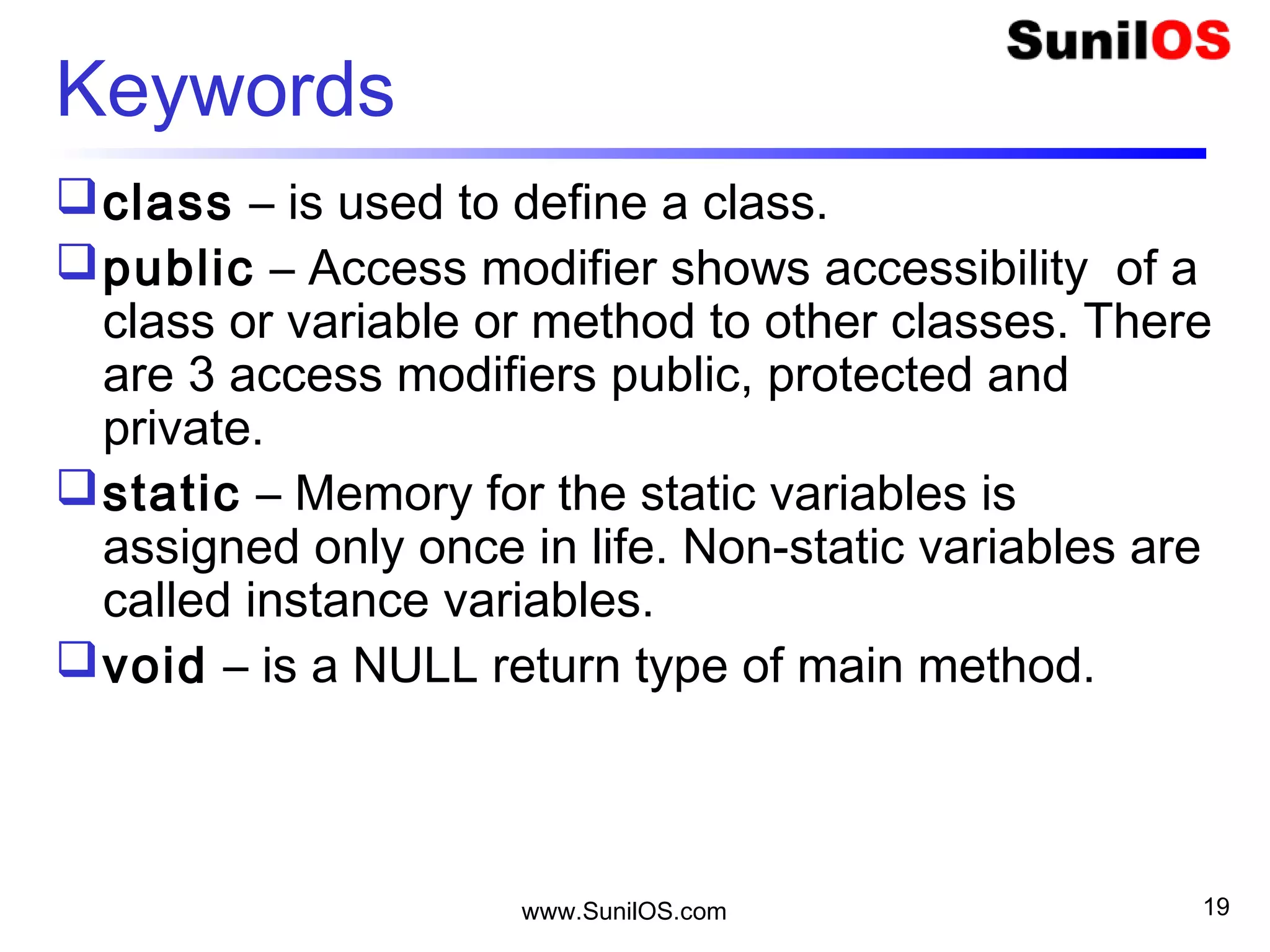
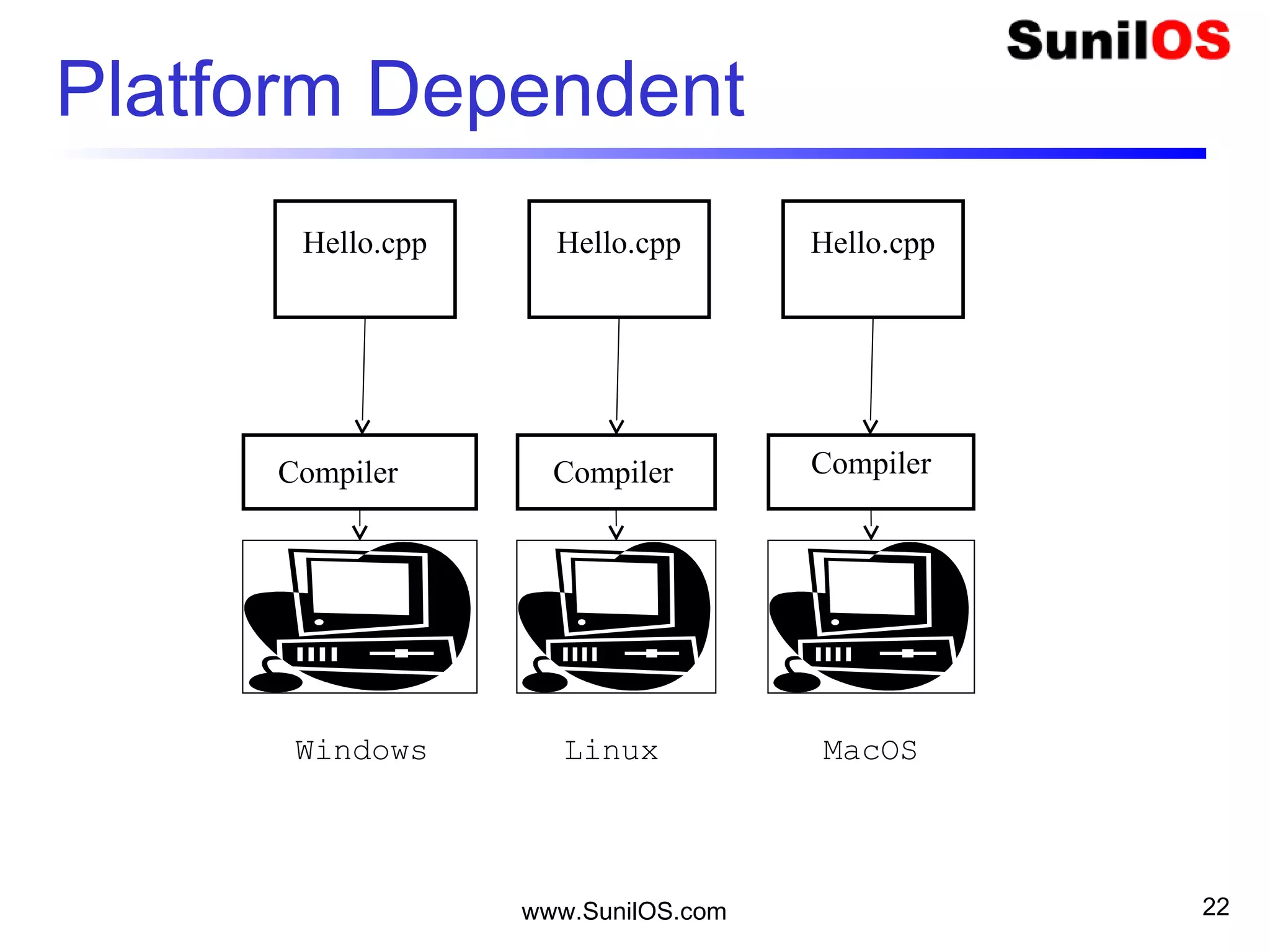
C++ is an object-oriented programming language that is based on classes and objects. A C++ program is made up of classes, which contain methods and variables. The basic building block of a C++ program is the class. A class defines the structure and behavior of an object. Objects are instances of classes that contain their own set of properties and behaviors. The main() method acts as the entry point for program execution. C++ supports features like functions, arrays, control statements, strings and more.



















![www.SunilOS.com 37
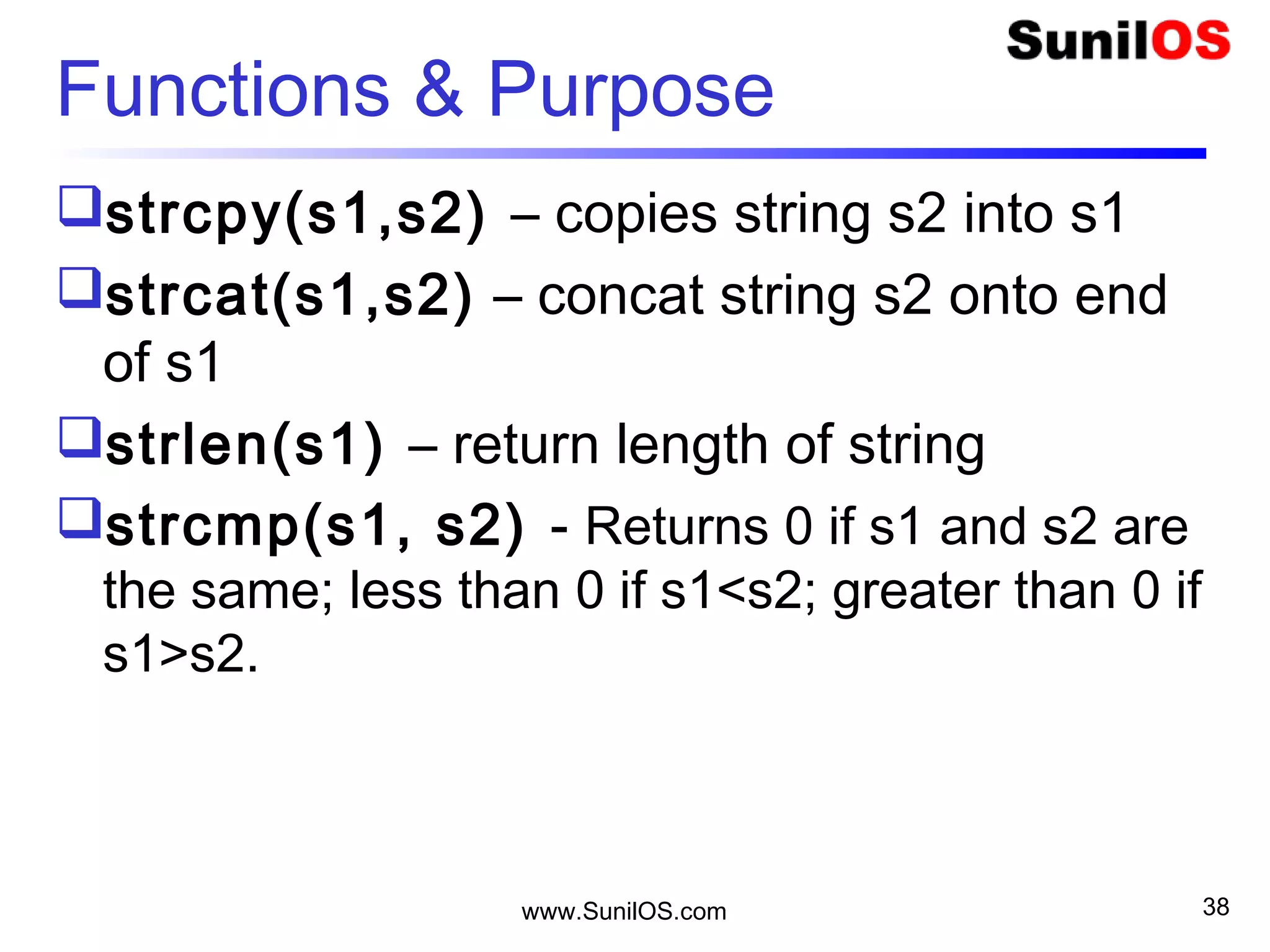
String.h
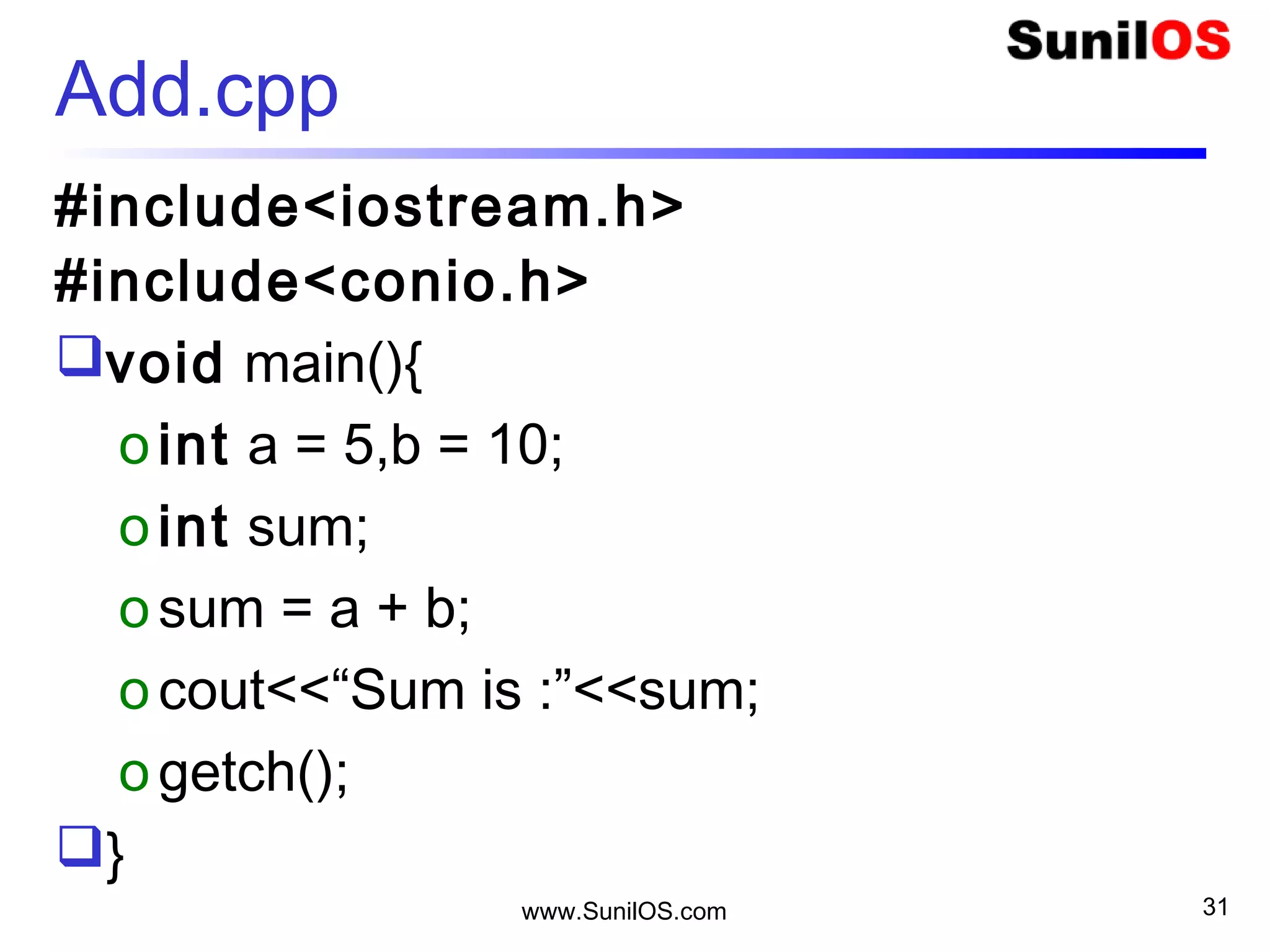
Create a String “Hello”;
char name[6] = { ‘V’ , ’i’ , ’j’ , ’a’ , ’y’ , ’0’ };
char name[6] = “Vijay”;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-37-2048.jpg)

![www.SunilOS.com 40
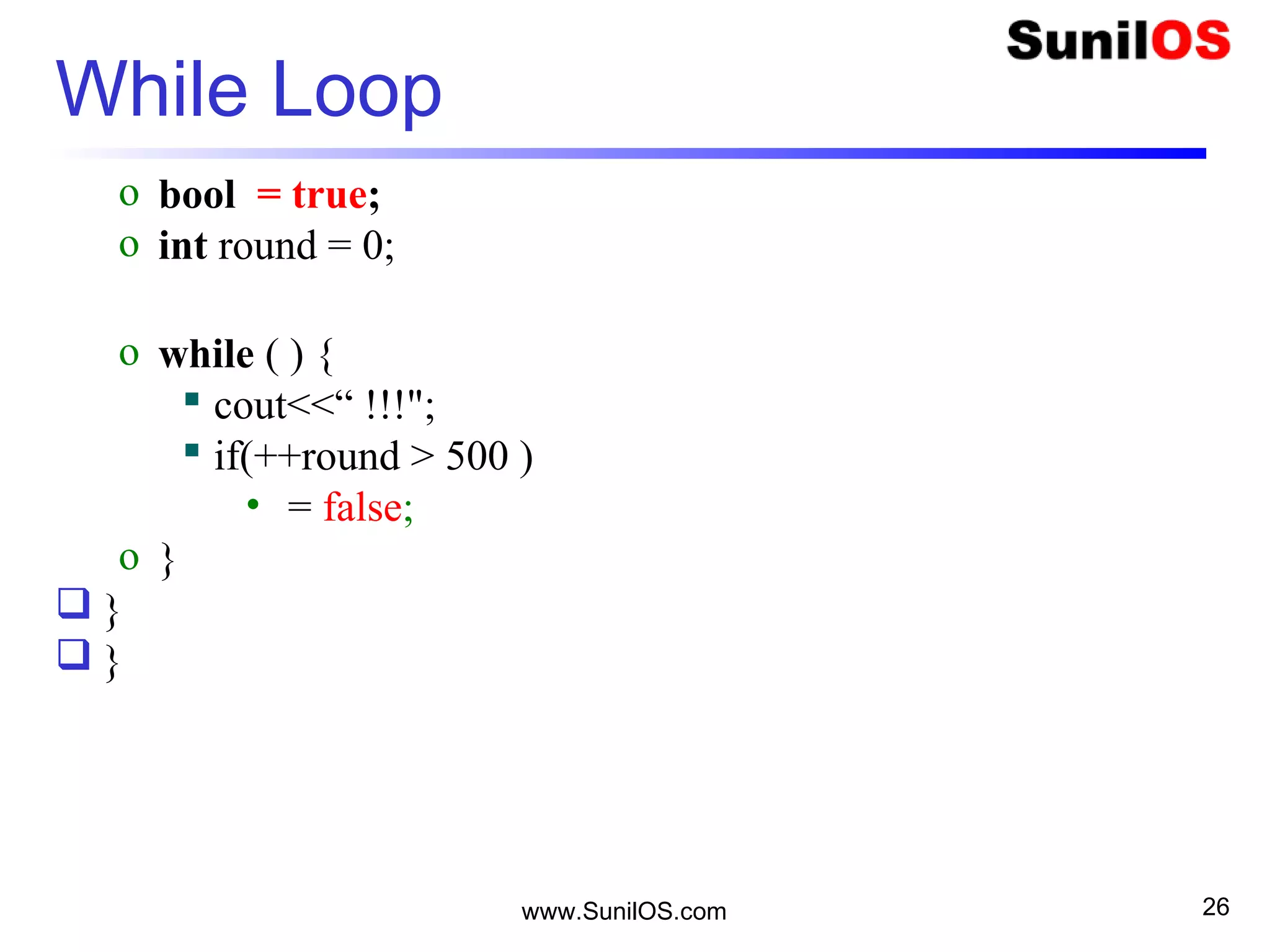
10
One Dimension Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
length
int table[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-40-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 41
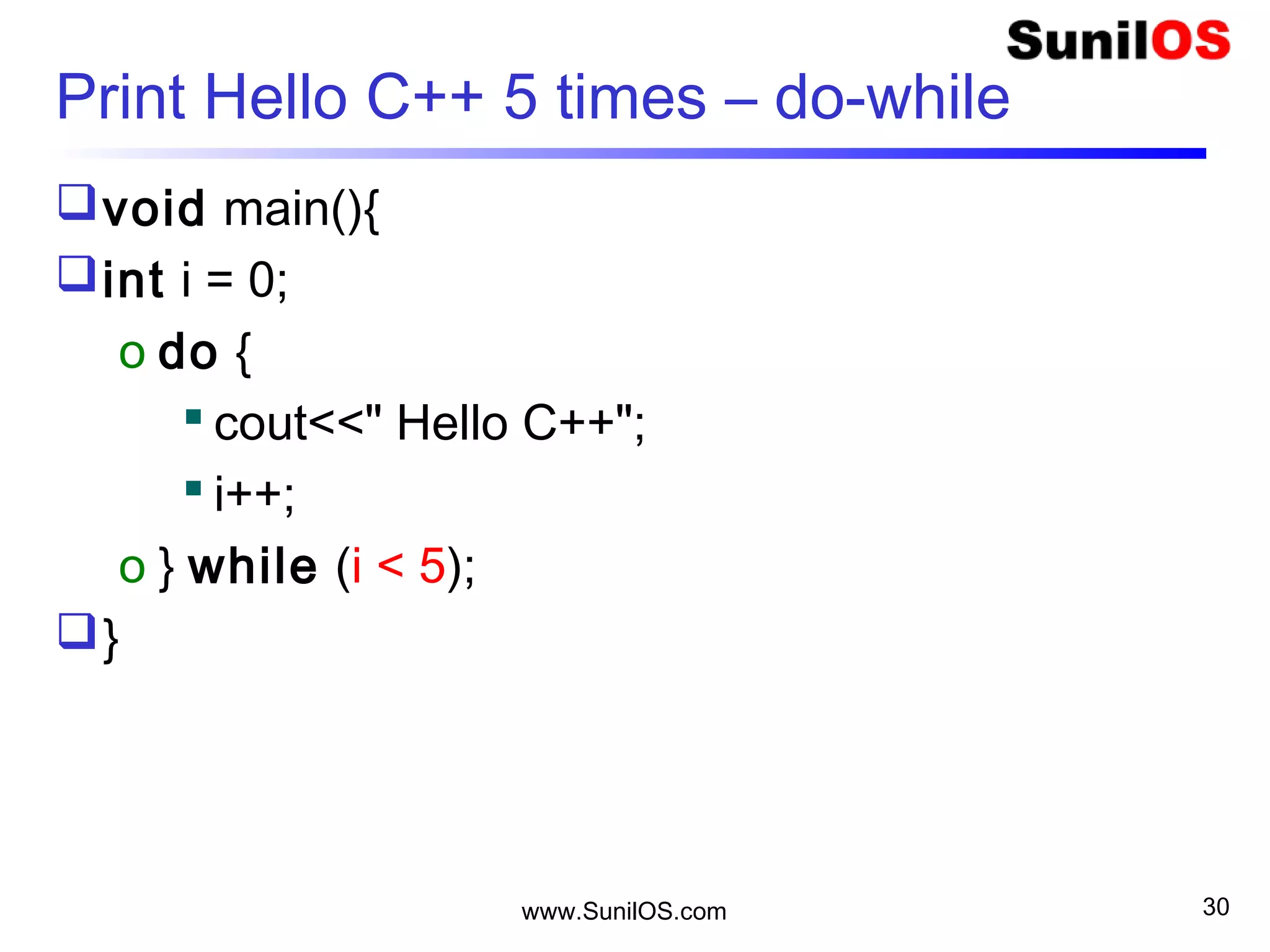
10
Initialize an Array
20
[0]
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
length
int table[10] ;
table[0] =2;
table[1] =4;
….
Or
int table[] =
{2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18,20};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-41-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 42
Other Data Type Arrays
char chList[10] ;
chList[0] = ‘A’….
o Or
char chList[] = {‘A’,’B’,’C’,’D’,’E’}
double douList[10] ;
douList[0] = 2.5….
o Or
double douList [] = {2.5 , 5.6 , 8.6 , 8.2}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-42-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 43
One Dimension Array
int table[10];
table[0] =2;
table[1] =4;
......
table[1] =20;4B
10
[0]
[1]
[9]
length
2
4
20
1000
1000
table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-43-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 44
10length
2D Array
[0]
20
18
..
10
8
6
4
2
[1]
[8]
[9]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[n]
30
27
..
15
12
9
6
3
40
36
..
20
16
12
8
4
90
81
..
45
36
27
18
9
100
90
..
50
40
30
20
10
…
[0] [1] [2] [7] [8]
9
9
..
9
9
9
9
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-44-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 45
int table[5][5];
table
1010
1000
1000
1011
1111
1010
1011
1111](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-45-2048.jpg)
![www.SunilOS.com 46
Define an Array
int table[10][9];
table[1][5] = 5;
Passing function to array
o void functionName(int array_name[5]){
…………
…………
o }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-160530153845/75/C-46-2048.jpg)