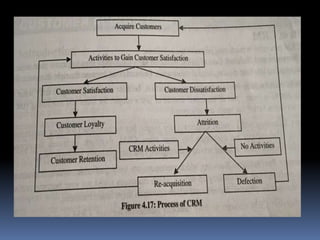
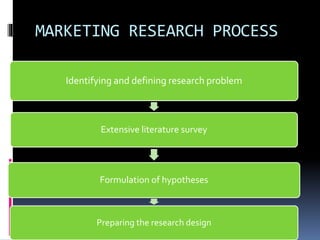
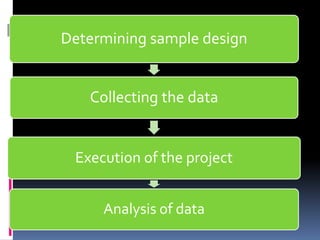
This document discusses building customer satisfaction and relationship management. It covers key topics such as the importance of customer satisfaction, tools and strategies for building strong customer relationships, measuring customer satisfaction through surveys and other methods, and defining and discussing customer relationship management. The overall goal is to understand how to create value for customers, maintain good customer relations, and ensure customer loyalty over time through effective relationship management strategies and practices.