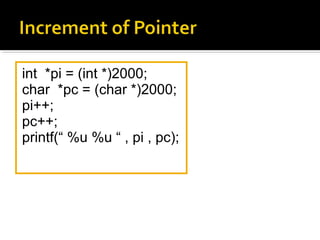
The document contains code snippets demonstrating pointer concepts in C like pointer size, pointer arithmetic, passing pointers to functions, static vs extern variables, multiple definitions, etc. It also contains examples showing memory layout of variables in .o files and executable using nm utility. Conflicts due to multiple definitions and resolving them with static keyword is also demonstrated.





![void update(int *p)
{
p = p + 1;
}
int main( )
{
int arr[ ] = {10 , 12 , 25 , 45};
int *ptr = arr;
update(ptr);
printf(“*ptr = %d “ , *ptr);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-7-320.jpg)
![void update(int *p)
{
*p = *p + 1;
}
int main( )
{
int arr[ ] = {10 , 12 , 25 , 45};
int *ptr = arr;
update(ptr);
printf(“*ptr = %d “ , *ptr);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-8-320.jpg)

![void update(char *str)
{
str[0] = ‘H’;
}
int main( )
{
char name[ ] = “Nimisha”;
char *ptr = name;
update(ptr);
printf(“ %s n” , name);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-10-320.jpg)
![void update(char *str)
{
*++str = ‘a’;
}
int main( )
{
char name[ ] = “Nimisha”;
char *ptr = name;
update(ptr);
printf(“ %s n” , name);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-11-320.jpg)
![int main( )
{
char names[]
[10]={“OBAMA”,”PUTIN”,”MODI”,”CAMEROON”};
printf(“ %__ “ , *(names + 2) + 3);
printf(“ %__ “ , **(names + 2) + 3);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-12-320.jpg)
![int main( )
{
char names[][10]={“OBAMA”,”PUTIN”,”MODI”,”CAMEROON”};
1. printf(“ %s “ , *(++names));
2. printf(“ %s “ , ++*(names));
3. printf(“ %c “ , ++**(names));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-13-320.jpg)
![int main( )
{
char *names[10]={“OBAMA”,”PUTIN”,”MODI”,”CAMEROON”};
1. printf(“ %s “ , *(++names));
2. printf(“ %s “ , ++*(names));
3. printf(“ %c “ , ++**(names));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-14-320.jpg)
![struct Student
{
int id;
char name[20];
};
int main( )
{
struct Student s1 = {1 , “Ayushi”};
struct Student s2 = {2 , “Ayushi”};
if(s1.name == s2.name)
printf(“Equal”);
else
printf(“Not Equal”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-15-320.jpg)
![char *names[ ] = {“Nimisha”,”Devender”,”Vikram”,”Balwant”};
printf(“ %d “ , sizeof(names));
printf(“ %d “ , sizeof(names[0]));
char names[ ][10] = {“Nimisha”,”Devender”,”Vikram”,”Balwant”};
printf(“ %d “ , sizeof(names));
printf(“ %d “ , sizeof(names[0]));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-16-320.jpg)
![void display( char *names[ ])
{
printf(“Display : %d n “ , sizeof(names));
}
int main( )
{
char *names[ ] = {“Nimisha”,”Devender”,”Vikram”,”Balwant”};
printf(“Main : %d n“ , sizeof(names));
display( names );
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-17-320.jpg)




![[sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc -c f1.c
[sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc -c f2.c
[sikander@localhost ~]$ nm f1.o
U func
00000000 T main
U printf
00000004 C x
[sikander@localhost ~]$ nm f2.o
00000000 T func
00000004 C x
[sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc f1.o f2.o
[sikander@localhost ~]$ nm a.out
080495ac B x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-22-320.jpg)

![ [sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc -c f1.c
[sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc -c f2.c
[sikander@localhost ~]$ nm f1.o
00000000 D x
[sikander@localhost ~]$ nm f2.o
00000000 D x
[sikander@localhost ~]$ gcc f1.o f2.o
f2.o(.data+0x0): multiple definition of `x'
f1.o(.data+0x0): first defined here
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-24-320.jpg)




![const int x = 10; //Read Only
int main( )
{
const int y = 5; //Stack
printf(“Enter the value for local const variable : “);
scanf(“ %d”,&y);
printf(“Local Const = %d n” , y);
printf(“Enter the value for global const variable : “);
scanf(“ %d”,&x);
printf(“Global Const = %d n”,x);
}
[sikander@localhost ~]$ ./a.out
Enter the value for local const variable : 89
Local Const = 89
Enter the value for global const variable : 6
Segmentation fault](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-29-320.jpg)
![ [sikander@localhost ~]$ nm f1.o
00000000 t display
0000000a T main
00000005 T print
static void display()
{
}
void print()
{
}
int main( )
{
display( );
print( );
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cquestions-160316121757/85/C-questions-30-320.jpg)