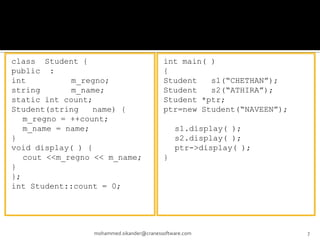
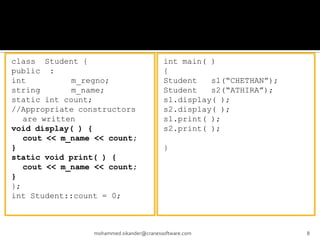
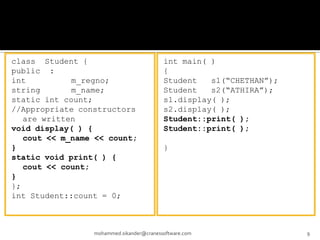
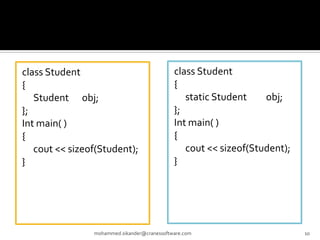
The document discusses C++ concepts like static data members, static member functions, static objects, constant data members, and constant member functions through examples. It includes code snippets demonstrating how to declare and use static data members and static member functions. It also shows examples of constant data members, constant member functions, and constant objects in C++.












![class MyStack
{
public :
int *buffer;
int top;
const int SIZE ;
public :
MyStack(int sz = 5)
{
top = -1;
SIZE = sz;
buffer = new int[sz];
}
};
Sikander 17
int main( )
{
MyStack s1 = MyStack(10);
cout << sizeof(s1);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staticandconstmembers-160224094644/85/Static-and-const-members-17-320.jpg)





