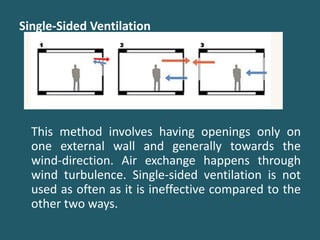
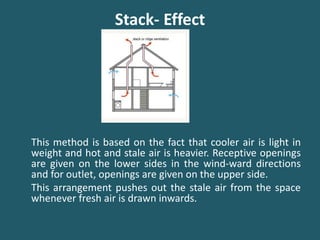
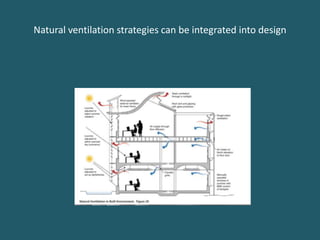
Natural ventilation uses natural forces like wind and buoyancy to introduce fresh air into buildings. It ventilates spaces by providing oxygen, diluting contaminants, and promoting air movement for comfort. There are three main natural ventilation methods: single-sided ventilation using only openings on one wall, cross-ventilation using openings on opposite walls, and stack effect using cooler air intake on the lower sides and warmer air exhaust on the upper sides. Natural ventilation has advantages like energy savings, no need for ducts or machinery, more natural light, lower maintenance costs, and potential health benefits compared to mechanical ventilation. Factors like wind direction, building orientation, topography, vegetation and the size and placement of openings need to be considered for effective