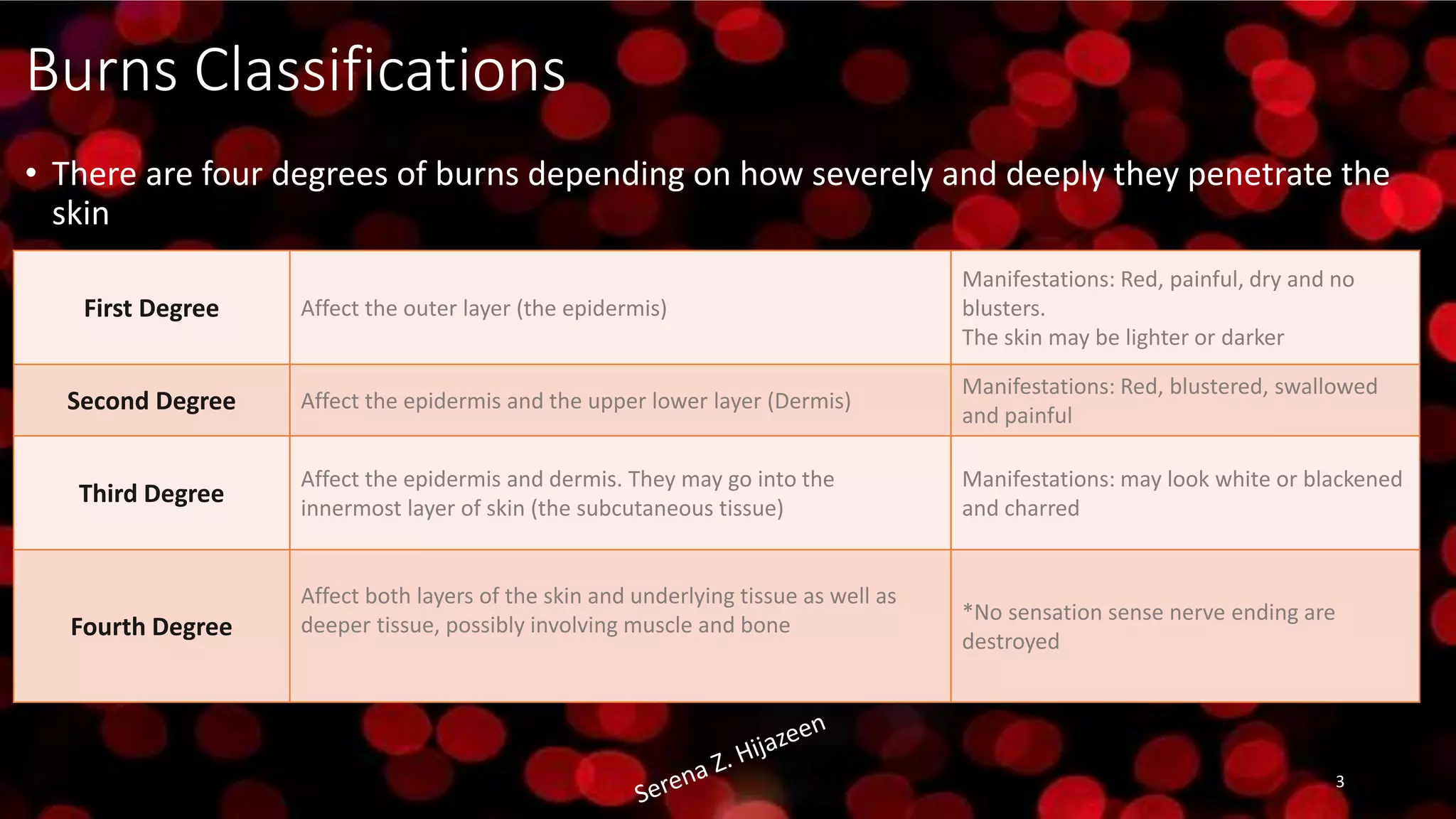
The document outlines various types and classifications of burns, including heat-related and chemical burns, alongside their degrees (first to fourth). It details home treatment options for first- and second-degree burns, as well as the imperative actions to take for more severe third- and fourth-degree burns, emphasizing the importance of avoiding harmful remedies like butter and ice. Additionally, it discusses potential complications from burns and highlights pharmaceutical products suitable for first aid.