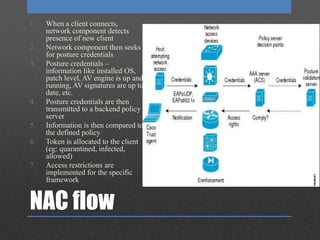
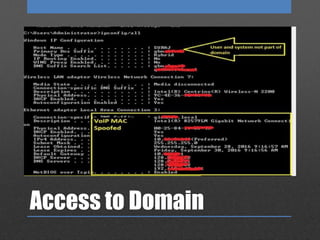
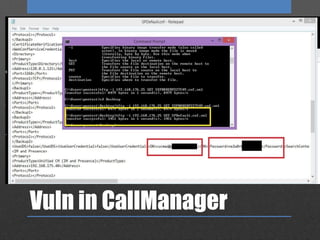
The document discusses Network Access Control (NAC), which is designed to prevent unauthorized access to internal networks by assessing devices' identity and security posture. It identifies two NAC bypass techniques, including exploiting vulnerabilities in non-authentication capable devices like VoIP phones, and suggests mitigations such as restricting access to network configurations and implementing firewalls between VLANs. Overall, it highlights critical security concerns and responses in managing network access.