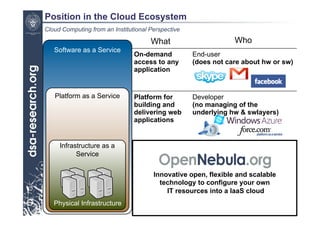
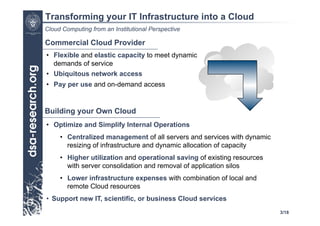
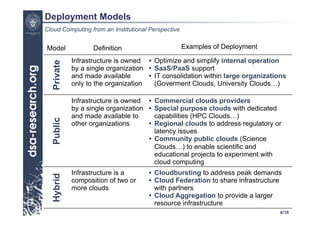
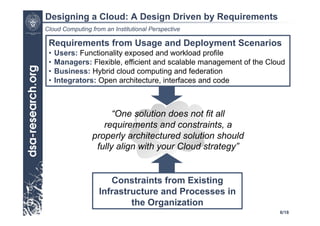
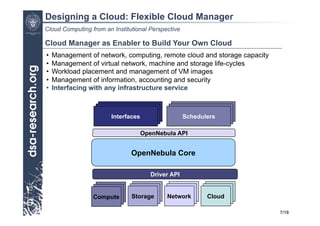
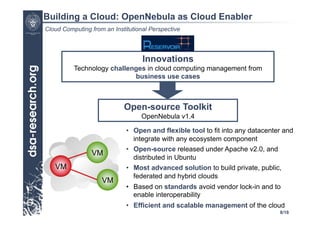
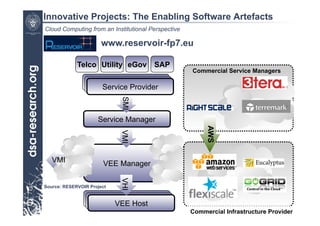
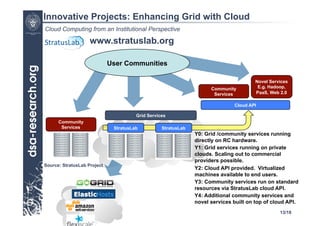
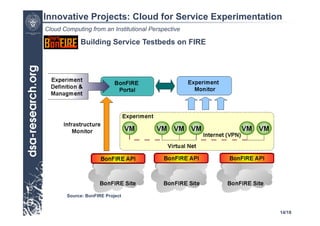
This presentation discusses cloud computing from an institutional perspective. It provides an overview of cloud deployment models including private, public and hybrid clouds. It also discusses using OpenNebula as an open-source toolkit to build a flexible cloud infrastructure that can optimize internal operations and support new IT services. Finally, it summarizes some innovative European projects using cloud computing technologies like RESERVOIR, StratusLab and BonFIRE.