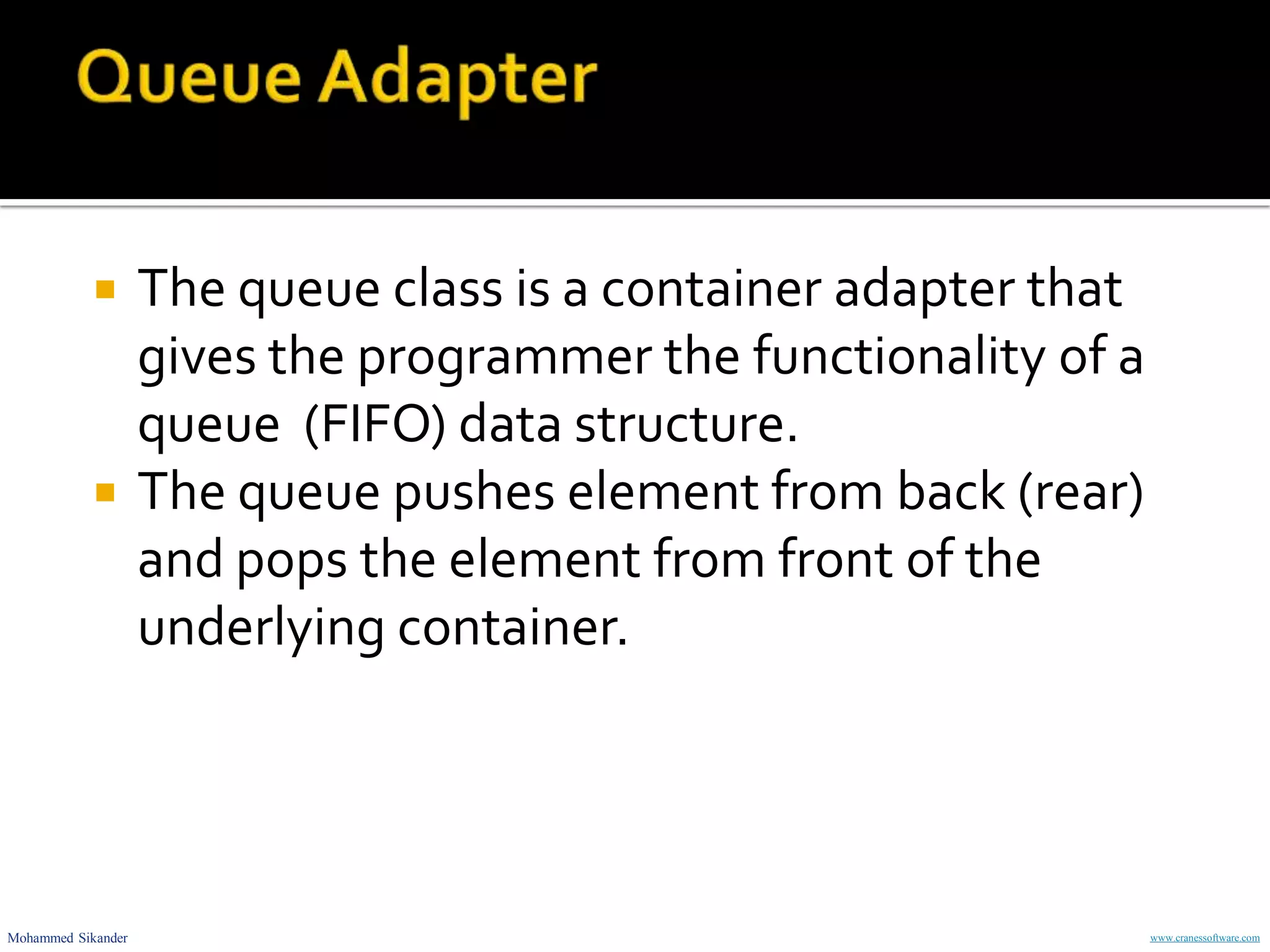
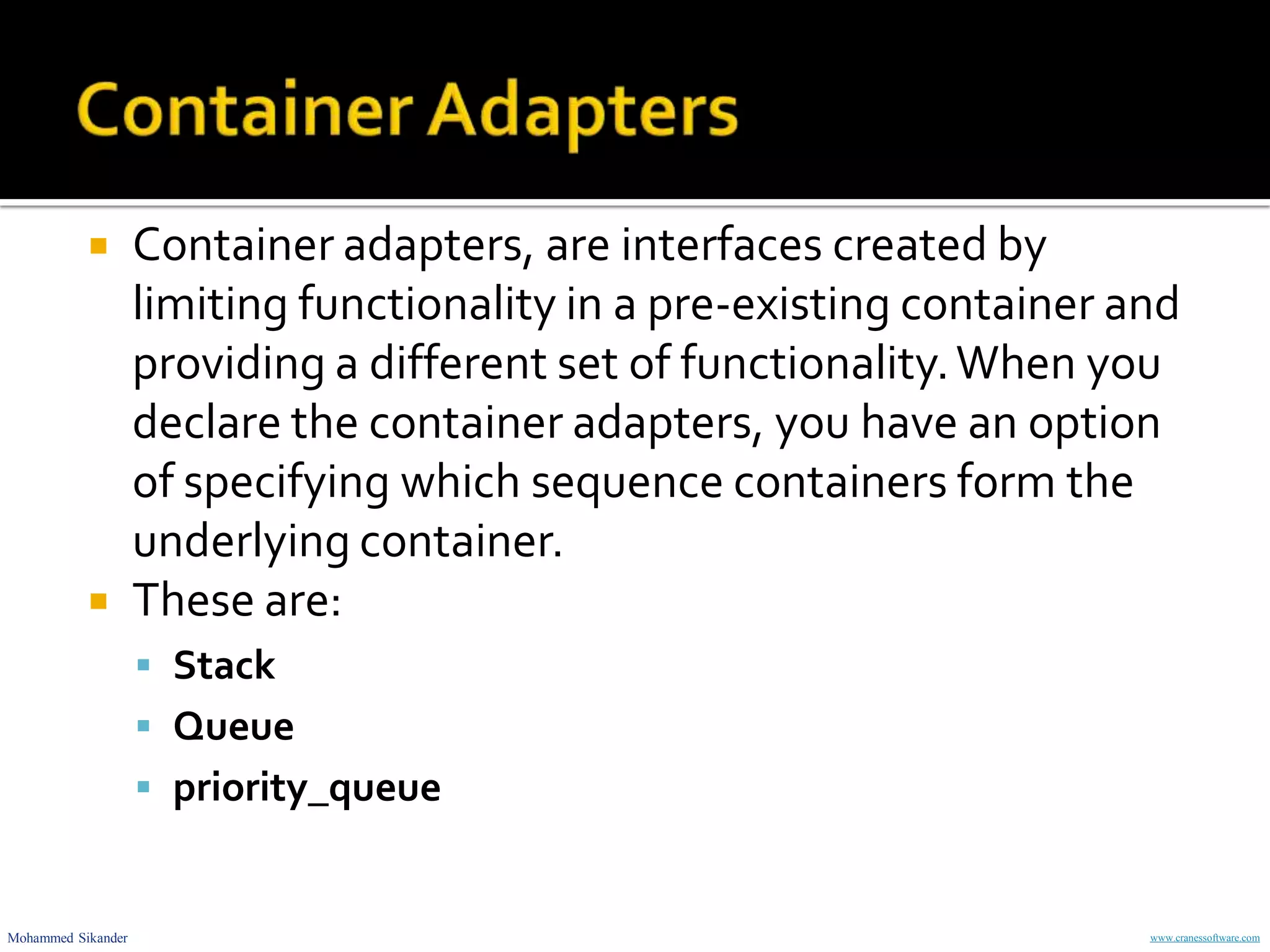
Container adapters like stack, queue and priority_queue provide interfaces to common data structures like LIFO stack, FIFO queue and sorted priority queue. They are implemented using underlying containers like deque, list, vector. The document explains various container adapter classes and their member functions, and provides code examples to demonstrate their use for problems like reversing a string, checking balanced parentheses and merging cookies.




![Mohammed Sikander www.cranessoftware.com
#include <stack>
int main( )
{
string str;
cout << “Enter the string : “;
cin >> str;
stack <char> stk;
for(int i = 0 ; i < str.length() ; i++)
stk.push(str[i]);
cout <<“The reverse string is n”;
while(stk.empty() == false )
{
cout <<stk.top() ;
stk.pop();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/containeradapters-160314052830/75/Container-adapters-6-2048.jpg)
![Mohammed Sikander www.cranessoftware.com
Given a sequence consisting of parentheses, determine whether the
expression is balanced. A sequence of parentheses is balanced if every open
parentheses can be paired uniquely with a closed parentheses that occurs
after the former. Also, the interval between them must be balanced.You will
be given three types of parentheses: (, {, and [.
{[()]}
{[(])}
{{[[(())]]}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/containeradapters-160314052830/75/Container-adapters-7-2048.jpg)
![Mohammed Sikander www.cranessoftware.com
bool checkparenthesis(string s) {
stack <char> stk;
for(int i = 0 ; i < s.length() ; i++) {
if(s[i] == '[' || s[i] == '(' || s[i] == '{')
stk.push(s[i]);
else {
if(stk.empty() == true)
return false;
if(s[i] == ']' && stk.top() == '[‘) {
stk.pop(); continue;
}
else if(s[i] == '}' && stk.top() == '{‘) {
stk.pop(); continue;
}
if(s[i] == ')' && stk.top() == '(‘) {
stk.pop(); continue;
}
return false;
}
}
return stk.empty() ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/containeradapters-160314052830/75/Container-adapters-8-2048.jpg)