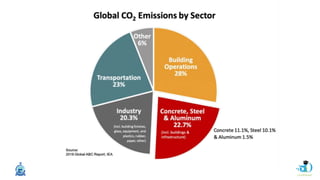
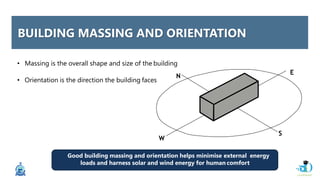
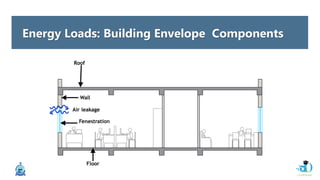
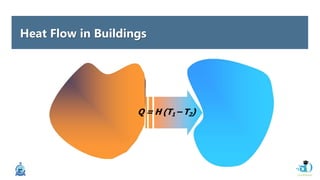
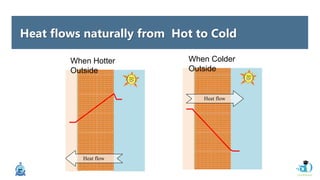
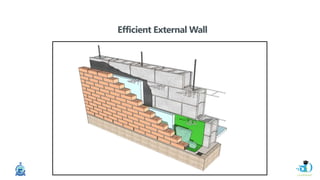
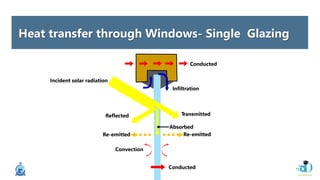
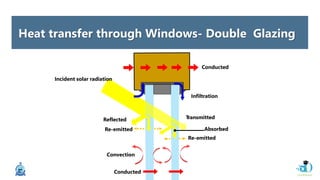
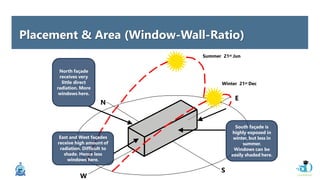
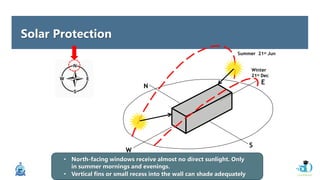
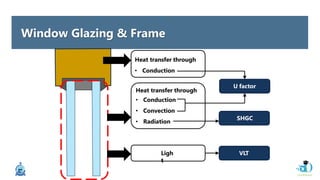
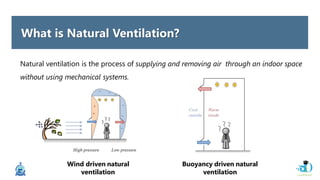
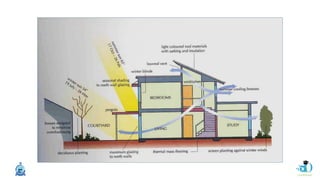
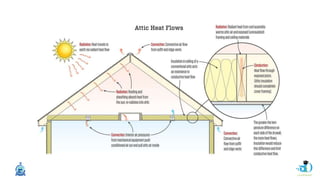
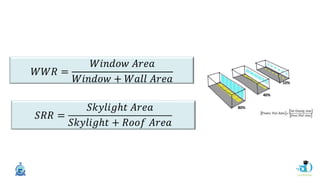
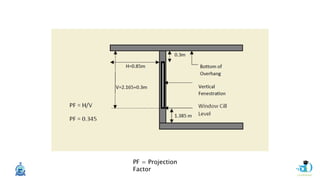
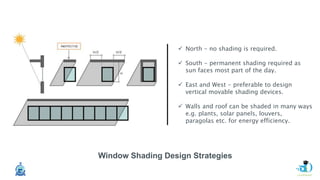
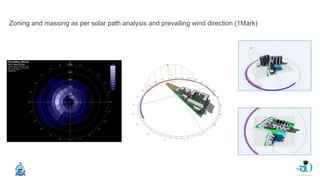
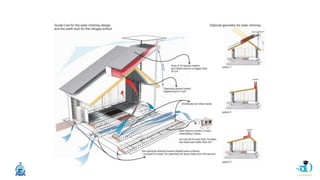
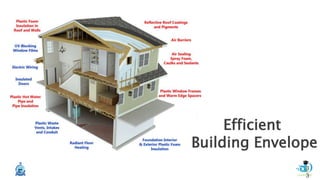
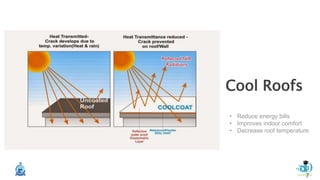
The document discusses passive design strategies for building envelopes and wall window ratios. It covers topics like building massing and orientation to minimize external energy loads, the building envelope as the boundary between interior and exterior, heat transfer through different envelope components like walls and windows, and the need for insulation and glazing to reduce heat transfer. It also talks about designing window placement and shading to control solar heat gain and the benefits of natural ventilation strategies.