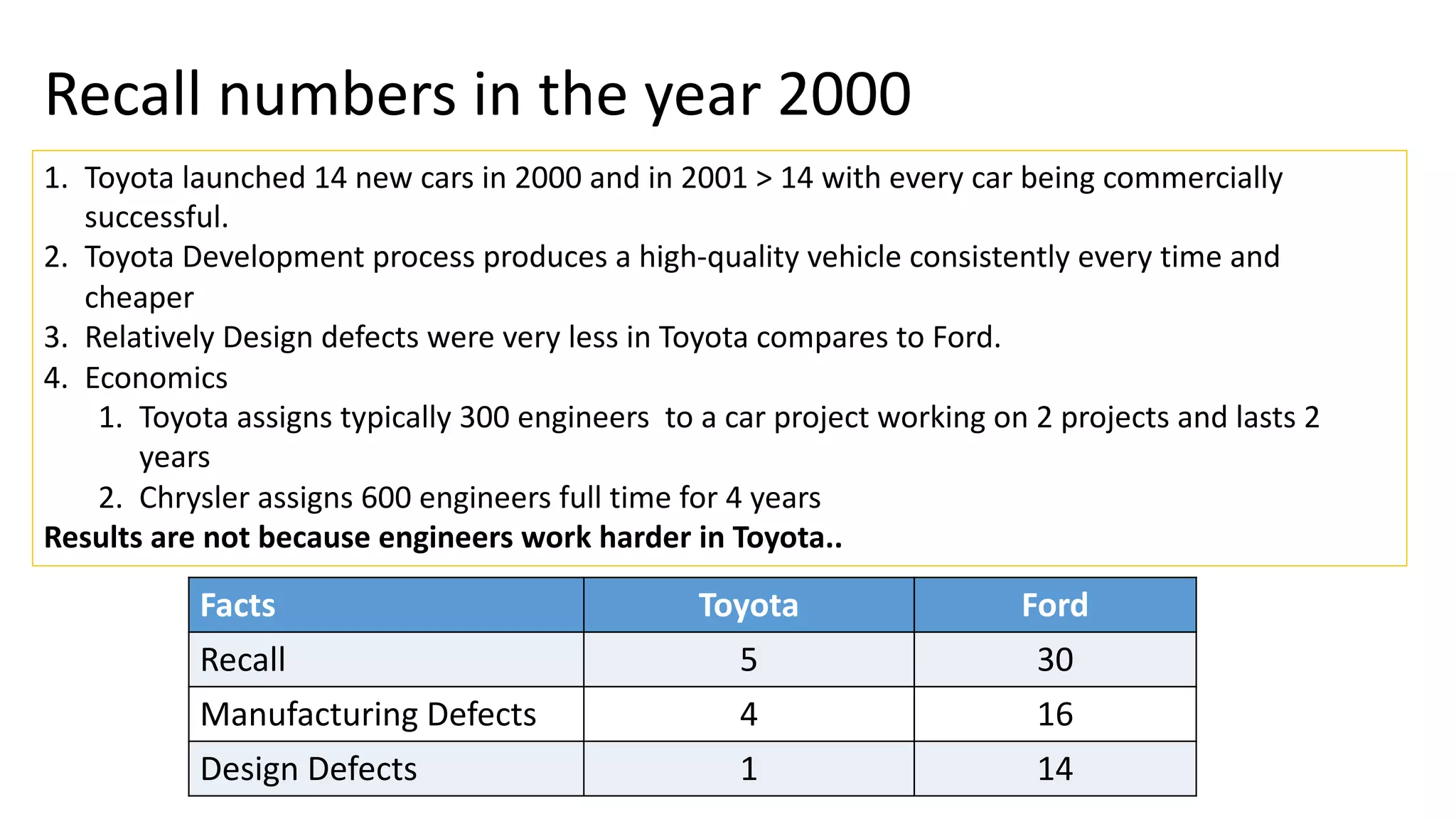
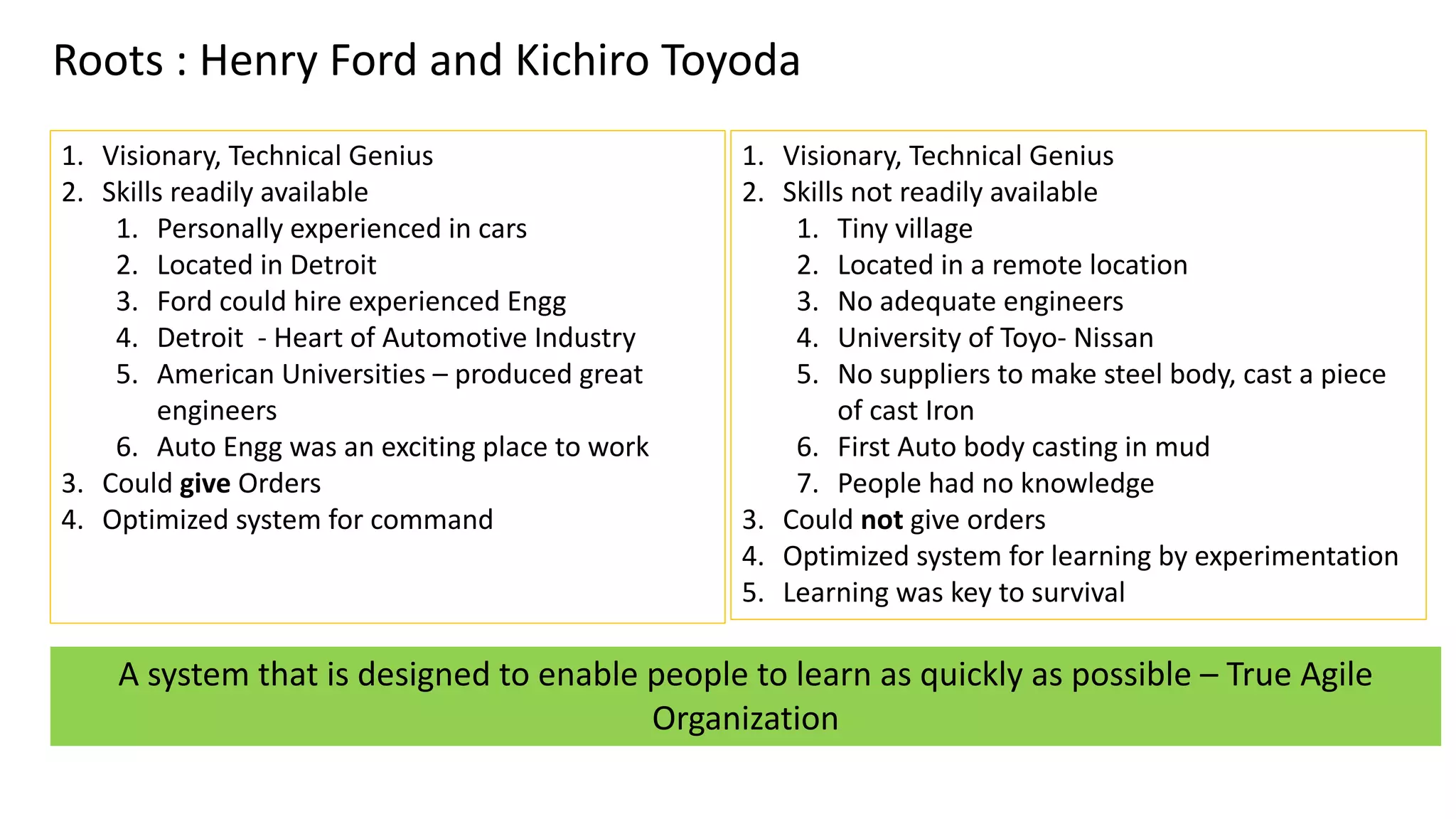
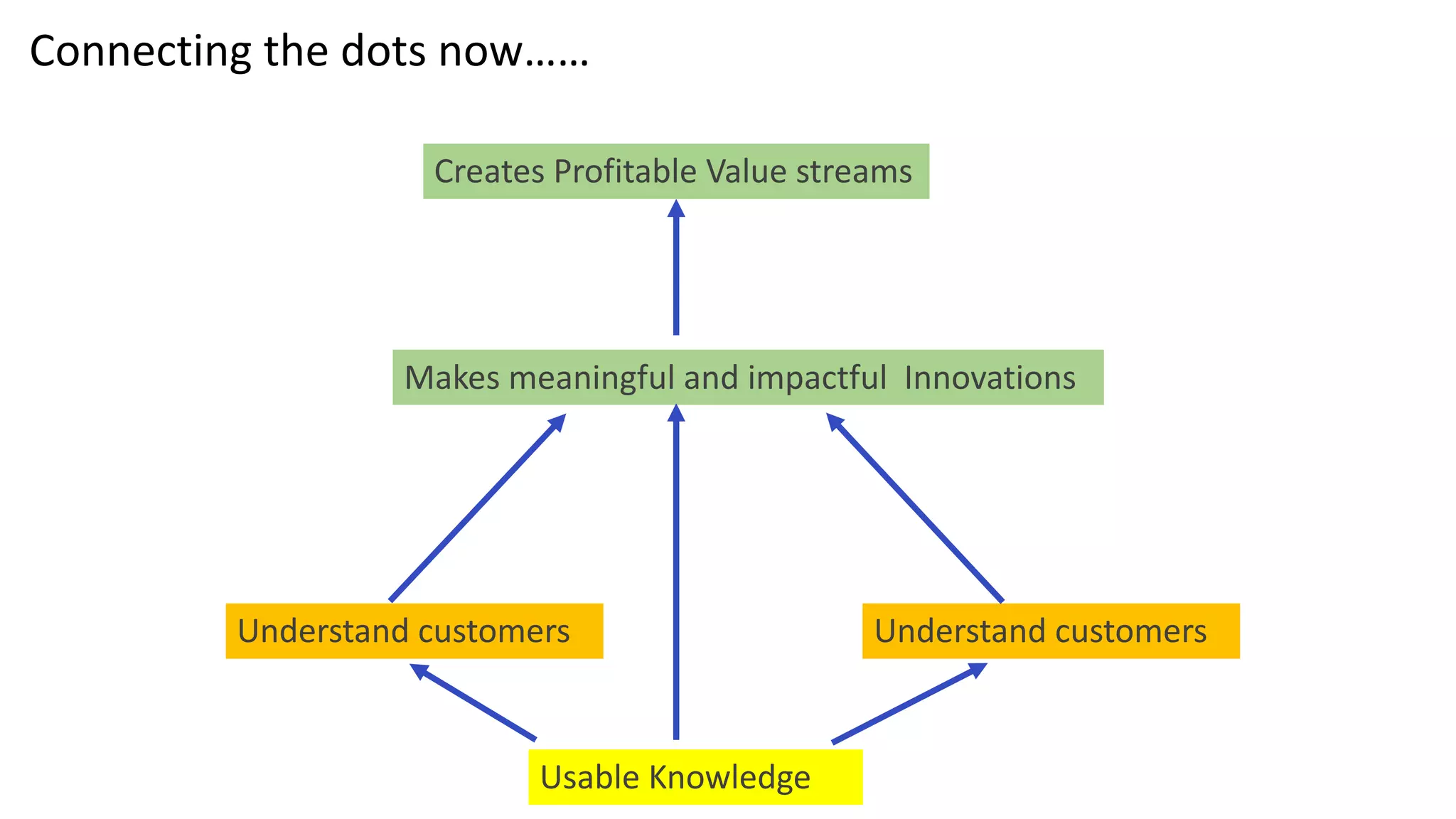
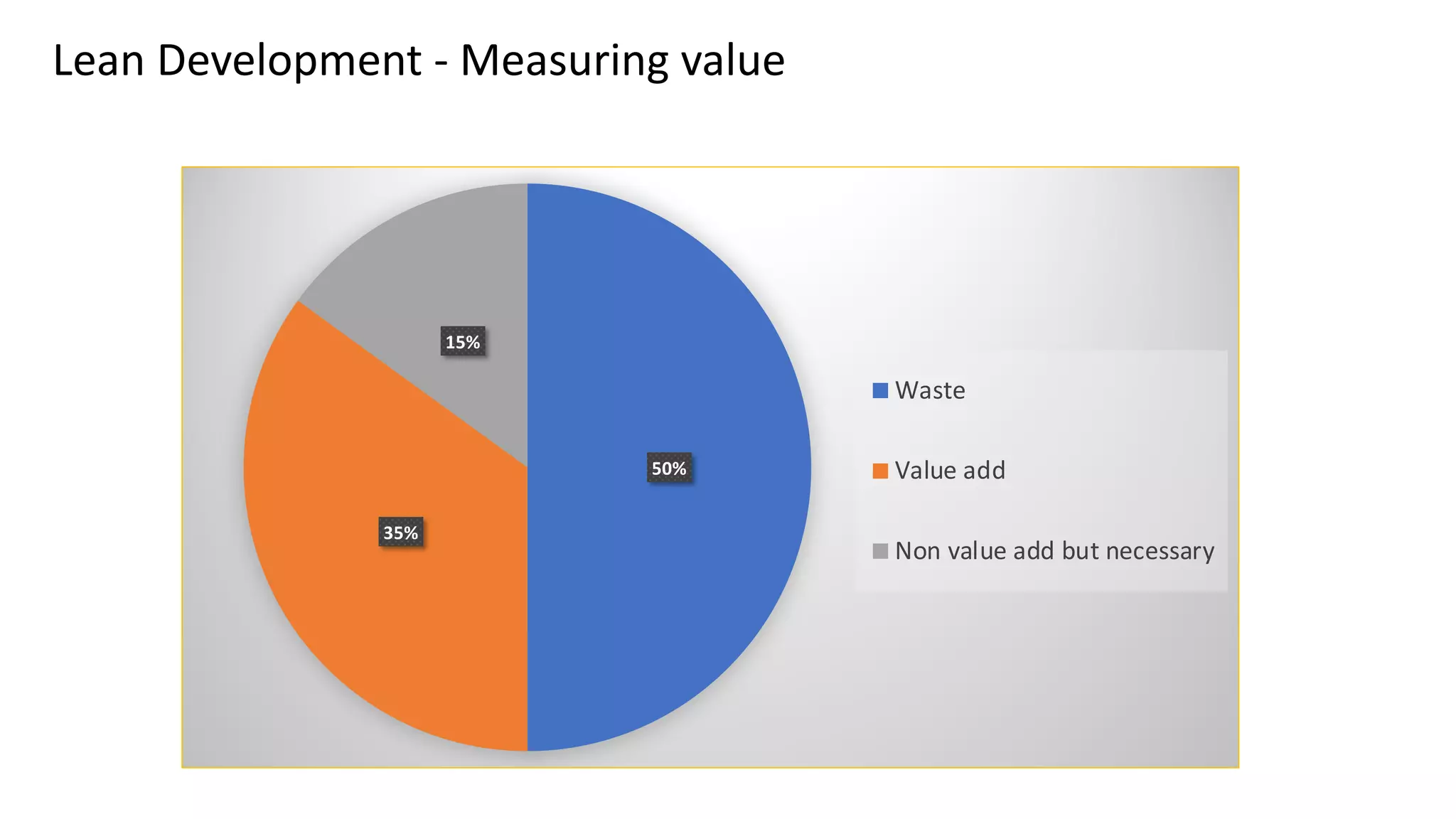
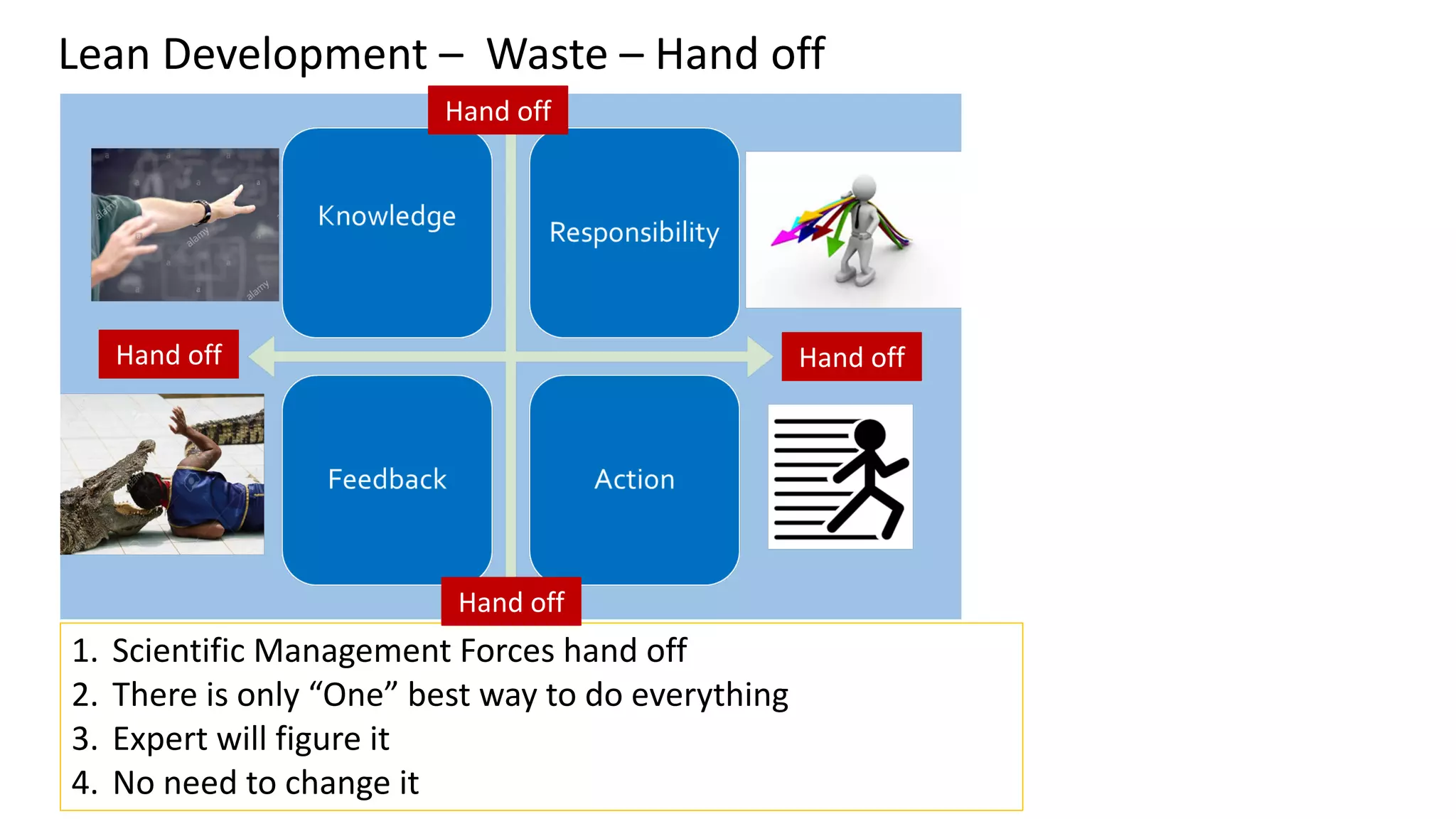
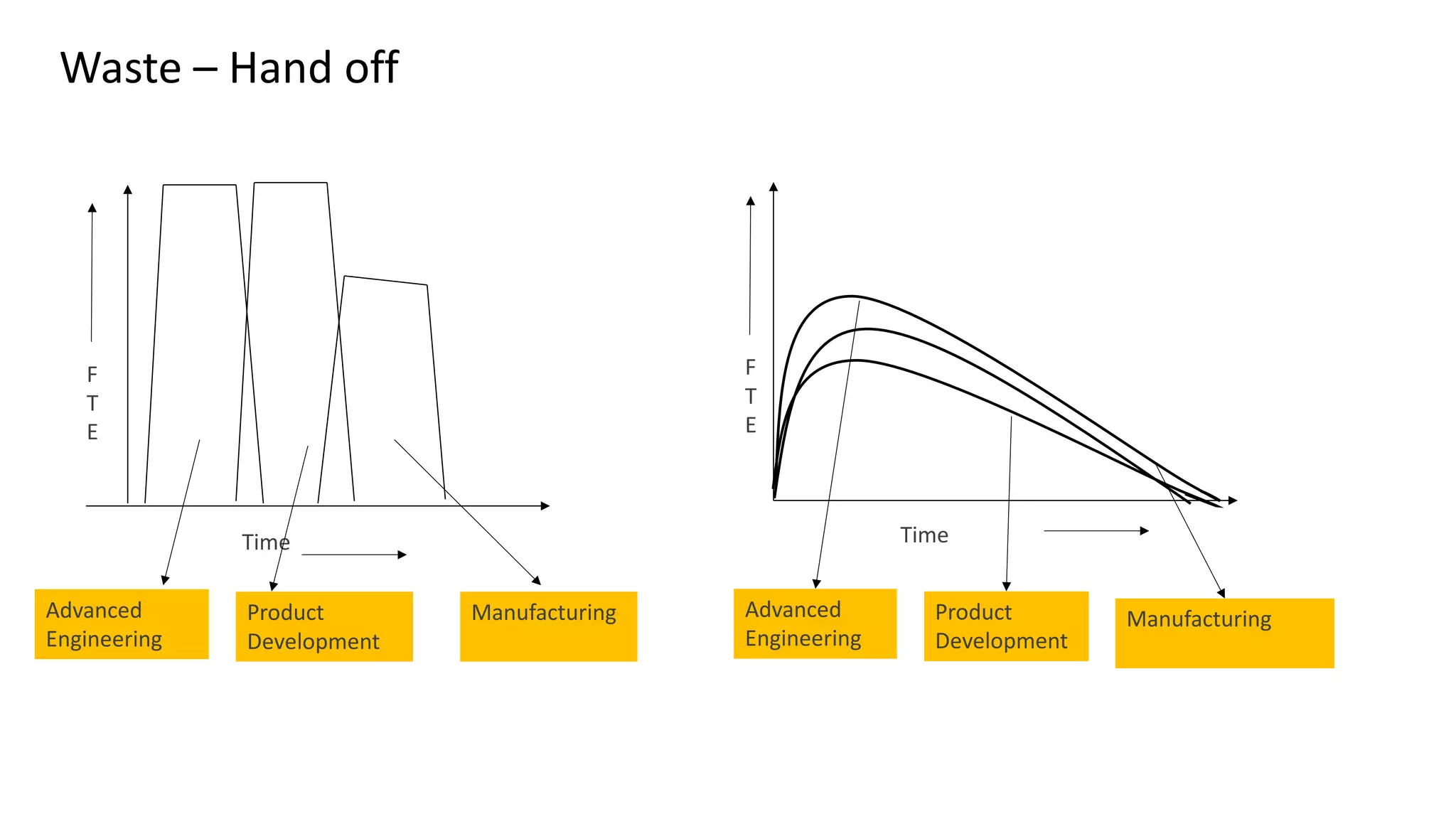
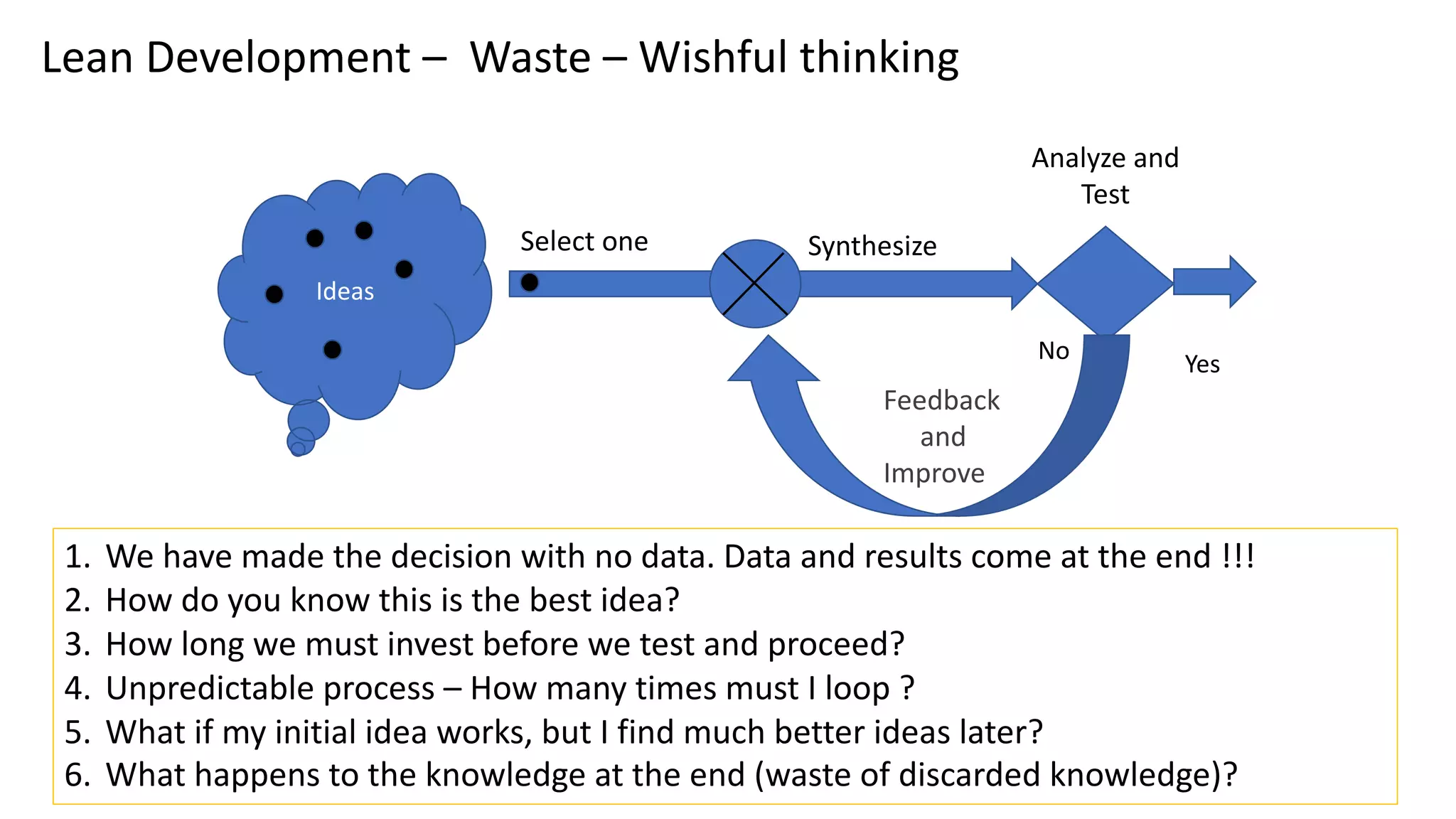
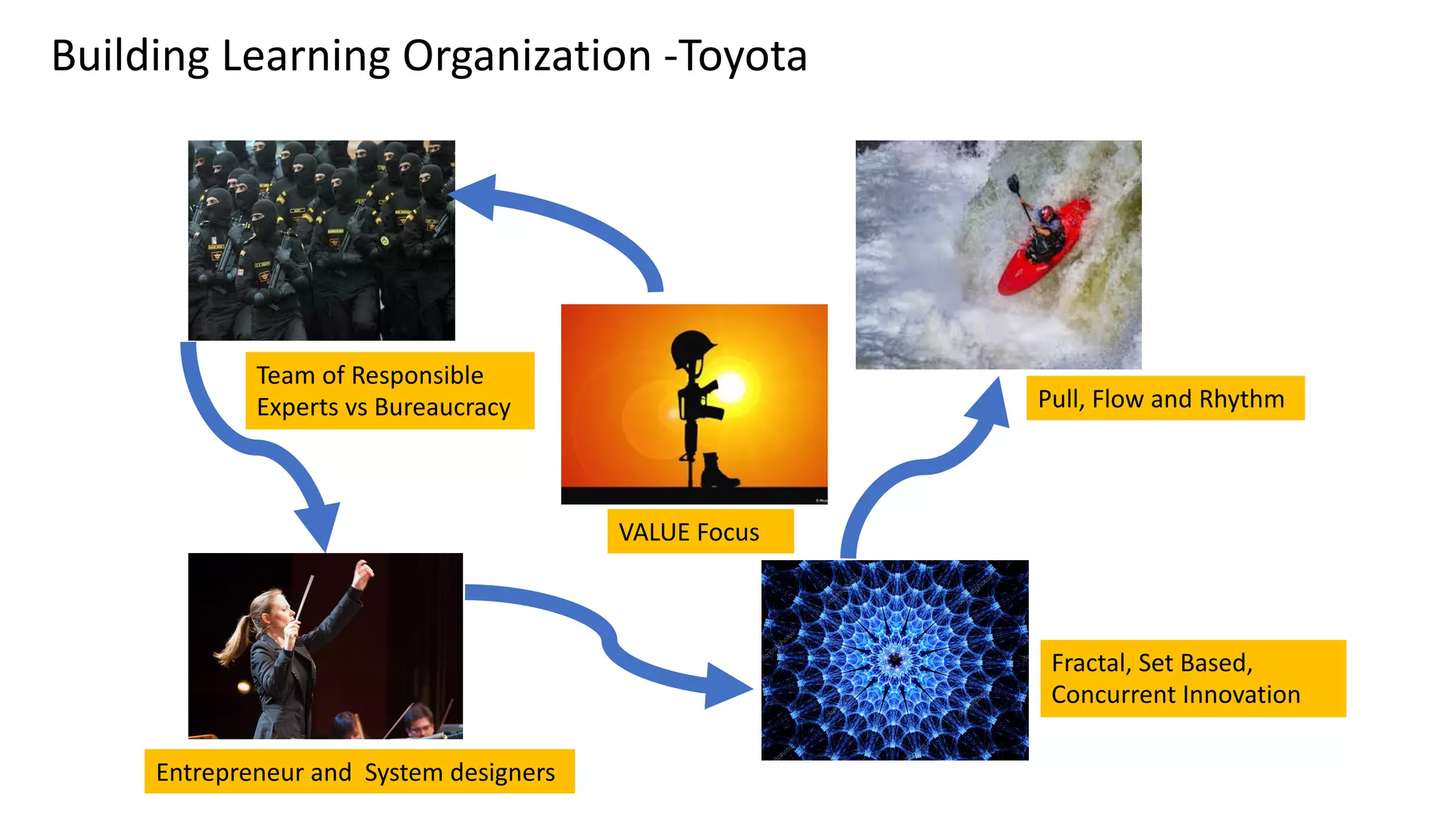
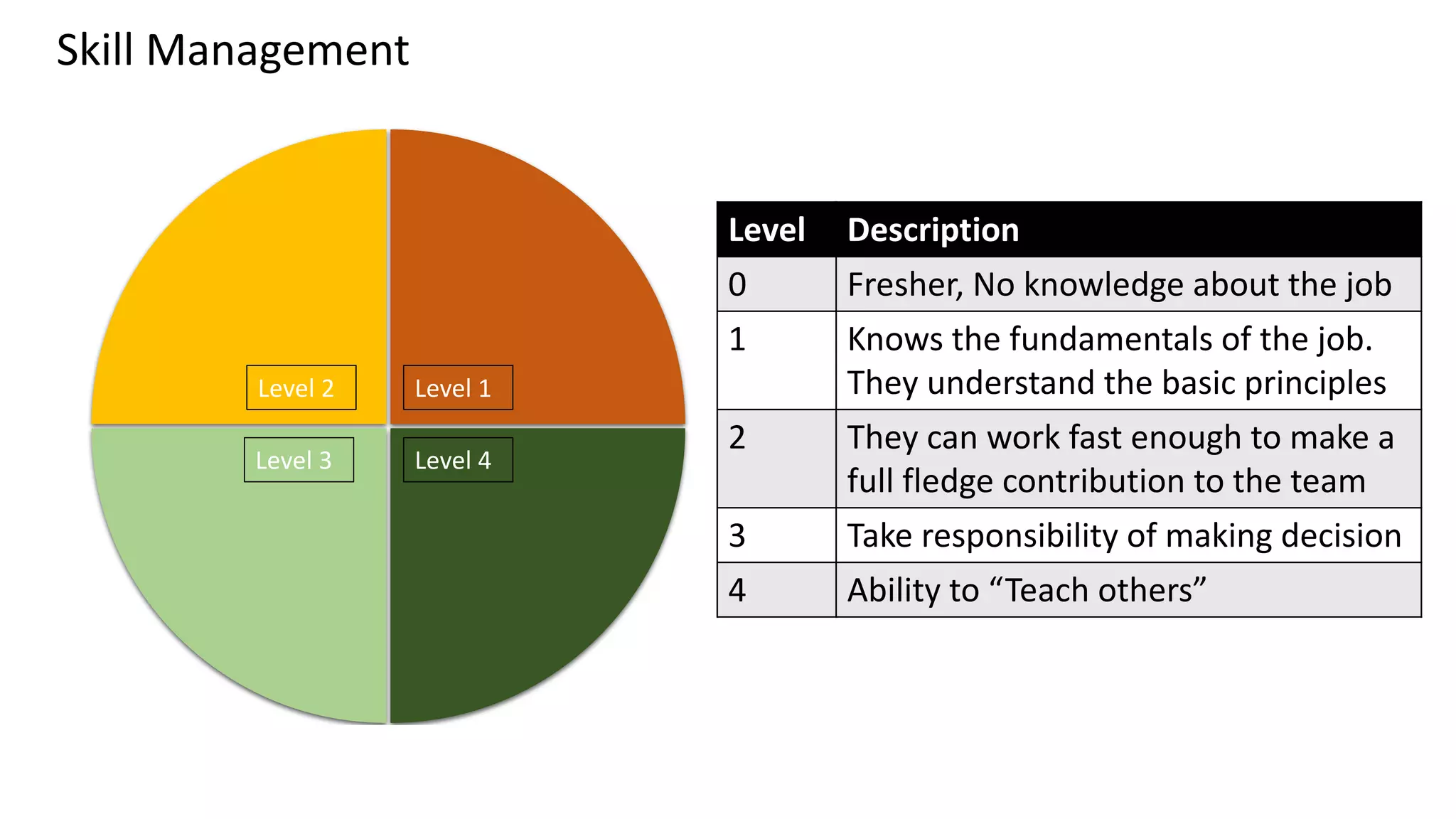
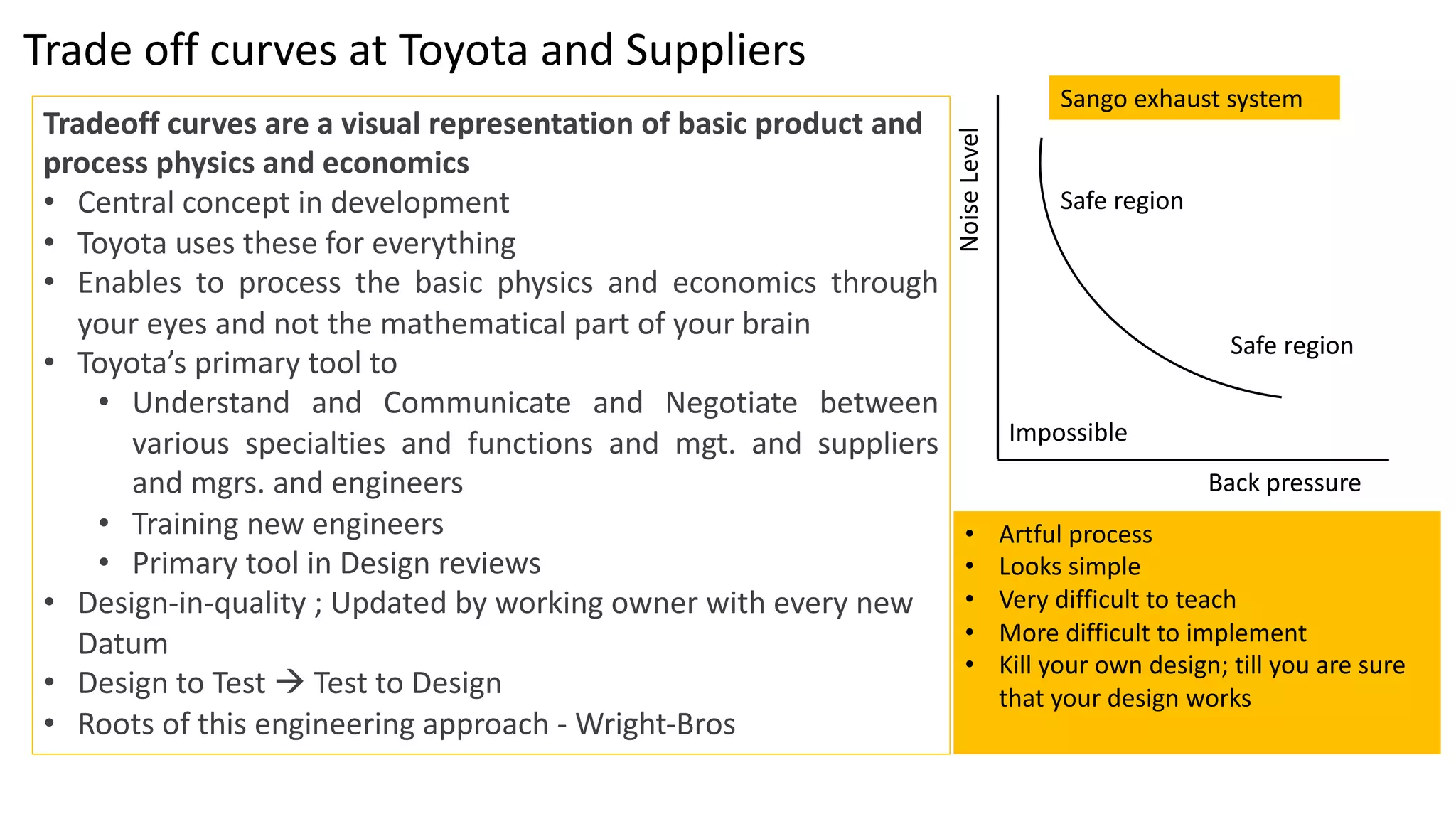
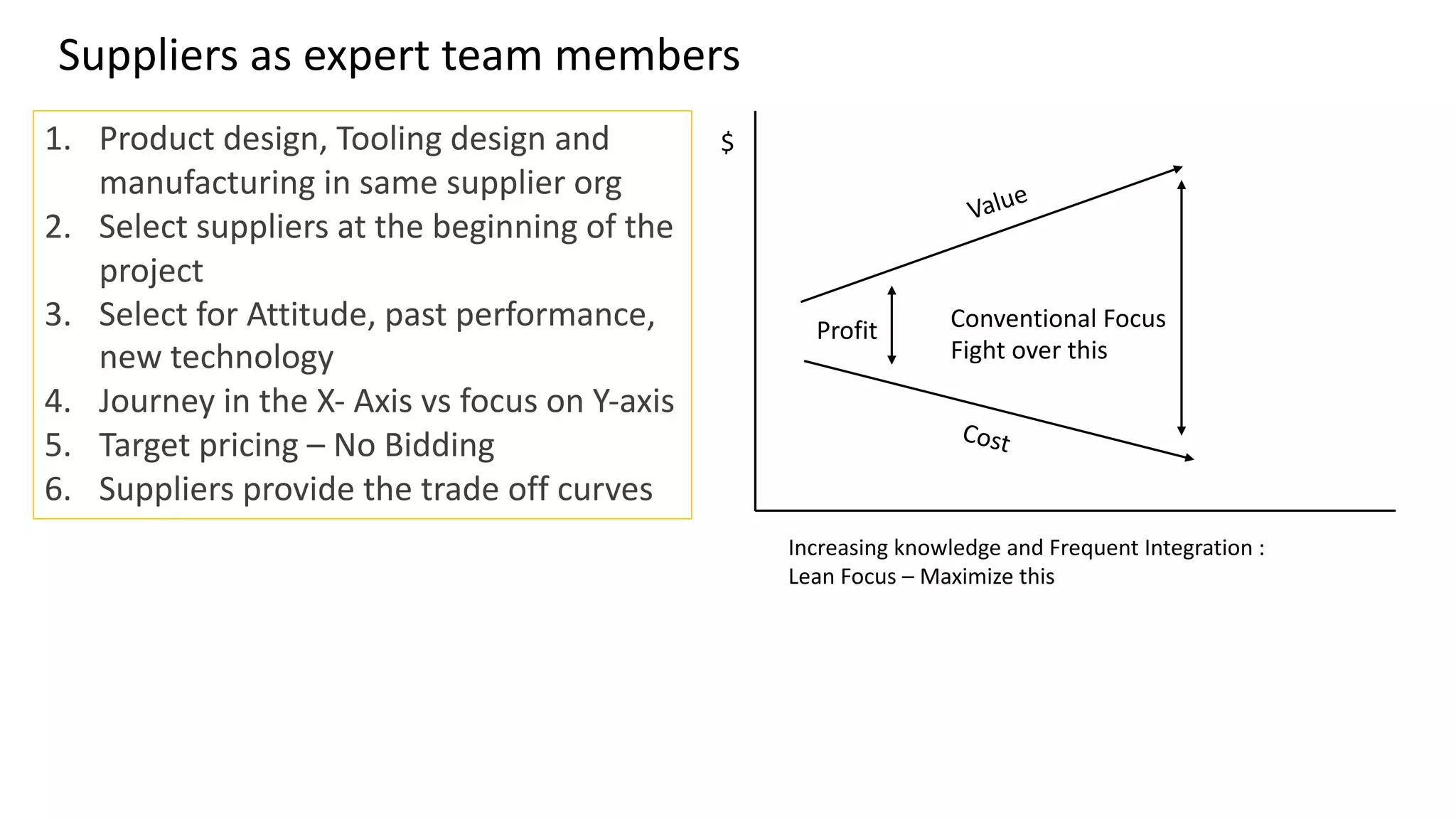
This document discusses Toyota's successful development process, highlighting its ability to produce high-quality vehicles quickly and cost-effectively. It contrasts Toyota's methods with those of U.S. automakers, underscoring the importance of eliminating waste in development while fostering a culture of learning and innovation. Key themes include the significance of usable knowledge, the role of management in coaching, and strategies for lean development to enhance operational value streams.